![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Kinetic-molecular theory |
particles of matter are always in motion |
|
|
|
Ideal gas |
A hypothetical gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory
|
|
|
|
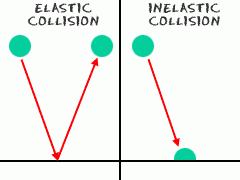
Elastic collision |
Collision between gas particles and container walls, and there is no net loss of total kinetic energy |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
spontaneous mixing of the particles of two substances caused by their random motion |
|
|
|
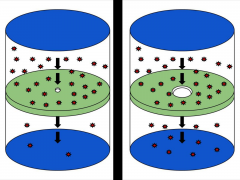
Effusion |
A process by which gas particles pass through a tiny opening |
|
|
|
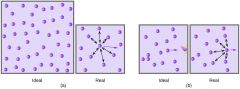
Real gas
|
A gas that does not behave completely according to the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory |
|
|
|
5 assumptions of kinetic theory |
1. Tiny particles are far apart 2. Elastic collision 3. Particles are in continuous motion 4. No attraction between particles 5. Temperature of gas depends on average K.E. |
|
|
|
5 properties of gases |
1. Expansion 2. Fluidity 3. Low density 4. Compressibility 5. Diffusion and Effusion |
|
|
|
Fluid |
A substance that can flow and take the shape of its container |

|
|
|
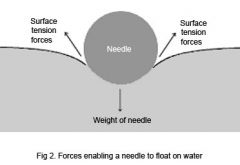
Surface tension |
Force that pulls parts of a liquids surface tension together, decreasing surface area to the smallest possible size the at |
|
|
|
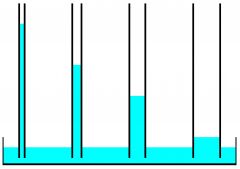
Capillary action |
The attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid |
|
|
|
Vaporization |
Liquid or solid changes to a gas |
|
|
|
Freezing |
Physical change of a liquid to solid by removal of energy as heat |

|
|
|
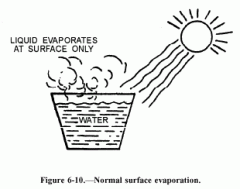
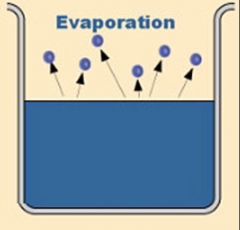
Evaporization |
Particles escape from the surface of a non boiling liquid and enter gaseous state |
|
|
|
6 properties of liquids |
1. Relatively high densities 2. Incompressibility 3. Ability to diffuse 4. Surface tension 5. Evaporation and boiling 6. Formation of solids |
|
|
|
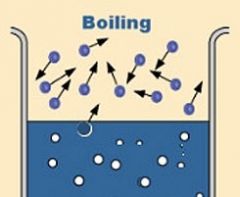
Boiling |
Change of liquid to bubbles of vapor that appears throughout the liquid |
|
|
|
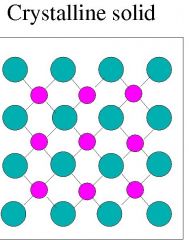
Crystalline solids |
Solids that consist of crystals |
|
|
|
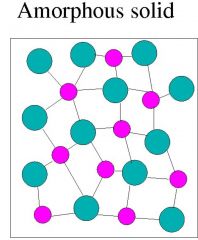
Amorphous solids |
Particles are arranged randomly |
|
|
|
Melting |
Physical change of a solid to a liquid, by the addition of energy as heat |

|
|
|
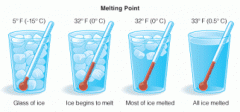
Melting point |
Temperature at which solid becomes a liquid |
|
|
|
Supercooled liquids |
Substances that retain certain extent liquid properties even at temperature wich they appear to be solid |

|
|
|
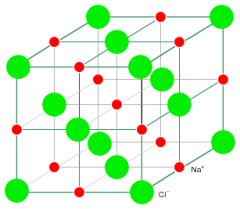
Crystal structure |
The total three-dimensional arrangement of particles of a crystal |
|
|
|
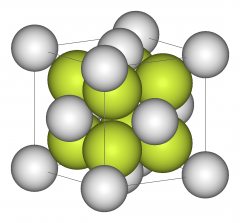
Unit cell |
Smallest portion of a crystal lattice that shows the three-dimensional pattern of entire lattice |
|
|
|
4 properties of solids |
1. Definite shape and volume 2. Definite melting point 3. High density and incompressibility 4. Low rate of diffusion |
|
|
|
4 properties of crystals solids form |
1. Ionic crystals 2. Covalent network crystals 3. Metallic crystals 4. Covalent molecular crystals |
|
|
|
2 major types of amorphous solids |
1. Glasses 2. Polymers |
|
|
|
Phase |
Any part of a system that has uniform composition and properties |
|
|
|
Condensation |
Process by which gas changes to a liquid |
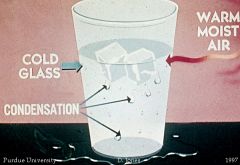
|
|
|
Equilibrium |
A dynamic condition in which two opposing changes occur eat equal rates in a closed system |
|
|
|
Equilibrium vapor pressure |
The pressure exerted by vapor in equilibrium with its correct liquid at given temperature |
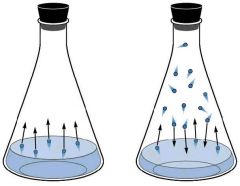
|
|
|
Volatile liquids |
Liquids that evaporate readily |

|
|
|
Boiling point |
The temperature at which the equilibrium vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure |
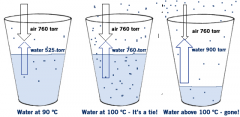
|
|
|
Molar enthalpy of vaporization |
The amount of energy that is needed to vaporize one mole of liquid at the liquids boiling point at constant pressure |
|
|
|
Freezing point |
Temperature at which the solid and liquid are at equilibrium at 1atm pressure |
|
|
|
Molecular enthalpy of fusion |
The amount of energy as heat required to melt one mole of solid at the solids melting point |
|
|
|
Sublimation |
Change of solid directly to a gas |

|
|
|
Deposition |
Change of gas directly to a solid |

|
|
|
Phase diagram |
A graph of temperature vs pressure that conditions under which the phase substance exits |
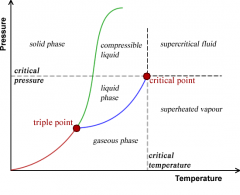
|
|
|
Triple point |
Indicates the temperature and pressure conditions at which the solid, liquid and vapor can coexist at equilibrium |
|
|
|
Critical point |
Indicates the criticical temperature and pressure |
|
|
|
Critical temperature |
Temperature above which the substance cannot exit in liquid state |
|
|
|
Critical pressure |
Lowest pressure at which the substance can exit as a liquid at the critical temperature |
|

