![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the vertebrae of the spine? |
|
|
|
Purpose of spine bones |
|
|
|
C1 |
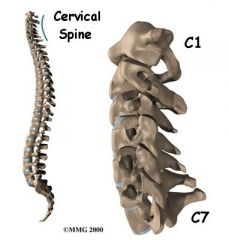
Articulates with occipital bone of skull |
|
|
L5 |
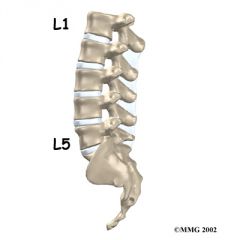
Articulates with sacrum |
|
|
Does the size of vertebrae increase from cervical to lumbar? |
Yes |
|
|
Does each vertebrae contain anterior and posterior elements? |
Yes |
|
|
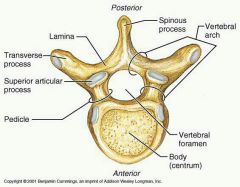
Vertebral Body |
|
|
|
Pedicles and lamina |
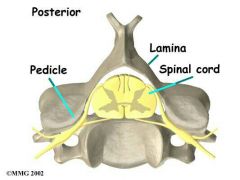
Join anteriorly at body and posteriorly at the spinous process to form the vertebral foramen |
|
|
Vertebral foramen |
Space for spinal chord |
|
|
Spinous and transverse processes |
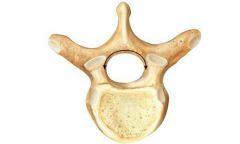
Bony protuberances |
|
|
Where do ribs attach? |
|
|
|
True ribs |
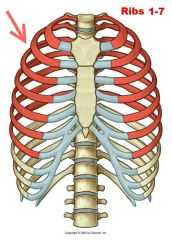
|
|
|
False ribs |
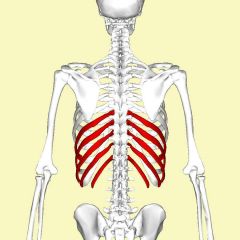
|
|
|
Floating ribs |
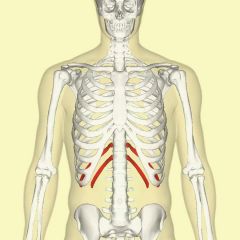
2 most inferior pairs of false ribs that don't attach to sternum |
|
|
Sacrum and coccyx |
|
|
|
Sacrum |
Large triangular bone |
|
|
Coccyx |
Bone formed of 3-5 fused vertebrae |
|
|
Lordosis |
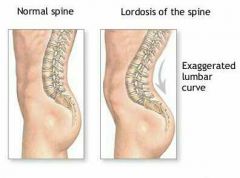
|
|
|
Kyphosis |
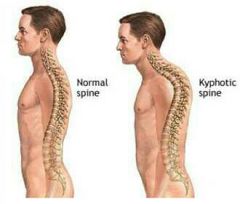
|

