![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Someone is experiencing chest pain- what should you do? |
1. Take an assessment. -About the pain -OLDCART -is it a MI? Angina?
2. O2 therapy if necessary (<93)
3. Administer GTN if eligible
4. Talk to senior. 12 lead ECG. |
|
|
What is a prothrombin time or INR test? |
Blood test that measures how long it takes for blood to clot. Used for: -check bleeding problems -check if medicine to prevent blood clots is working. Too high= increased bleeding Too low= blood clots not prevented. 0.8-1.1 is normal range |
|
|
What is a coronary angiogram? |
X-ray test to study narrow, blocked, enlarged or malformed arteries in the heart. Shows extent and severity of the disease. How is it done? -liquid dye is injected through a catheter into a desired artery access point. (Usually arm or groin) -dye makes blood vessel visible in x-ray. |
|
|
What is a coronary by pass surgery? |
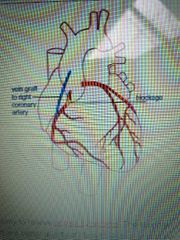
-Mainly done to relieve angina symptoms -Surgery improves blood flow to the heart muscle |
|
|
What is angioplasty? |

Treatment that uses stents to improve blood flow to heart by opening narrowed or blocked coronary artery. Stent is made of metal mesh. |
|
|
What are the 3 types of atrial fibrillation? |
Paroxysmal AF Comes and goes. Lasta minutes-days Persistent AF Lasts 7+ days Long standing persistent/permanent Ongoing for over a year |
|
|
List some things to remember about hip joint replacements in post-operative care? |
- Do NOT turn on affected side
- Place pillow between legs when turning on unaffected side - Use pillow to maintain abduction after hip replacement to prevent dislodging the prosthesis and to prevent contracture - Avoid flexing hip - assist to high straight back chair |
|
|
In New Zealand, what percentage of adults and children are obese? |
1 in 3 adults (32%) 47% Maori, 65% Pacific 1 in 8 children 17% Maori, 30% Pacific |
|
|
The nurse is administering Furosemide to the patient. Which complication is the patient at risk for? |
Arrhythmia |
|
|
What is a hysterectomy? |
Surgery to remove all parts of the uterus. Post OP your body goes through menopause |
|
|
How do you management heart burn/reflux in pregnancy? |
-eat smaller meals more frequent -eat slowly -drink water between meals not during -avoid eating before bed -avoid chocolate, fatty foods, spicy foods, acidic foods and caffeine -maintain upright after a meal |
|
|
Why is rubella dangerous? |
Complications mainly occur in adults. It can cause brain infections and bleeding problems. The primary medical danger is the infection of pregnant women because it can cause congenital rubella syndrome in developing babies |
|
|
What does reduction mean in relation to fractures? |
Surgical procedure to repair a fracture or dislocation to the correct alignment. Can be: Open where fracture fragments are exposed surgically by dissecting the tissues Closed Manipulation of the bone fragments without surgical exposure |
|
|
What is the purpose of a drain after surgery? |
Fluid may collect inside your body in the surgical area. This makes an infection or other problems more likely. |
|
|
What is the difference between pitting and non-pitting oedema? |
Pitting -respond to pressure -will leave an indentation when pressed even when finger is removed -Sign of liver, heart or kidney problems Non-pitting -doesn't cause any lasting indentation -Often a sign affecting the thyroid or lymphatic system |
|
|
What is dependent edema? |
Gravity-related swelling in lower body. Usually due to limited mobility due to paralysis, stroke, ALS |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure? |
-Headache -Vomiting without nausea -ocular palsies -Altered level of consciousness -back pain |
|
|
What is a generalized tonic clonic seizure? (Grand mal seizure) |
People can experience both phases or just one of them. Affects both cerebral hemispheres
Tonic phase -Stiffening of the limbs -Breathing may decrease or cease may decrease or cease
Clonic phase -Jerking of the limbs and face -Breathing returns, may be irregular
Post seizure -Lethargic, want to sleep -Possibly confused, headache
|
|
|
How often should you move a bedridden patient? |
Once at least every 2 hours. A person in a chair should move at least once ever 1 hour - or 15minutes if possible |
|
|
What is atelectasis? |
When the alveoli dont fill with air. -Complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or lobe.
-Occurs when alveoli within the lung become deflated or filled with alveolar fluid.
-Common after surgery.
Symtpoms: -difficulty breathing -rapid, shallow breathing -Wheezing, cough |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock? |
Tachycardia Hypotension Cool/clammy skin Weak peripheral pulses Anxiety Decreased urinary output |
|
|
What are some nursing interventions for a hypovolemic patient? |
1. ABCD -place o2 if necessary 2. Place in trendeleburg position 3. If bleeding, apply firm direct pressure 4. Obtain 2x IV access (>18 gauge) 5. Fluids: crystalloids and colloids solution following 3:1 rule |
|
|
What are some signs and symptoms of atrial fibrillation? |
-Can be asymptomatic -Fatigue, dizziness, weakness -Palpitations -Dyspnea -Hypotension Common causes include age, Gene's, heart disease |
|
|
What is multiple sclerosis? |
Disease that affects the nerves of the brain and spinal cord. Women are twice as affected. Onset age 20-40 Symptoms: depends on area of brain and cord affected. It is unpredictable -eyesight, vision -muscle spasms -muscle and nerve pain e.g. tingly -weakness of coordination of limbs -fatigue |
|
|
What is dystonia? |
Involuntarily muscle contractions that cause repetitive or twisting movements |
|
|
What causes polyuria in diabetes? |
Osmotic diuresis secondary to hyperglycemia |
|
|
Signs and symtpoms of diabetic ketoacidosis? |
Polyuria Polydipsia Nausea and vomiting Abdominal pain Weakness or fatigue SOB Fruity breath Confusion Hyperglycemia High ketones in urine |
|
|
What is a kidney injury? |
Sudden episode of kidney failure or damage that happened within a few hours or days. It causes a build up of waste products in your blood and makes it hard for your kidneys to keep the right balance of fluid in your body. Symptoms: -Little urine leaving body -swelling in legs, Ankles, eyes -fatigue or tiredness -confusion -nausea Causes: -decreased blood flow -direct damage to kidneys e.g. sepsis -blockage of urinary tract |
|
|
What is an isotonic solution and what does it do? |
Same concentration on the inside and outside which in normal conditions the cells intracellular and extracellular are both isotonic
Increase extracellular fluid volume
E.g. Blood loss, surgery, dehydration, fluid loss Fluids: -normal saline -5% dextrose -Lactated ringers |
|
|
What is a hypotonic solution and what does it do? |
The cell has a low amount of solute extracellularly and wants to shift inside the cell to get back to normal. This causes CELL SWELLING -Can cause cell to burst Used when: -Cell is dehydrated -DKA or hyperglycemia Fluids: -0.45% saline |
|
|
What is a hypertonic solution and what does it do? |
The cell has excessive amount of solute extracellularly and osmosis is causing water to rush out of the cell intracellularly to the extracellular area
Causes CELL TO SHRINK Used: In ICU (has high risk of fluid overload) |
|
|
What is a normal hemoglobin range for men and women? |
Women: 120-160 Men: 130- 170 |
|
|
What is the normal platelet level for an adult? |
150-400 x10/L |
|
|
What are normal potassium range levels? |
3.5-5 mEq/L |
|
|
What are normal sodium levels? |
135-145 mEq/L |
|
|
What are normal calcium range? |
2.2 - 2.6mmol/L |
|
|
What are the following blood components used for transfusion? 1. Red cells 2. Platelets 3. Fresh frozen plasma |
1. Red cells Treat anemia or sever bleeding 2. Platelets Stop bleeding. Used in ICU and cancer treatments 3. Fresh frozen plasma Replacing clotting factors and other blood proteins |
|
|
Answer the following about hyperkalemia 1. Signs and symtpoms 2. Causes 3. Nursing interventions |
1. Signs and symptoms -Muscle weakness -Urine production (renal failure) -Respiratory failure -Weak pulse, low BP, arrhythmia -twitches, cramps
2. Causes -burns, tissues damages (cellular movement from intracellular to extracellular) -renal failure -addison's disease -drugs e.g. ACE inhibitors, NSAIDS
3. Interventions -monitor cardiac, renal, GI -stop IV potassium and PO -initiate potassium restricted diet -Prepare patient for dialysis -Adminoster hypertonic solution of glucose and insulin to pull potassium into the cell
|
|
|
What is potassium responsible for? |
Nerve impulse conduction and muscle contraction. Most of it is found in the intracellular part of the cell |
|
|
Answer the following about hypokalemia 1. Signs and symptoms 2. Causes 3. Nursing interventions |
1. Signs and symptoms Remember 'slow and low' -Weak pulse (irregular and thread) -orthostatic hypotension -Depression ST, flat T wave, prominent U wave -shallow respirations with diminished breath sounds -confusion, weak, leg cramps
2. Causes: -Drugs e.g. laxatives, diuretics, corticosteroids -Too much water -Cushing syndrome -heavey fluid lost e.g. diarrhea, vomiting, sweating 3. Nursing interventions -Cardiac monitor -Respiratory status, neuro, GI, output -Monitor electrolytes Mg, glucose, Na, calcium -Administer supplements |
|
|
What is the role of calcium? |
Plays a huge role in bone and teeth along with muscle/nerve function, cell and blood clotting. Calcium is absorbed in the GI system and stored in bones then excreted by the kidneys |
|
|
What are causes of hypocalcemia? |
-Low parathyroid hormone -Wound drainage -Celiacs and crohn's disease -Acute pancreatitis -Low vitamin D levels -chronic kidney issues |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia? What are the nursing interventions? |
Signs and symptoms -confusion -muscle spasms in calves or feet -Arrythmias (prolonged QT interval) -reflexes hyperactive Nursing interventions -safe environment (risk of fall, fractures, seizures -Administer IV calcium slowly -PO calcium with vitamin D -Encourage high calcium food |
|
|
What are the causes, signs and symptoms and nursing interventions of hypercalcemia?
|
Causes: -Hyperparathyroidism/thyroidsism -Increased intake of calcium -Thiazide, diuretics and renal failure -lithium usage
Signs and symptoms -Weakness of muscles -EKG changes shortened QT interval -Absent reflexes -disorientated, constipated -kidney stone formation
Nursing interventions Mild: -Hydration -monitor cardiac, GI, renal, neuro -monitor for stone formation Moderate: Administer calcium reabsorption inhibitors e.g. calcitonin Severe: Prepare for dialysis
|
|
|
What is a transient ischemic attack? |
Mini or warning stroke that resolves withing minutes to hours -Early warning sign for an actual stroke (could happen within 48hours) |
|
|
What are the stages of wound healing? |
1. Haemotasis (immediately)-damaged blood vessels constrict -temporary platelet aggregation on the inner walls of damaged blood -clot formation occurs 2. Inflammation (1-4 days post injury) -blood vessels dilate to allow antibodies, WBC, growth factors, enzymes and nutrients to reach the wounded area -increased exudate levels at the wound site 3. Proliferation (4-12 days post injury) -fibroblasts lay hed of collagen and fills defect and produces new capillaries -wound edges pull together -epithelialization 4. Remodeling (12 days - 2 years) -increase tensile strength of wounds -phase starts when wound has closed |
|
|
What is angina? |
Results from ischemia. Heavy, tight, pressure chest feeling. It happens when the heart isnt getting enough blood, therefore, the muscle cramps and functions abnormally. Stable angina: Predictable times e.g. ain after exercising, resolves within a few minutes and disappears with rest. Unstable angina: randomly happens, doesnt get better with rest, each episode worsening |
|
|
What is the role of sodium in the body? |
Regulates water inside and outside the cell
Hyponatremia symptoms -seizures -abdominal cramps, loss of appetite -confusion -Shallow respirations Hypernatremia symptoms -fever, flushed skin -restlessness, agitated -increase fluid retention -edema, confused -decreaded urine output |
|
|
Agranulocytosis is a condition which bone marrow doesn't make enough white blood cells- therefore extremely low. What are some signs and symptoms of this? |
Can be asymptomatic -sudden fever -chills -sore throat -weakness in limbs -mouth ulcers, bleeding gums |
|
|
What is carcinoma? |
-most common type of cancer -begins in epithelial tissue of the skin or in the tissue that lines organs |
|
|
What is haemolysis? |
Rupture it destruction of red blood cells Symptoms include -dark urine -jaundice -heart murmur -tachycardia -enlarged spleen and liver |
|
|
How do beta blockers work? |
Affects epinephrine and norepinephrine. Blocks sympathetic nervous system of heart Keeps heart rate low, dilates vessels |
|
|
How do ACE inhibitors work? |
Prevents vasoconstriction by blocking angiotensin 1 and 2 |
|
|
How do Angiotension receptor blockers (ARBS) work? |
Works by causing vasodilation by blocking aldosterone and angiotension |
|
|
What is postictal state? |
-Alternated state of consciousness after an epileptic seizure. -Last 5-30 minutes Characterized by: -Drowsiness, confusion -nausea -hypertension -headache |
|
|
What is ABG for? |
Arterial blood gas Measure the acidity or alkalinity of blood |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis? |
Kussmauls respiration Confused, weak Hypotension Cardiac changes |
|
|
What is diazepam used for and how does it work? |
Anxiety. Is a benzodiazepine. Works by increases GABA. Side effects -tiredness, drowsy, fatigue, muscle weakness -headache -ataxia -dry mouth -nausea, constipation -vertigo |
|
|
What is Digoxin? |
Works by helping the heart to maintain strong, steady heart beat
Used for Heart failure, cardiogenic shock, AF Side effects Toxicity (vomiting, anorexia, vision changes) -electrolyte imbalances -fatigue, headache, diarrhea
|
|
|
How quick IV does frusemide work? |
It should start after 2-5 minutes. Peaks at 30 minutes |
|
|
GTN side effects? |
Headache Dizziness Light headed Feeling faint when you stand up |
|
|
Rapid, fast acting, intermediate, long acting and premixed insulin are all used in NZ. What are some names, action and times for administering? |
Rapid acting Novorapid -With food -Onset: 10-20min -Duration: 3-5 hours Fast acting Actrapid -20-30min before eating -Onset: 30min -Duration: 8 hours Intermediate Protaphane -Twice daily, 20-30min b4 eating/bed -May be used with rapid acting -Onset: 90min -Duration: 16-22hours Long acting Lantus (Glargine) -1-2x daily. Not related to meals -Onset: 30min -Duration: 16-24 hours Premixed - Penmix -1-2x daily 30min before meal (am & pm) -Onset: 30min -Duartion: 24hours Premixed - Humalog -1-3x daily with food (immediately) -Onset: 10-20min -Duration: 16-22 hours |
|
|
What are side effects for morphine? |
-Dizzy, sleepy, tired -Reduced concentration -Nausea or vomiting -Constipation -Headache, dry mouth |
|
|
What is an anxiolytic? |
Drug used to reduce anxiety |
|
|
What is potassium chloride? |
Used to prevent or treat low blood levels of potassium Side effects Anaphylaxis Severe throat irritation High potassium level Stomach bleeding Bloating, vomiting |
|
|
What is dysarthria? |
Slurred speech |
|
|
In 2012 a new Code of Conduct was released. It was created by the council describing the behaviour that nurses are expected to uphold. What are the 4 core values that this Code is framed around? |
Respect Trust Integrity Partnership |
|
|
Measles is highly contagious viral illness that causes skin rash and fever. When is a person with measles infectious? And what are the signs and symptoms? |
Infectious from 5 days before and 5 days after the rash appears. Symptoms Begin to show 10-14 days after infection. There are 3 stages. Stage 1 -Last 3-4 days -Fever, runny nose, cough, loss of appetite, conjunctivitis -Tiny white/blie spots on inside of mouth Stage 2 -Blotchy red rash appears (4-5days) -Rash starts on head/face (often on hairline or behind ears) then spreads to arms and legs -Most unwell day 1 or 2 of rash Stage 3 -Rash fades, brownish stain on skin |
|
|
What are some complications of measles? |
Common: Ear infections Diarrhoa (can lead to dehydration) Febrile seizures Pneumonia *main cause of death Inflammation of the brain can occur. |
|
|
What symptoms are concerning for measles, therefore, a Doctor should be called? |
Trouble breathing Stiff neck Drowsiness and unable to wake someone up Coughing up green or yellow mucus Back pain Sore ears Seizure Not passing urine for 10 hours |
|
|
What is hemoptysis? |
Coughing up blood |
|
|
Roughly 8 hours after first drink, withdraw symtpoms begin They peak after 24-72 hours. What are signs of alcohol withdrawal? |
Mild Nausea and vomiting Heart palpitations Fatigue Tremors Anxiety, agitation, depression Mood swings
Moderate Increased BP, temp and resp Irregular heart rate Confusion, irritability Mood disturbances
Severe Hallucinations Fever Seizures Seizures Severe confusion and agitation Detox treatment Benzodiazepine e.g. dizaepram
|
|
|
What are the 3 phases schizophrenia ? |
1. Prodomal stage -first realization by family that something is wrong -Vague changes Symptoms: Loss of interest, decrease personal cares, sleep disturbances, changes in mood, anxiety/depression As this develops, more intense symptoms may appear: Supiciousness, racing or delayed thoughts, unusual perceptions 2. Acute phase -earliest time it can be diagnosed -psychotic symptoms 3. Recovery phase -Reduction or absence in symptoms. |
|
|
Define the following Alogia Avolition/Apathy |
Alogia Poverty of speech Avolition/Apathy Loss of interest in usual activities, lack of motivation |
|
|
What are the 4 main medications used to treat tuberculosis? |
RIPE Rifampin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol |
|
|
What are the 3 different types of acute kidney injury |
Prerenal Occurring before the kidneys Intrarenal occurring in the kidneys Postrenal after the kidneys |
|
|
What are Clozapine adverse effects? |
Sedation Hypersalivation Constipation Acid reflux Urinary incontinence Hypotension ECG abnormalities Tachycardia Agranulocytosis
|
|
|
Where does the acute otitis media occur? |
In the eustachian tube |
|
|
Why is progesterone important during pregnancy? |
Helps maintain the uterine line throughout pregnancy. It helps with breast development and breastfeeding |
|
|
What does calcium and potassium do for the body |
Calcium: -builds bones and teeth -Activity of enzymes -contraction of muscles and heart -blood clot Potassium: -regluate fluid balance -regulate muscle contractions -regulate nerve singles |

