![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the Characteristics of Staphylococci?
|
- >40 species exist
- All exposed tracs e.g. GI and Respiratory are lines with mucus membranes that staph can live on - All part of normal skin and mucosal membrane fora - Coagulase positive or negative - Most important coag positive species is staph aureus: Found in moist skin folds |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Streptococci?
|
- Gram Positive cocci
- Facultative anaerobes - aerobic respiration with oxygen and fermentation without. |
|
|
|
What Is Virulence?
|
The extent of damage that a pathogen can cause
|
|
|
|
What is Pathogenicity
|
The ability of an organism to cause disease
|
|
|
|
What three features of staph contribute to pathogenicity?
|
1) Evasion from phagocytosis
2) Production of enzymes 3) Production of Toxins |
|
|
|
Compare virulence factors of Staphylococcus Aureus and Epidermis
|
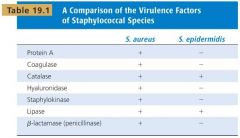
|
|
|
|
How does S.aureus use protein A?
|
Coats itself with protein A and binds to the stem of class A antibodies interfering with the antibody response and complement
|
|
|
|
How does S aureus use coagulase?
|
Coagulase reacts with prothrombin in the blood. Resulting complex is called staphylothrombin, which enables protease to convert fibrinogen to fibrin = blood clot. Coagulase is tightly bound to the surface of the bacterium S. aureus and can coat its surface with fibrin upon contact with blood. The fibrin clot may protect the bacterium from phagocytosis and isolate it from other defenses of the host.
|
|
|
|
How does Staphylococcus aureus species use hyaluronidase as a virulence factor?
|
Hyaluronidase is known as a spreading factor - The staph encoroperates the hyaluronidase into the slime layer thus the bacteria is not recognised as being foreign. They also break down the hyaluronic acid so they can spread through the body
|
|
|
|
How does Staphylococcus use staphylokinase?
|
Used to dissolve the fibrin clot when nutrients are required and also aid in spreading
|
|
|
|
How does Staphylococcus use lipase as a virulence factor?
|
Breaks down the lipids so that the bacteria can then inhibit the areas that the colonise.
|
|
|
|
How does staphylococcus use Beta lactamase as a virulence factor?
|
Uses it as drug resistance against beta lactams such as penicillin
|
|
|
|
How is a staphylococcus infection transmitted?
|
Direct contact from person-person or from contaminated clothing, bet sheets and medical instruments.
Both S. aureus and epidermis are common causes of healthcare associated infections. Type of infection dependant on the immune status of the host and the virulence factors various strains may express. |
|
|
|
What are the three categories of disease?
|
1) Non-invasive
2) Cutaneous 3) Systemic |
|
|
|
What is a Non-invasive disease?
|
Usually do not spread to or damage other organs and tissues. e.g. Staphylococcal food poisoning usually occuring after eating contaminated food - reheating has no effect as it it heat labile.
|
|
|
|
What is a Cutaneous disease?
|
Cutaneous diseases are related to the skin e.g. Impetigo of which 80% is caused by staph aureus and 20% by staph epidermis
|
|
|
|
What is a Systemic disease?
|
A disease effecting a number of tissues with a common function e.g. TSS in which staph enters a wound and if absorbed in the blood stream it causes nausea, vommiting, BP decrease, skin peeling. Of which 10% of cases are fatal
|
|
|
|
What Streptococcus species are human opportunistic pathogens?
|
S.Pyogenes: causes strep throat- Group A
S.Pneumoniae: causes pneumonia S.agalactiae: Colonises the reproductive tract and can cause meningitis of the newborn- Group B |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of group A Streptococci?
|
- Known to infect pharynx and skin - following colonisation can invade deeper tissues and spread to organs
- Large innoculum required and disease usualy results when competing microflora are depleted / host has poor immune status |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Group B streptococci?
|
- Usually live harmlessly inside the digestive system and in the vagina.
- Strep B can sometimes cause urinary tract infections (UTIs), skin infections, bone infections, blood infections and pneumonia, particularly in vulnerable people, such as the elderly and those with diabetes. |
|
|
|
What is a major disease caused by streptococcus pyogenes?
|
Necrotising fascitis
Despite being in the normal gut flora of 20% of adults it can destroy the fascia (connective tissue surrounding muscle) - eventually destroys it and only way to stop it is scraping away the dead tissue |
|
|
|
What is Streptococcus pneumoniae?
|
-Common bacterial pathogen with 92 strains known to cause infectious disease,
- Found in nasopharynx of 20% of adults - Diplococcus on gram stain - Alpha haemolytic on blood agar in aerobic conditions and Beta haemolytic in anaerobic conditions |
|
|
|
What is alpha, beta and gamma haemolysis?
|
Alpha: Formation of a halo/ partial discolouration around colonies -Partial RBC haemolysis
Beta: Complete breakdown of RBC Gamma: No effect on the RBC |
|
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of Staph Epidermis?
|
Gram positive
Cocci Arranged in chains Catalase + Coagulase - Gamma haemolytic |
Gram stain
Cell shape Arrangement Catalase test Coagulase test Haemolysis |
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of Staph Aureus?
|
Gram positive
Cocci Arranged in chains Catalase positive Coagulase positive Beta haemoytic |
|
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of Strep agalactiae?
|
Gram positive
cocci (pointed) Arranged in diplococci Catalase negative Beta haemolytic |
|
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of Strep pyogenes?
|
Gram positive
cocci (pointed) Arranged in chains / clusters Catalase negative Beta haemolytic |
|
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of Strep pneumoniae?
|
Gram positive
cocci (pointed) Arranged in diplococci Catalase negative Beta haemolytic |
|

