![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain what happens once stimuli is detected as heat, pain, or slight touch |
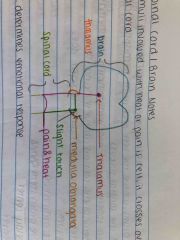
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Where does stimuli go once it is detected? |
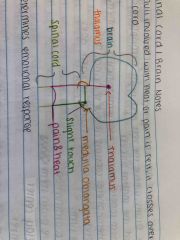
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What does the thalamus do? |
Detects emotional response |
|
|
Describe some characteristics of the brain |
• one of the largest organs • brain is smaller in female (no correlation to intelligence) |
|
|
__% of brain cells are present when _ ____ __ ____ |
90, a baby is born |
|
|
How many brain cells are killed once you drink an OZ of alcohol? |
30,000-50,000 |
|
|
How many genes control brain development? |
17 |
|
|
Over the thousands of years, did the brain get smaller or larger? |
Smaller |
|
|
What does the Frontal lobe in the brain do? |
• receives information from temporal lobe to interpret information * last part of the brain to develop, first part of the brain to die |
|
|
What does the parietal lobe do? |
• where all sensory impulses go/end up |
|
|
What is the Sagital Sulkes? |
The top of the brain, in the middle, where the left & right hemisphere divide |
|
|
What does the Left Hemisphere do? |
• controls analytical thinking • mathematics |
|
|
What does the Right Hemisphere do? |
• creative thinking • arts |
|
|
What is the audiometer center? |
• where original thought goes |
|
|
What does the cerebellum do? |
• controls muscle coordination • primitive brain stem |
|
|
What is the Pons role in the brain? |
• relay center for stimuli • sends impulses to proper regions of the brain • contains booster center for respiration |
|
|
Medulla Oblangata is in charge of what in the brain? |
• connects brain to spinal cord • contains reflex center • cardiac center • respiratory center (coughing, sneezing, vomiting) • where all sensory impulses cross over to the opposite side |
|
|
What does the Thalamus do? |
• maintains the alerting mechanism • controls emotion • pleasant & unpleasant |
|
|
What does the Lymbic System do? |
• ambition/ will power/ drive |
|
|
What does the Hypothalamus do? |
• connection to pituitary gland to brain • connects nervous and endocrine system • controls drinking, sex, and eating • “rewarding system” • regulates body temperature, appetite, and reproductive function • in charge of; oxytocin (contractions) • links psychic mind to the body • involves with maintaining awaken state |
|
|
What does the Hippocampus do? |
• region in brain where memory is initiated |
|
|
What affects does Meningitis have on the brain? |
• puts pressure on brain and spinal cord |
|
|
What is Arachnoid? |
• a spongy brain |
|
|
What does the fluid in the brain do? |
• suspends brain to prevent pressure on spinal cord • acts as a shock absorber |
|
|
What is Internal Hydrocephalus? |
• an increase in cerebral fluid ON the brain |
|
|
What is External Hydrocephalus? |
• a build up of fluid OUTSIDE the brain |
|
|
What is the Amygdala? |
• in charge of experiencing emotion |
|
|
What are Ingram’s? |
• folds in the brain that help with long term memory |
|
|
Alzheimer’s is.. |
• an allergy to Beta Amyloid protein |
|
|
The two types of Alzheimer’s are.. |
1. Early on-set ; 65, progressive, dangerous, “diaper-wear-er’s” 2. Late on-set ; late 70’s, slower progressing |
|
|
More _____ usage = more ______ |
• brain • oxygen |
|
|
What is a C.V.A? |
• cerebral, vascular, accident |
|
|
What is a Stroke? |
• interruption of oxygen or blood to the brain |
|
|
What does the Choroid Plexus do? |
• it is the blood-brain barrier • pushes fluid (C.S.E, cerebral spinal fluid) into ventricles, bundle of capillaries |
|
|
What is the Dura Mater? |
• a strong fibrous coating around the brain • protects |

