![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
actuaries |
study the financial implications of future contingent events |
|
|
contingencies imply? what kind (3) |
loss -physical injury/harm -emotional -economical/financial |
|
|
risk |
exposure to loss |
|
|
how to manage risk |
completely avoid it completely accept it limit exposure transfer to someone else (insurance |
|
|
need to know how much to charge |
approx value of loss probability of loss population - # of insured |
|
|
risk aversion |
willingness to pay more for the certainty of loss |
|
|
insurance premium covers (4) |
fee for the guarantee fee for profit margin insured's expected losses insurer's expenses |
|
|
premium collects money when |
upfront |
|
|
why do they collect premium upfront (2) |
establishes whos in the pool insures and invests it |
|
|
soa what they do |
society of actuaries long term contracts |
|
|
cas what they do |
casualty actuarial society short term contracts |
|
|
how does the bank get money |
savers invest and get paid interest people who borrow money have to pay interest banks charge more on loans than deposits |
|
|
principal deposit represented by the letter |
K |
|
|
growth factor |
1+i |
|
|
discount factor (v) |
1/(1+i) |
|
|
accumulating function |
A(n)=A(0)•(1+i)^n |
|
|
present value of multiple payments |
sum of pv of individual payments |
|
|
annuity |
equal payments of a fixed amount of each period for N periods |
|

|
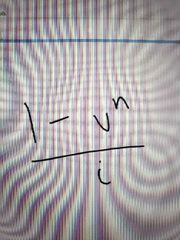
|
|

|

|
|
|
actuarial PV |

|
|
|
variance |

|
|
|
defined benefit pros and cons (employer) |
employee attraction asset pooling handcuffs low expense for short term employees holding risk ongoing fees lack of understanding of value difficult to alter course |
|
|
defined benefit plan pros and cons (employee) |
guaranteed retirement income not holding risk various optional forms of benefit generally no or low cost from paycheck not always portable changing jobs will more severely impact retirement savings difficult to understand employer could freeze/terminate |
|
|
flipping a coin is a |
binomial distribution |
|
|
to find loan |
P*an |
|
|
event |
must be clearly defined so we can agree it happened to agree if it can be covered |
|
|
trial |
1 attempt |
|
|
experiment |
many trials |
|
|
outcome |
result of trial |
|
|
sample space |
s, of all possible outcomes |
|
|
event |
subset of s |

