![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
General shape of spinal cord in a cross section |
Oval (AP compression) |
|
|
Depressions that lie on the anterior and posterior surface of the spinal cord |
Posterior median sulcus Anterior median sulcus |
|
|
Where the spinal cord begins and ends in an adult |
From the foramen magnum of the skull, to between L1 and L2 roughly |
|
|
The spinal cord goes to here in newborns |
The full length of the vertebral canal |
|
|
Regions of the spinal cord |
Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccygeal |
|
|
Spaces and structures surrounding the spinal cord from superficial to deep |
Vertebra Epidural space Dura mater Subdural space Arachnoid mater Subarachnoid space Pia mater |
|
|
Hole down the middle of spinal cord |
Central canal |
|
|
How the dura mater in the vertebral canal differs from dura in the cranial cavity |
Consists of one layer rather than two |
|
|
What portion consists of dendrites, cell bodies of neurons, glial cells, and unmyelinated axons |
Gray mater |
|
|
What portion is composed of myelinated axons |
White mater |
|
|
Where grey mater is located and how it’s shaped |
Centrally H shaped or butterfly shaped |
|
|
The anterior mass of gray mater that contain cell bodies of somatic motor neurons |
Anterior horns |
|
|
From T1-L2 what structures contain the cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons? (Fight or flight responses) |
Lateral horns |
|
|
Masses of grey matter that contain the axons of sensory neurons and cell bodies of interneurons |
Posterior horns |
|
|
Horizontal bar of grey matter that surrounds central canal within the spinal cord |
Grey commissure |
|
|
Fluid on central canal |
Cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
Where does white matter lie in relation to grey matter |
External |
|
|
Three regions of the white matter of the spinal cord |
Posterior funiculus Lateral funiculus Anterior funiculus |
|
|
Small attachments of a spinal nerve to the spinal cord |
Rootlets |
|
|
Numerous small attachments of rootlets converge to form what |
Ventral (anterior) root Dorsal (posterior) root |
|
|
Cell bodies associated with spinal nerves are found here |
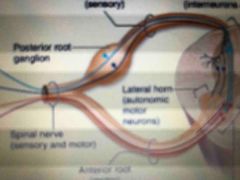
Dorsal root gangalion |
|
|
Spinal nerves are formed by the convergence of what within what |
Anterior and posterior roots within intervertebral foramina |
|
|
Number of pair of spinal nerves |
31 |
|
|
Regions of the spinal cord with spinal nerves associated with each region |
Cervicle: C1-C8 Thoracic: T1-T12 Lumbar: L1-L5 Sacral: S1-S5 Coccygeal region: CO |
|
|
Collection of nerves at the bottom of the spinal cord resembling a horse tail |
Cauda equina |
|
|
Two main branches of a spinal nerve |
Posterior ramus Anterior ramus |
|
|
Branches of the spinal nerve associated with autonomic nervous system |
Rami communications (communicating rami) |
|
|
Specific region of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve |
Dermatome |

