![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is cooling curve? |
It |
|
|
|
What is Volume? |
The amount of space occupied by a substance. |
|
|
|
What are molecules? |
Molecules are groups of two or more atoms bonded together and which can exist on their own. |
|
|
|
What is matter made up of? |
Matter is made up of atoms,molecules and ions. |
|
|
|
What are atoms? |
Atoms are the smallest units of a chemical element which have all the characteristics of the element. E.g. iron is made of iron atoms |
|
|
|
What is Density? |
The amount of mass in a specific volume |
|
|
|
What is Matter? |
Matter is any tangible substance that has mass and occupies space. |
|
|
|
What are Ions? |
Ions are electrically charged particles. •They may be formed from a single atom,e.g. The potassium ion,K+ |
|
|
|
What is Partcle? |
Minute portion of matter. |
|
|
|
What does the particulate theory of matter state? |
It states that all matter is made up of particles. |
|
|
|
What is one example of diffusion? |
Potassium |
|
|
|
An example of Osmosis |
A strip of paw paw |
|
|
|
What is Brownian Motion? |
The visible movement of small pieces of solid. |
|
|
|
What is Osmosis? |
The movement of water molecules through a differentially permeable membrane. |
|
|
|
What is Diffusion? |
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of high concentration to low concentration until the particles are evenly distributed. |
|
|
|
What are the evidences that support particulate theory of matter? |
Diffusion,Osmosis,Brownian Motion |
|
|
|
What is Mass? |
The amount of particles in a substance. |
|
|
|
What are the three states of Matter? |
solid,liquid,gas |
|
|
|
How can matter be changed from one state to another? |
By heating or cooling. |
|
|
|
What is Melting? |
Melting is when solid changes to liquid when heated. |
|
|
|
What is Evaporation? |
The process by which liquid turns to vapour/gas when heated. |
|
|
|
What is Physical Change? |
changing the state of a substance without changing its chemical composition |
|
|
|
What is a change of state caused by? |
It is caused by a change in temperature and a change in kinetic energy. |
|
|
|
What are the four main ideas behind the PARTICULATE THEORY OF MATTER? |
•All matter is composed of particles. • The particles are in constant motion. •The particles have empty spaces between them. • The particles have forces of attraction. |
|
|
|
Explain the difference between the three states in terms of Volume Occupied,Forces of Attraction,Arrangement if Particles,Density and Motion of Particles. |

|
|
|
|
What are the uses of Osmosis? |
•To control garden pests •To preserve food |
|
|
|
What is Boiling? |
Boiling is when liquid is heated and turns to gas at particular temperature. |
|
|
|
What is Condensation? |
The change of state from gas to liquid. |
|
|
|
What is Freezing? |
The change of state from liquid to solid. |
|
|
|
What is Sublimation? |
The change of state from solid to gas or gas to solid. |
|
|
|
What is melting point? |
The constant temperature at which a solid changes state into a liquid. |
|
|
|
How is osmosis used to control garden pests and preserve food? |
•Slugs and snails are garden pests,whose skin is differentially permeable and always moist. When salt(sodium chloride) is sprinkled on slugs and snails,it dissolves in the moisture around their bodies forming into the solution. The slugs and snails die from dehydration. •Salt and sugar are used to preserve foods such asmeat,fish and fruit. - They draw water out of the cells. This prevents the food from decaying - They draw water out if microorganisms(bacteria and fungi). This prevents the food from decaying because it inhibits the growth of microorganisms. |
|
|
|
What is the difference between Evaporation and Boiling? |
1. Boiling occurs at a specific temperature while Evaporation can take place at any temperature. 2. Boiling takes place throughout the entirety of a liquid whereas Evaporation takes place on the surface. |
|
|
|
What is boiling point? |
The constant temperature at which a liquid changes state into a gas. |
|
|
|
What is heating curve? What is cooling curve? |

|
|
|
What is a Pure substance? |
A pure substance is composed of only one type of material. |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Pure substance? |
It has a fixed and constant composition Its properties are fixed and constant The component parts cannot be separated by physical means. |
|
|
|
Example of Element |
silver(Ag) is made up of individual silver atoms. |
|
|
|
One example of Pure substance |
Sugar |
|
|
|
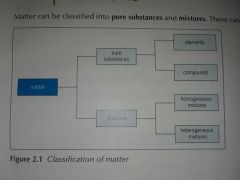
What is element? |
An element is a substance which cannot be broken down in any simpler substance by any physical or chemical process |
|
|
|
What is freezing point? |
The constant temperature at which a liquid changes state into a solid. |
|
|

What is filtration? |
Filtration is used to separate a suspended or settled solid and a liquid when the solid does not dissolve in the liquid.
|
The components are separated due to their different particle sizes. |
|
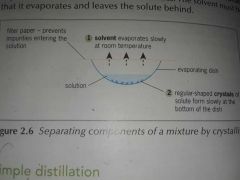
What is Crystallisation? |
Crystallisation is used to separate and retain the solid solute from the liquid solvent in a solution. |
The components are separated due to their different volatilities. |
|
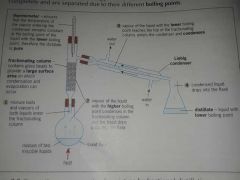
What is Fractional distillation? |
Fractional distillation is used to separate two(or more) miscible liquids with boiling points that are close together. |
|
|

What is separating funnel? |
A separating funnel is used to separate two(or more) immiscible liquids,e.g.oil and water. |
Immiscible liquids are separated due to their different densities. |
|
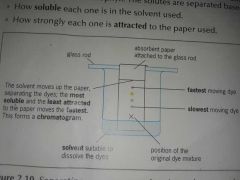
What is Paper Chromatography? |
A separation technique used to separate several solutes which are present in a solution. |
The solutes are separated based on: •How soluble each one is in the solvent used. •How strongly each one is attracted to the paper used. |
|
|
What are subatomic particles? |
They are the fundamental particles that make up an Atom. |
|
|
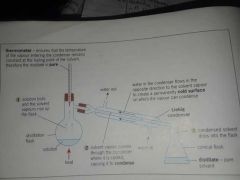
What is Simple Distillation? |
Simple distillation is used to separate and retain the liquid solvent from the solid solute in a solution. |
The components are separated due to their different boiling points. |
|
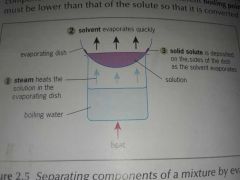
What is evaporation? |
Evaporation is used to separate and retain the solid solute from the liquid solvent in a solution. |
The components are separated due to their different boiling points. |
|
|
Name the Sub-atomic particles |
•Protons •Neutrons •Electrons |
|
|
|
What is a Pure Substance? |
A pure substance is composed of one kind of material only. |
|
|
|
What is a compund? |
A compound is a pure substance that is formed from two or more different types of elements which are chemically bonded together. |
|
|
|
What can matter be classified as? |
Matter can be classified into pure substances and mixtures. |
|
|
|
What is Mixture? |
A mixture consists of two or more substances(elements and/or compounds) physically combined together. |
|
|
|
Example of Mixture |
Sugar and water |
|
|
|
What can mixtures be classified into? |
•Homogeneous mixtures •Heterogeneous mixtures |
|
|
|
What is a homogeneous mixture? |
A uniform mixture. |
|
|
|
What is heterogeneous mixture? |
A non-uniform mixture. |
|
|
|
What is a type of Homogeneous mixture? |
Solution |
|
|
|
What are heterogeneous mixtures classified into? |
Suspensions and Colloids. |
|
|
|
What is a suspension? |
A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which minute,visible particles of one substance are dispersed in another substance. |
|
|
|
What is a Colloid? |
A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture in which minute particles of one substance are dispersed in another substance. |
|
|
|
Distinguish between a solution , colloid and a suspension the particle size,passage of light and sedimentation. |

|
|
|
|
What are Protons? |
Positively charged particles in the nucleus which is stationary and hold there by strong nuclear force. |
|
|
|
What is neutron? |
Uncharged particles in the nucleus which is stationary and held there by strong nuclear force. |
|
|
|
What are electrons? |
Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus on different energy shells. |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Sub-Atomic Particles? |
Relative Charge and Relative Mass |

|
|
|
What is Mass Number? |
The number protons and neutrons in an atom. |
|
|
|
What is Atomic Number? |
The number of protons in an atom. |
|
|
|
What are Isotopes? |
Atoms of the same element that has the same number of protons and different number of neutrons. |
|
|
|
What are the two types of Isotopes? |
1)Stable Isotopes 2)Radioactive/Unstable Isotope |
|
|
|
Explain Melting |

|
|
|
|
Explain Evaporation |

|
|
|
|
Explain Boiling |

|
|
|
|
Explain Condensation |

|
|
|
|
Explain Freezing |

|
|
|
|
Explain Sublimation |

|
|
|
|
What are radioactive isotopes? |
Isotopes with unstable nuclei,which break down. |
|
|
|
What is isotopy? |
Isotopy is the occurrence of atoms of a single element that have the same of protons but different numbers of neutrons. |
|

