![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
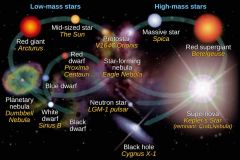
DEATH OF LOW MASS STAR |
1. After helium has fused into Carbon.
2. Expels its outer shells forming planetary nebulae
3. Core remains as a white dwarf eventually turning into a black dwarf |
|
|
DEATH OF A HIGH MASS STAR |
1. Can go two ways
2. Can turn into a neutron Star
3. It's tractors can overcome it and suck it in becoming a |
|
|
THE NATURE OF A DWARF STAR |
1. Has high mass but very small. Has half the mass of the sun compressed into a size slightly bigger than the earth.
2. Makes it very hot over 100000 kelvin hence on the spectrum of blue
3.Consists of Degenerate matter. This matter who's electron are you very close together. Gravity pulls them together pulling in more till they have nowhere to go. That's how a white dwarf stays stable without needing internal fusion. |
|
|
THE QUANTUM DWARF LIMIT |
• Quantum mechanics says that electrons must move faster as they are squeezed into a very small space.
• As a white dwarf’s mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light.
• Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be more massive than 1.4MSun, the white dwarf limit (or Chandrasekhar limit). |
|
|
WHITE DWARF SND A CLOSE BINARY SYSTEM |
• Mass falling toward a white dwarf from its close binary companion has some angular momentum . • The matter therefore orbits the white dwarf in an accretion disk. • The temperature of accreted matter eventually becomes hot enough for hydrogen fusion . • Fusion begins suddenly and explosively, causing a nova. This is called a white Dwarf Super nova. |
|
|
NEUTRON STAR |
• Neutron stars can be considered nuclei with extremely high mass numbers A neutron star is the ball of neutrons left behind by a massive-star supernova. Degeneracy pressure of neutrons supports a neutron star against gravity. |
|
|
HOW DOES ELECTRON DEGENERACY CREATE A NEUTRON STAR
|
Electron degeneracy pressure goes away because electrons combine with protons, making neutrons and neutrinos. Neutrons collapse to the center, forming a neutron star. |
|
|
HOW DOES ELECTRON DEGENERACY CREATE A NEUTRON STAR
|
Electron degeneracy pressure goes away because electrons combine with protons, making neutrons and neutrinos. Neutrons collapse to the center, forming a neutron star. |
|
|
PULSAR STARS |
• A pulsar is a neutron star that beams radiation along a magnetic axis that is not aligned with the rotation axis. • The radiation beams sweep through space like lighthouse beams as the neutron star rotates. |
|
|
NEUTRON STAR LIMIT |
• Quantum mechanics says that neutrons in the same place cannot be in the same state. • Neutron degeneracy pressure can no longer support a neutron star against gravity if its mass exceeds about 3Msun. • Some massive star supernovae can make a black hole if enough mass falls onto core. |
|
|
WHAT SUPPORTS A STAR AGAINST GRAVITY. |

|
|
|
BLACK HOLE |
A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying. Light cannot escape that's why they are invisible |
|
|
HOW DO BLACK FORMS FORM |
Stellar black holes are made when the center of a very big star falls in upon itself, or collapses. When this happens, it causes a supernova. A supernova is an exploding star that blasts part of the star into space. |
|
|
WHAT OS THE STRUCTURE OF A BLACK HOLE |
• The “surface” of a black hole is the radius at which the escape velocity equals the speed of light. • This spherical surface is known as the event horizon. |
|
|
WHAT HAPPENS ENTERS A BLACK HOLE |
As far as we know, gravity crushes all the matter into a single point known as a singularity. It will pull the matter into a mass as thin as a hair. |
|
|
HOW TO MEASURE ABLACK HOLE |
BH themselves are tiny & invisible !! Must look for their influence on other (visible) things
BH themselves are tiny & invisible !! Must look for their influence on other (visible) things Scientists s believe there is a black hole in the middle of our Milky Way .
|

