![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define cost of capital |
Amount that must be earned to meet required return for all investors
Each category of investment has a different risk, the cost of capital is a weighted average of all different categories- it is referred to as the weighted average cost of capital |
|
|
How is the cost of capital calculated? |
Cost of equity capital: CAPM = rf + B (rm - rf) GGM = D1/ r - g Cost of debt capital: =interest rate (1-tax rate) |
|
|
How does one calculate the weighted average cost of capital? |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
How can one calculate cost of equity with ordinary shareholders? |
2 methods (GGM - gordons growth model aka Dividend discount model) (CAPM - capital asset pricing model) |
|
|
When should one use GGM (DDM) method to estimate cost of equity? |
-can only be used by entities that pay dividends -model assumes that dividends grow at a constant rate annually, which is not always the case |
|
|
What other method can one use to estimate cost of equity besides DDM (GGM)? |
Capital asset pricing method, because it measures risk with the beta coefficient |
|
|
Explain the dividend discount model (GGM): |
-size, frequency and stability of dividend payments depend on entity’s dividend policy -ordinary shareholders expect dividend increase each year- therefore adopt policy whereby dividends increase at constant rate each year -the constant dividend growth model states that the market price of a share is assumed to be the present value of the future dividends |
|
|
What is the formula for GGM |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the formula for the capital asset pricing model? |

Formula: |
|
|
What does the beta coefficient measure in the CAPM? |
Measures market risk |
|
|
How does one calculate market risk? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Discuss the cost of equity for preference shareholders |
-dividends are paid to preference shareholders and distributed after tax profits Therefore preference dividends are not deductible for tax purposes, irrespective of whether or not the preference shares are redeemable |
|
|
What does the cost of preference shares depend on? |
Whether they are redeemable or not |
|
|
How can one calculate cost of preference shareholders equity? |
If preference shares are non redeemable: cost can be calculated using perpetuity principles (perpetuity makes payments indefinitely) If shares are redeemable: cost can be calculated using annuity principles (annuity makes regular payments throughout a specific time frame but has an expiry date) |
|
|
What is the formula for calculating non redeemable preference shares? |
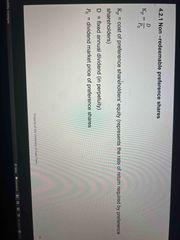
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Discuss cost of debt |
-the cost of debt is the return that the entity’s lenders demand on new debt - it is the interest rate that entities must pay on debt If debt is non redeemable- the cost of debt can be calculated using perpetuity principles If debt is redeemable- the cost of debt can be calculated using annuity principles |
|
|
What is the main difference between calculating cost of shares and cost of debt? |
The shares on the debt is tax deductible whereas dividend on shares is not tax deductible |
|
|
How is the interest on cost of debt tax deductible? |
The cost of debt offer a tax shield which means companies are allowed to treat interest payment as an expense, therefore the taxable income of a company will be lower than if it had been financed by equity only |
|
|
How does one calculate mon redeemable debt? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is weighted average cost of capital? |
-overall return that an entity must generate on its existing assets to maintain the value of an ordinary share, preference shares and debt |
|
|
Why must the WACC be determined? |
-each cost of a capital component has a different cost -the different costs are due to different levels of risk that different capital providers attach to the entity -debt generally cheapest source of funding thus the lowest cost of capital |
|
|
What is the cheapest source of funding? |
Debt |
|
|
What is the second cheapest source of funding? |
Preference is the second cheapest source |
|
|
What is the most expensive form of funding? |
-ordinary shareholders capital |
|
|
How can weighting of average cost of capital be determined ? |
Is determined by using book values or market values of these sources Market values are preferred because they provide a more accurate measure of an entity’s value |
|
|
What is book value? |
Net value of firm’s assets found on its books or balance sheet |
|
|
What is market value? |
Company’s worth based on the total value of its outstanding shares in the market (market capitalisation) |
|
|
Give a summary of how to calculate cost of capital |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
How does one calculate weighted average cost of capital? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the importance of the WACC in investment decisions? |
-determines which potential project are worthwhile for capital investment purposes and which are not -business only make investment if expected return is greater than WACC -in situation where multiple investments are considered: -accept only investments with positive differences between the IRR and the WACC -start with the investment with the highest positive difference |

