![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
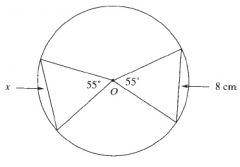
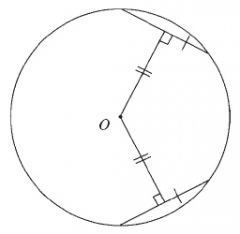
Equal angles subtended at the centre of the circle cut off equal chords.
|
|
|
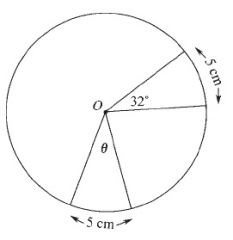
Equal arcs subtend equal angles at the centre of the circle.
|
|
|
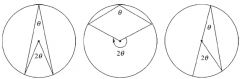
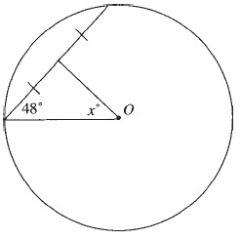
The angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle at the circumference subtended by the same arc.
|
|
|
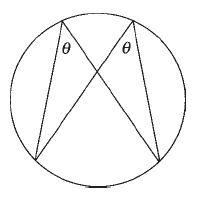
Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal.
|
|
|
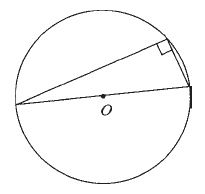
The angle in a semicircle is a right angle.
|
|
|
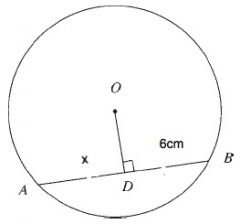
A perpendicular line from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
|
|
|
A line from the centre of a circle that bisects a chord is perpendicular to the chord.
|
|
|
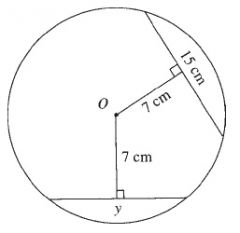
Equal chords are equidistant from the centre of the circle.
|
|
|
Chords that are equidistant from the centre are equal.
|
|
|
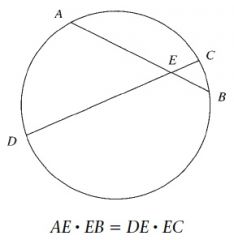
The products of intercepts of intersecting chords are equal.
|
|
|
Concyclic points are points that lie on the circumference of a circle.
|
|
|
Any 3 non-collinear points are concyclic .
|
|
|
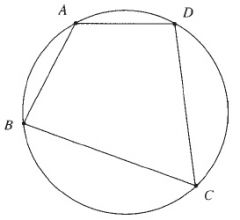
A cyclic quadrilateral is a figure whose 4 vertices are concyclic points .
|
|
|
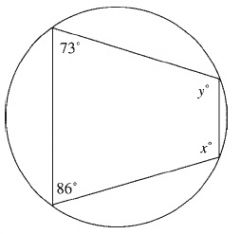
The opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary.
If the opposite angles of a quadrilateral are supplementary, then the quadrilateral is cyclic. |
|
|
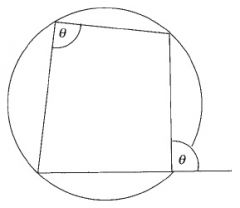
The exterior angle at a vertex of a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to the interior opposite angle.
|
|
|
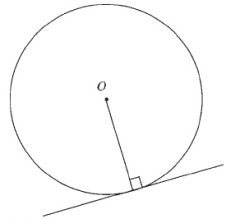
The tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius drawn from the point of contact.
The line perpendicular to the radius at the point where it meets the circle is a tangent to the circle at that point. |
|
|
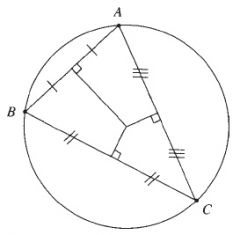
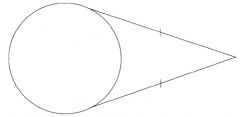
Tangents to a circle from an exterior point are equal.
|
|
|
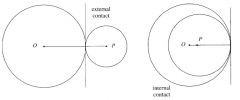
When two circles touch, the line through their centres
passes through their point of contact. |
|
|
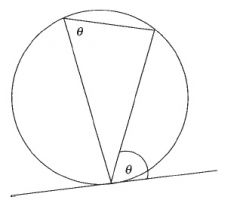
The angle between a tangent and a chord through the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment.
|
|
|
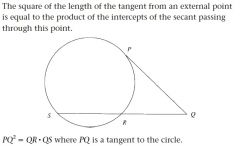
|

