![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do enzymes act like catalysts in metabolic reactions?
|
A metabolic reaction is a reaction that sustains life. Enzymes can speed up these reactions in two ways by breaking down molecules are joining them together.
|
|
|
What are breaker enzymes?
|
Speeds the breaking of large molecules into smaller ones.
|
|
|
What are builder enzymes?
|
Speeds the joining of small molecules into large ones.
|
|
|
How does temperature affect the functions of enzymes?
|
Temperature speeds up the rate of reaction of enzymes (more collisions) until it is denatured (peak rate), at which point the enzyme is no longer usable, as it’s shape has been permanently changed. The rate of reaction will then decrease.
|
|
|
Describe an experiment showing the effect of temperature on enzymes.
|
Test the enzyme catalase (in potatoes), by adding hydrogen peroxide to it in temperatures of 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 degrees. Add the Hydrogen Peroxide to the potatoes and put in water baths. Measure the highest point of froth.
|
|
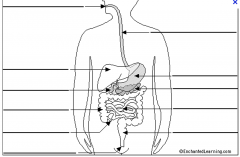
Label the parts of the alimentary canal (from top to bottom).
|
1) Mouth
2) Oesophagus 3) Liver 4) Stomach 5) Pancreas 6) Gall bladder 7) Small intestine 8) Large intestine 9) Appendix 10) Rectum 11) Anus |
|
|
What is the function of the mouth?
|
Food is chewed. It is mixed with saliva which has amylase that breaks down starch to glucose.
|
|
|
What is the function of the oesophagus?
|
Passes the food to the stomach. It has circular muscles in its wall. They contract and squeeze the food to push it. This is called peristalsis.
|
|
|
What is the function of the stomach?
|
Makes digestive juices, containing proteases that start the digestion of proteins to amino acids. Juices also contain hydrochloric acid, because protease works best in acidic pH, and the acid kills germs. Muscular walls churn up the food making sure it is mixed up well with the juices. A ring of muscle opens up to allow food to pass into the small intestine.
|
|
|
What is the function of the small intestine?
|
Very long, food is squeezed along. Pancreatic Juice (from pancreas) and intestinal juice (from glands of small intestine) is added, which contains all 3 enzymes to digest the food. Alkaline bile which neutralises the stomach acid enters from the bile duct which is made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder. Bile emulsifies fats (breaks large drops of of fats into small droplets). This increases the surface area of fats for lipase enzymes to act upon.
|
|
|
What is the function of the large intestine?
|
Water is absorbed into blood. Remaining waste becomes faeces, stored in rectum.
|
|
|
What are the processes of ingestion, digestion and egestion?
|
Ingestion - Taking in food/water
Digestion - The breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream Egestion - different from excretion, the removal of undigested food/faeces. |
|
|
What is absorption?
|
Absorption of nutrients into the blood stream.
|
|
|
What is assimilation?
|
Giving nutrients to cells.
|
|
|
Explain how peristalsis works.
|
Peristalsis is waves of muscle contractions that squeeze in order to move push food along. When the circular muscles contract, the longitudinal muscles relax and the gut becomes narrow. When the longitudinal muscles contract and the circular muscles relax, the gut widens.
|
|
|
What are the names of the enzymes that break down carbohydrates into glucose and what are their functions?
|
Amylase breaks down starch into sugar.
Maltase breaks down maltose into glucose. |
|
|
How does the structure of a villi help with absorption of small molecules in the small intestine?
|
The villi give the small intestine an increased surface area. They have a thin lining and a good blood supply, which allows the small molecules to pass through the thin wall and into the many capillaries.
|

