![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Potential problems of Observational Studies |
Confounding Variables Extending Results Inappropriately Using Past as a Source of Data |
|
|
Good Experiment Qualities |
Random Allocation Use of Control Group Use of Placebo Use of Blinding |
|
|
Experimental vs Observational |
Exp can claim causality (intervention causes a change in dependent variable), obs uses survey or similar, but cannot claim causality, used when experiment would be unethical |
|
|
Confounding Variables |
Cannot claim causal link No random allocation of treatment so external factors affecting results |
|
|
Extending Results Inappropriately |
Sample must be representative of larger population if inference is to be drawn (many use convenience studies that are not) |
|
|
Using Past as a Source of Data |
Retrospectively done, using memory of participants. Problems with recollection, usually bias, skew. Also, confounding variables might have changed in the meantime |
|
|
What is Reliability |
Repeatability and consistency of sample, as much as possible. Impossible for same results, so remove confounding factors to greatest extent possible |
|
|
What is Validity |
Strength of final result, does it accurately represent wider world. Is there bias? Is it representative? |
|
|
Types of Non-Sampling Error |
Non response error Selection error Response error Self selection error Survey error |
|
|
Non-Response Error |
If response rate is low, bias could be present. Respondents tend to extreme views compared to population |
|
|
Selecting Error |
Specifically group is over or under represented, bias occurs if they have differing opinion to population |
|
|
Response Error |
Social pressure not to give unpopular answer so not true reflecting of belief |
|
|
Self-Selection Error |
Respondents decide to answer or not, over represent those with strong opinions /knowledge, bias |
|
|
Survey Error |
Wording of questions, order of questions, type of options influences survey results |
|
|
What are Non-Sampling Errors |
Errors in data collection process as a result of factors other than taking the sample |
|
|
Sampling Error |
Unavoidable, sampling variation Difference between estimate and true value of parameter |
|
|
Factors affecting Sampling Error |
Sample Size (30 big enough for populations is 1000, bigger better) Sample Design (method) Variability within Population |
|
|
Properties of Good Survey Questions |
Q measures one idea No jargon or technical terms No leading questions Allow for possible responses |
|
|
Sampling Methods |
Simple random Systematic Stratified (simple random from groups of population) Cluster (form clusters and sample of clusters are used) Non random (convenience, quota) Self selected |
|
|
ProCon Non Random Sampling |
Likely to be not representative of population |
|
|
ProCon Cluster Sampling |
Easier and cheaper Relies on clusters being representative of the population |
|
|
ProCon Stratified Sampling |
Each strata is representative Requires prior knowledge |
|
|
ProCon Self Selected Sampling |
High chance sample is unrepresentative of the population Only get people with strong opinions |
|
|
ProCon Simple Random Sampling |
Free from bias but could be unrepresentative Time consuming and impossible with large populations |
|
|
ProCon Systematic Sampling |
Likely to be representative, quick age easy ish, cannot be used if data has cyclic patterns, awkward with large population |
|
|
ProCon Internet Self-administered |
Low cost, quick data, large geographic distribution, complex questionnaire Bias to those without, self selection bias, non response bias |
|
|
ProCon Face to face interview |
Good control of question order and quality of responses, appropriate for sensitive issues High cost, slow data, clustered geographical distribution |
|
|
ProCon Written self-administered |
Low cost, wide geographical distribution, handles sensitive issues Low response rate, no knowledge about non response, long time, biased self selection |
|
|
ProCon Telephone interview |
Good control of question order and quality of responses, appropriate for sensitive issues Bias to those without, cannot pick up, low response rate, long time |
|
|
Rule - Claim with no Comparison |

Margin of error using above |
|
|
Rule - Comparison within One Group |

Double because each group has each variation Confidence interval mustn't include 0 |
|
|
Comparison between Two Independent Groups |
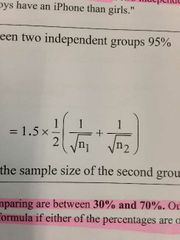
Confidence interval mustn't include 0 |
|
|
Worry Questions |
Who funded it Was there a hidden agenda Analyse the three potential problems Is there non response / other nonsampling error Analyse methodology Analyse method and approach of poll or survey Cam they make the inference |
|
|
Reason for Random Allocation |
Ensures all experimental units have same probability of receiving intervention option. Creates groups with similar characteristics apart from intervention or not. Allows attribution of cause effect |
|
|
Reason for Control Group |
Establish base line reaction Treated same way minus intervention |
|
|
Reason for Placebo Group |
Dummy treatment so wondering if there is actual usefulness |
|
|
Reason for Blinding |
Helps eliminate blinding in measurement of response Single - Participants or researcher knows Double - Neither know, only know after measurements taken |

