![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Rare Event Rule for Inferential Statistics?
|
If, under a given assumption, the probability of a particular observed event is extremely small, we conclude that the assumption is probably not correct.
|
|
|
What is an event?
|
any collection of results or outcomes of a procedure.
|
|
|
What is a simple event?
|
is an outcome or an event that cannot be further broken down into simpler components.
|
|
|
What is the sample space?
|
a procedure consists of all possible simple events. That is the, the sample space consists of all outcomes that cannot be broken down any further.
|
|
|
What does P denote?
|
Probability
|
|
|
What does A, B, and C denote?
|
Specific events. Even A , event B etc.
|
|
|
Explain P(A)?
|
denotes the probability of event A occuring.
|
|
|
What is the formula for Relative Frequency Approximation of Probabili`ty?
|
Number of times A occurred
P(A) = ------------------------------------------ Number of times the procedure was repeated. |
|
|
What is the classical approach to Probability (requires equally likely outcomes) formula?
|
Number of ways A can occur
P(A) = ---------------------------------------- Number of different simple events |
|
|
What is the classical approach to Probability (requires equally likely outcomes) formula in simple terms?
|
s
P(A) = ___ n |
|
|
What is subjective probabilities?
|
P(A) , the probability of even A, is estimated by using knowledge of the relevant circumstance.
|
|
|
What are the 3 approaches to finding a probabilty?
|
relative frequency approach, classical approach, & subjective probability.
|
|
|
Explain the relative frequency approach and show examples?
|
Using the relative frequency approach we obtain an approximation instead of an exact value. Use n to determine the # of observation in a large sample.
|
|
|
Explain the classical approach and show examples?
|
the approach has equally likely outcomes but n= total # of observations in the experiment. We will use this most often.
|
|
|
Explain the subjective approach and show examples?
|
in subjective the opinion counts. Like we take into account changes in safety rules, new technologies, etc to determine accidents in workplace
|
|
|
How do express probabilities?
|
Always express probabilities as a fraction or decimal number between 1 and 0. (Dr. Ibara like 0.0001 spaces)
|
|
|
What number is the probability of an impossible event?
|
zero = 0
|
|
|
What number is the probability of an event that is certain to occur?
|
One = 1
|
|
|
What does it mean when- for any even A, the probability of A is between 0 and 1 inclusive?
|
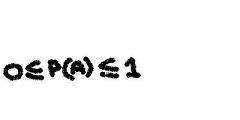
|
|
|
What is the symbol for the complement of even A?
|

|
|
|
What does complement of an event mean?
|
consists of all outcomes in that event does not occur.
|
|
|
What is a compound event?
|
any event combining two or more simple events.
|
|
|
What is the addition rule formula?
|
P(A or B)= P(in a single trial, event A occurs or Event B occurs of they both occur).
|
|
|
What is the significance of "or" in probabilities?
|
They can either mean A occurs or B occurs or A&B occurs
|
|
|
What is the formula for the formal addition rule?
|
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A & B)
where P (A & B) denotes the probability that A and B both occur at the same times as an outcome in a trial or procedure. |
|
|
What is the intuitive addition rule?
|
to find P(A or B), find the sum of the number of ways event A can occur and the number of ways event B can occur, adding in such a way that every outcome is counted only once. P(A or B) is = to that sum, divided by the total # of outcomes in the sample space.
|
|
|
When are events A & B disjointed or mutually exclusive?
|
If they cannot occur at the same time
|
|
|
What are the 3 rules of complementary events?
|
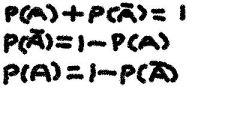
|
|
|
What is the notation for conditional probability?
|
P( B|A ) represents the probability of even B occurring after it is assumes that even A has already occurred. (we can read B|A as "B given A" or as "event B occurring after even A has already occured.")
|
|
|
What is the term when the occurrence of even A does not affect the probability of the occurrence of the other?
|
Events A and B are independent of each other.
|
|
|
If A and B are not independent, they are said to be what?
|
dependant
|
|
|
What is the formal multiplication rule?
|
P(A and B) = P(A) X P( B|A )
If A and B are independent events, P( B|A ) is the same as P(B) |
|
|
What is the intuitive multiplication rule?
|
When finding the probability that event A occurs in one trial and event B occurs in the next trial, multiply the probability of even A by the probability of even B , but be sure that the probability of even B takes into account the previous occurrence of even A.
|
|
|
What is treating dependent events as independent: the 5% guideline for cumbersome calculations?
|
If calculations are very cumbersome and if a sample size is no more than 5% of the size of the population , treat the selection as being independent (even if the selections are made without replacement, so they are technically dependent).
|

