![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
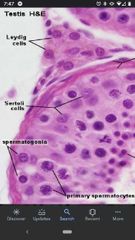
Leydig Cells |
Acted on by LH (leutinizing hormone) to produce testosterone. Found outside the seminiferous tubules. |
|
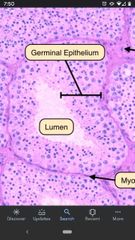
Lumen of Seminiferous tubules |
Central cavity of the tubules into which mature sperm are released. |
|
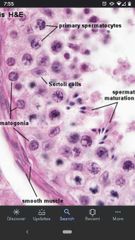
Primary Spermatocytes |
Diploid cells that undergo the first meiotic division to give rise to secondary spermatocytes. Located closer to basal surface of seminiferous tubules. |
|
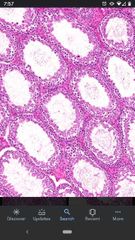
Seminiferous tubules |
Tightly coiled structures in which the sperm develop. Located within the testes. |
|
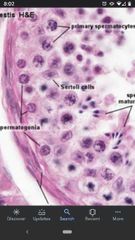
Sertoli cells |
"Nurse" cells that nourish developing sperm and anchor spermatids during maturation. Respond to FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) to initiate spermatogenesis. |
|
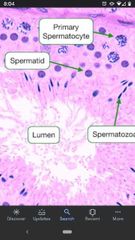
Spermatids |
Haploid cells that undergo spermiogenesis to become mature sperm. Closer to lumen of seminiferous tubules. |
|
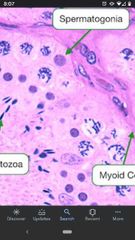
Spermatogonia |
Diploid cells that undergo mitotic division to give rise to primary spermatocytes. Found along the basal surface of the seminiferous tubules. |
|
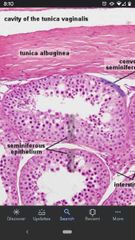
Tunica albuginea |
Connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules portion of the testes. |
|
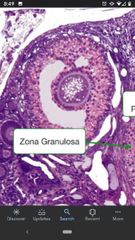
Antral follicle (vesicular follicle) |
Developing follicle w/ small pockets of antral fluid developing within the layers of follicle cells. |
|
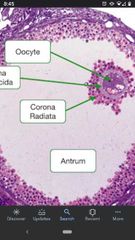
Antrum |
The fluid-filled space found in antral or Graafian follicles; also called the follicular cavity. |
|
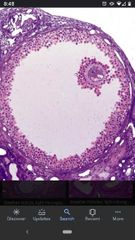
Graafian follicle |
Mature follicle containing a large fluid -filled antrum. |
|
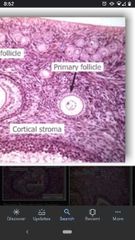
Primary follicle |
Developing follicle containing a primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal follicle cells. |
|
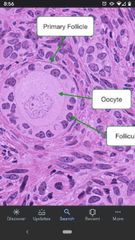
Primary oocyte |
The form of the developing oocyte from 3 months of human fetal development until meiosis resumes shortly before ovulation. |
|
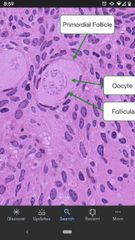
Primordial follicle |
Non-growing follicle containing a primary oocyte stalled in prophase of the first meiotic division and surrounded by a single layer of flattened follicle cells. (Meiotic arrest until puberty). |
|
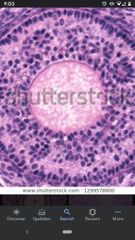
Secondary follicle |
Developing follicle containing a primary oocyte surrounded by more than one layer of follicle cells, BUT NO ANTRUM. |
|
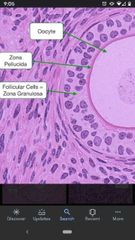
Zona pellucida |
Acellular material secreted between the oocyte and follicle cells. |

