![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
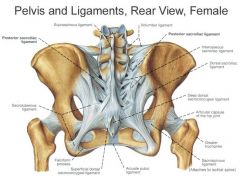
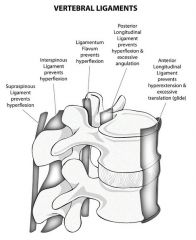
Is anterior sacral or posterior sacral ligament stronger?
|
Posterior
|
|
|
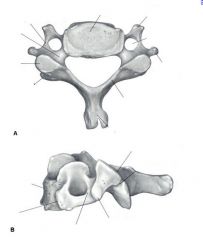
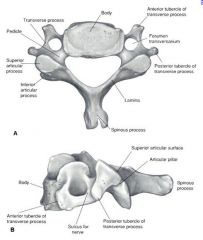
What are the 3 primary areas for bone formation of vertebrae?
|
1. Vertebral Body 2. Spinous Process 3. Facet joints
|
|
|
What is the zygoapophyseal joint?
|
inbetween the superior and inferior articular facets of vertebrae
|
|
|
What shape is the most common for the zygoapophyseal joint?
|
Flat
|
|
|
What are the facet orientations in the T, C, L spine?
|
L- 90 T- 60 C- 45
|
|
|
What motion is primarily limited at lumbar spine?
|
rotation
|
|
|
What is the largest avascular structure in the body?
|
IVD
|
|
|
What are the rations between IVD height and vertebral body height in the L, T, C spines?
|
L- 1:3 T- 1:5 C- 2:5
|
|
|
What direction are the annulus fibrosis fibers running in the L spine?
|
65 degrees in opposite directions w/ each layer
|
|
|
What is the function of the vertebral end plate?
|
anchors annulus propulsus to vertebral body, overtime becomes bone
|
|
|
Where does the spinal cord end?
|
L1-L2 --> cauda equina
|
|
|
What muscles act is pole muscles for the thoracolumbar fascia?
|
Erector spinae, multifidus
|
|
|
What muscles act as 'guy wires' for the thoracolumbar fascia?
|
Glut max, lats, internal/external obliques, TA
|
|
|
What is the primary function of the quadratus lumborum?
|
Eccentrically control sidebending
|
|
|
What is the main function of the multifidus muscle?
|
Compress vertebral segments to limit shear forces
|
|
|
Why do spinal cord injuries occur in the T-spine most frequently?
|
The spinal canal is narrower
|
|
|
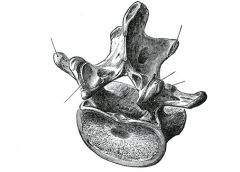
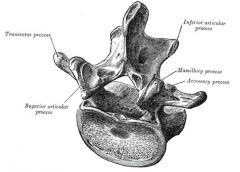
What vertebrae are considered typical? atypical?
|
Typical: T2-T9, Atypical: T1, T10-12
|
|
|
Why is the thoracic vertebrae limited in extension?
|
oblique direction of spinous processes --> bony approximation
|
|
|
What is the rule of threes to figure out what T vertebrae you are on?
|
T1-3: Same level as spinous process T4-6: spinous process 1/2 level below T7-9: Spinous process 1 full level below T10: One full level below T11: one half level below T12: same level
|
|
|
What ribs are classified as true, false and floating?
|
True: 1-7, False: 7-10, Floating: 11-12
|
|
|
Where is the superior costotransverse ligament?
|
Between ribs
|
|
|
Where is the radiate ligament?
|
Attaching ribs and VB
|
|
|
What are the 2 distinct regions of the C-spine?
|
Upper (C1-2) lower (C3-7)
|
|
|
What is the yes and what is the no joint
|
yes- Atlanto-occipital. No- atlantoaxial
|
|
|
Where is the uncovertebral joint (also what spinal levels)?
|
Lateral portion of vertebral bodies of C3-7
|
|
|
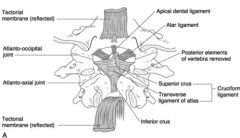
What ligament does the posterior longitudinal ligament become?
|
Tectorial membrane
|
|
|
What spinal levels have the transverse foramen?
|
C1-6
|
|
|
What muscles does the levator scapulae counter (in sagittal and frontal planes)
|
Sagittal: scalenes. Frontal: Splenius
|
|
|
What muscle does the SCM counter?
|
Upper trapezius
|
|
|
What 2 muscles are considered the 'transverse abdominus' of the cervical spine?
|
Longus colli and capitus
|
|
|
What is the orientation of the annular fibrosis in the C-spine?
|
vertical
|

