![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
IV- Omitted Variables |
Events other than treatment that provide alternative explanation for results |
|
|
|
IV: Trends in Outcomes |
Observation change as a function of time not because our treatment necessary |
|
|
|
IV: Misspecified Variance |
Overstating statistics test because of omitting group error |
|
|
|
IV: Mismeasurement |
Changing on measurement that can cause differences |
|
|
|
IV: Political Economy |
Endogenous policy changes due to governmental responses to variables associated with past or expected future outcomes. Ex. Government lowering interest in response to an incoming recession |
|
|
|
IV: Simultaneity |
Joint determination of outcomes Ex. Interest rates of 5 and 10 year bonds being correlated- no causal relationship. |
|
|
|
IV: Selection |
Assignment of treatment are done in a way that could provide correlation for other reasons |
|
|
|
IV: Attrition |
Loss of participants |
|
|
|
IV: Omitted Interactions |
Differential trends in treatment and control groups |
|
|
|
EV: Unrepresentative group |
The treatment and control don’t represent the entire population of interest |
|
|
|
EV: Geographic |
Does not generalize across population in geography |
|
|
|
EV: History |
Does not generalize across time |
|
|
|
Ethics: Beneficence |
Maximize potential benefits of the study for participants |
|
|
|
Ethics: Non-Maleficence |
Minimize the potential for harm or potential risks- physical, psychological, and social |
|
|
|
Ethics: Autonomy |
Right to self determination, Informed Consent, Capacity, free power |
|
|
|
Ethics: Respect for Persons |
Every person deserves the respect for being an individual Privacy and confidentiality No legal protection for privacy |
|
|
|
Ethics: Vulnerable Populations |
Federal law protects: children, elderly, mentally disabled, and prisoners States or universities may protect: minorities, fetuses, AIDS patients, economically disavtaged |
|
|
|
Ethics: Justice |
Fairness- will participants gain the benefits if they are taking the risk |
|
|
|
Central Limit Theorem |
The sampling of a population with a mean mu will be a normal distribution when n is large. |
|
|
|
Law of Large Numbers |
As sample size increase, a random sample producing a mean approaching the population mean |
|
|
|
Point Estimate property: unbiased |
Biased parameter will systematically under or over estimate the true value Variance can be proven to be unbiased when standard deviation is not. |
|
|
|
Point Estimate property: efficiency |
When choosing between multiple unbiased estimators (mean or median) or techniques (maximum likelihood, method of moments), we prefer the sampling distribution with the smallest variance |
|
|
|
Point Estimate property: Consistency |
Point estimator remains close to the value when the parameter increase its sample size |
|
|
|
Point Estimate property: sufficiency |
Uses all the information in a sample Useful when raw data is too much and statician can confirm that it will not impact the results |
|
|
|
Point Estimate property: Robust |
Extent to which an estimation are adversely effected by violations of the underlying assumption Assuming our data is normal when it is not |
|
|
|
Binomial Distribution: Description |
Occurs when 1. There are a fixed number of n observations and k trials 2. The trials are independent 3. The outcome is binary (success/fail) 4. The probability of success is the same for each trial Ex. A coin toss |
4 |
|
|
Binomial Distribution: Model |
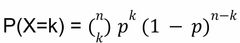
Back (Definition)
|
n = number of trials k = number of successes p = probability of a single trial being a success |
|
|
Binomial Distribution: Mean |
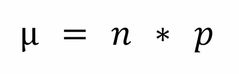
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Binomial Distribution: Variance |
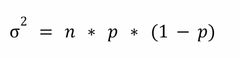
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Poisson Distribution: Description |
COUNT DATA Concerned with the average number of successes per observation Occurs when: 1. The number of successes are independent 2. The probability of success is the same for all observations of equal size and proportional to the size of the unit 3. The probability of a success that 2 or more successes will occur in a unit approaches zero as the size decreases |
3 |
|
|
Poisson Distribution: Model |
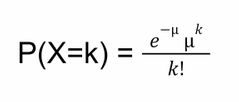
|
Mu = mean number of successes per failure K = number of successes |
|
|
Poisson Distribution: Mean |
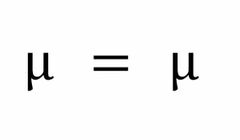
|
|
|
|
Poisson Distribution: Variance |
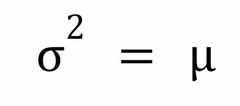
|
|
|
|
Normal Distribution: Description |
1. Bell shaped 2. Symmetric 3. Mean, median, and mode are all identical 4. Frequencies gradually decreasing at both ends of the curve 5. The mean and the variance completely define the distribution 6. The mean and the variance are independent |
6 |
|
|
Normal Distribution: Model |
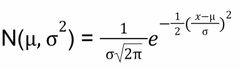
|
|
|
|
Standard Normal Distribution: Model |
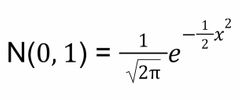
|
|
|
|
Standard Normal Distribution: Mean |
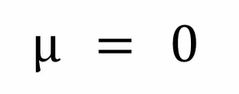
|
|
|
|
Standard Normal Distribution: Variance |
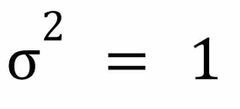
|
|
|
|
Uniform distribution: Description |
Spreads the probability for being chosen equally across a range from a to b |
|
|
|
Uniform distribution: model |
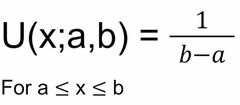
Else 0 |
|
|
|
Uniform distribution: Mean |
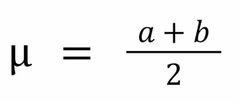
|
|
|
|
Uniform distribution: Variance |
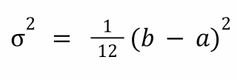
|
|
|
|
Negative Binomial Distribution |
How many binary outcomes trials must I conduct to get the keg success. Ex. How many times do I need to flip a coin to get 5 heads |
|
|
|
Multinomial Distribution |
Binomial distribution where there are more than 2 possible outcomes |
|
|
|
Gamma Function |
A large number of distribution related to the gamma function Recursive Contains many asymptotes |
|
|
|
Chi-Squared Distribution |
Used in sampling theory Uses degrees of freedom A normal distribution times itself |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Intersection Where both event may occur |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Union Where either event does occur Ex. A or B |
|
|

Front (Term) |
B is a subset of A |
|
|
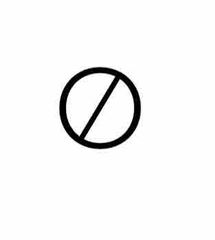
Front (Term) |
Disjoint or mutually exclusive |
|
|

Means in layman terms |
What is the probability of B if we know A has occurred |
|
|
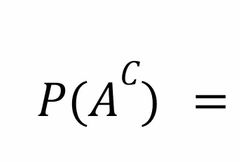
Front (Term) |
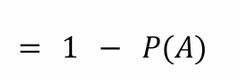
Back (Definition) |
|
|
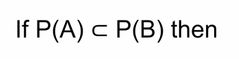
Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|

Front (Term) |
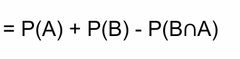
Back (Definition) |
|
|

Front (Term) |
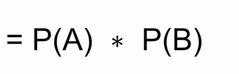
Back (Definition) |
|
|
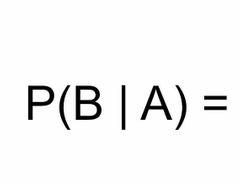
Front (Term) |
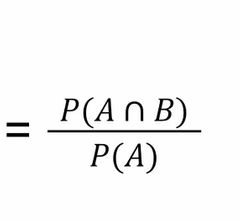
Back (Definition) |
|
|
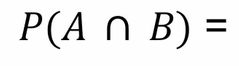
Front (Term) |
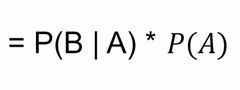
Back (Definition) |
|

