![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What watery substance fills the anterior eye cavity?
|
aqueous humor
|
|
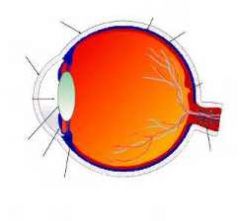
name the marked structures
|
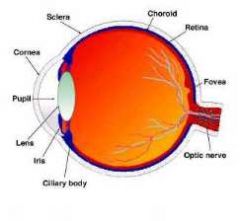
structures of the eye
|
|
|
What gel-like substance fills the posterior eye cavity?
|
vitreous humor
|
|
|
The ______ and ______ make up the fibrous tunic.
|
cornea; sclera
|
|
|
1) pinna
2) temporal bone 3) tympanic membrane 4) semi-circular canals 5) cochlea 6) vestibular nerve 7) external canal 8) hammer 9) anvil 10) stirrup 11) auditory tube |
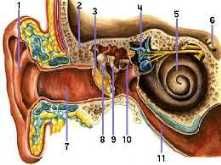
name the marked structures
|
|
|
the middle, pigmented layer of the eye
|
choroid layer
|
|
|
The choroid layer contains the ___ and _____ structures.
|
ciliary body; iris
|
|
|
white connective tissue layer of the eye
|
fibrous tunic (sclera)
|
|
|
modified sebaceous glands that lubricate the eye
|
meibomian glands
|
|
|
what is the conjuctiva?
|
red lining of eyelid
|
|
|
smooth muscle that attaches the lens to the iris of the eye
|
ciliary body
|
|
|
innermost tunic of the eye
|
sensory tunic, or retina
|
|
|
____ provide black and white and peripheral vision, while ____ receive color information.
|
Rods; cones
|
|
|
blind spot where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball
|
optic disc
|
|
|
area containing only cones; provides for greatest visual acuity
|
fovea centralis
|
|
|
similar to blood plasma; provides nutrients to lens and cornea
|
aqueous humor
|
|
|
Aqueous humor is reabsorbed into venous blood through the ______.
|
canal of Schlemm
|
|
|
What is refraction?
|
bending of light rays when light passes from one medium and meets the surface of a different medium
|
|
|
During accommodation for close vision, do the ciliary muscles contract or relax?
|
the ciliary muscle contracts and pulls the ciliary body inward and anteriorly
|
|
|
What is the clinical term for someone who has problems seeing close objects?
|
Hyperopic
|
|
|
What is the clinical term for someone who has problems seeing distant objects?
|
Myopic
|
|
|
What is the clinical name for "old person's vision" or gradual loss of accommodation with age?
|
presbyopic
|
|
|
The sensory hair cells of the organ of Corti are supported on the___ ____.
|
basilar membrane
|

