![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
LIVER Gross Anatomy |
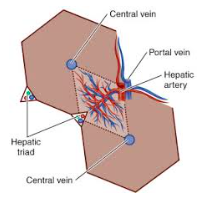
- Coronary lig: liver to diaphragm. - Falciform lig: midline of liver to midline of abdomen. - Round lig: remnant of umbilical vein, embeded in falciform l. - V. porta (afferent from GI) - A. Hepatica (afferent) - V. Hepatica (efferent, enters V. cava) - Functional subunit ="hepatic lobule", hexagonal, 1-2 mm - Central/terminal hepatic vein -> zone 3,2,1 -> triade a. hepatica, v. porta and bile duct. - Acinus = rhombus-shape btw two central veins to two hepatic triades. |
|
|
LIVER Anatomy, everything else |
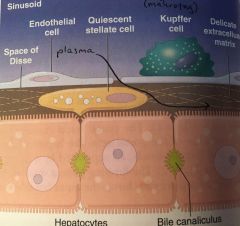
- Space of Disse: space btw endothelial cell and hepatocytes, where plasma can flow freely to distribute/uptake substances. - Kuppfer cells: macrophages of liver - Stellate cell/lipocyte: in Space of Disse, storing Vit A which is released under stress -> synthesize collagen -> hepatic fibrosis. - Canals of Hering: cholangioles draining bile from centrilobular area and direct it to bile ducts. |
|
|
LIVER What does the liver do? |
- Bilirubin metabolism (from hemoglobin) - Bile acid metabolism (absorption of fats and vitamins) - Carbohydrate metabolism (glucose -> glycogen, gluconeogenesis) - Lipid metabolism (breakdown of fats s.a. cholesterol) - Xenobiotic metabolism (foreign substance defence, p450 enzymes ER) - Protein synthesis (plasma-, lipo-, clotting factors 2, 5, 7-13; conversion of ammonia (from protein breakdown) to urea). - Immune function (first line of defense as draining GI). |
|
|
LIVER Types of liver damage |
1. Random hepatucellular degeneration. - Single cell necrosis throughout liver or multifocal areas 2. Zonal hepatocellular degeneration. - Centrilobular (periacinar, zone 3), midzonal (zone 2), periportal (centroacinar, zone 1). Liver pale, friable, rounded edges. 3. Massive hepatocellular degeneration. - Necrosis of entire hepatic lobule and or adjacent lobules (not the entire liver) (zones 3, 2 and 1). |

