![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Quantitative answer to why black holes are black |
-escape velocity exceeds speed of light within Schwarzschild radius Rs = 2GM/c^2 linearly proportional to mass of black hole |
|
|
How can we use the fact that black holes create distortions of the spacetime continuum to observe black holes? |
-gravitational lensing of background sources -merging of black holes creates spacetime ripples (gravitational waves) |
|
|
General relativity & black holes |
-spacetime tells matter (and radiation) how to move, matter tells spacetime how to curve -black holes have the most profound effects near/below the event horizon (Schwarzschild radius) |
|
|
What does light do when passing through a gravitational field? |
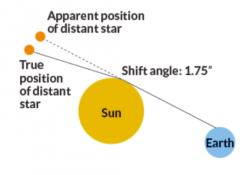
-gets bent -key prediction of general relativity theory (verified experimentally in 1919 during a solar eclipse) -bit hard to measure because sun is bright |
|
|
Tell me about gravitational lensing |
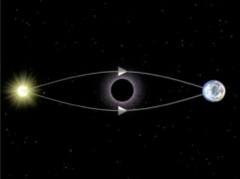
-black holes distort spacetime strongly near event horizon --> extreme light bending -modelling of the lensed image can let you weigh foreground galaxy and its black hole |
|
|
What happens when black holes collide? |
-ripples in spacetime - propagate as gravitational waves -if there are accretion discs, these are perturbed and the brightness of the electromagnetic emission vary |
|
|
What are gravitational waves? |
-'ripples' in the fabric of spacetime caused by violent and energetic processes (eg black hole collisions) -travel at the speed of light, carrying energy and angular momentum |
|
|
How go gravitational waves propagate & distort spacetime? |
deform spacetime in the direction perpendicular to propagation |
|
|
How are gravitational waves described? |
-strain amplitude, frequency & polarisation -+ polarisation compresses horizontal/vertical, x polarisation compresses diagonal |
|
|
How much do gravitational waves affect the size of stuff? |

not much - change the size of a 1km 'ruler' by 1 proton |
|
|
How do you measure gravitational waves? |
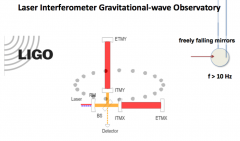
-red things are lasers going through 4km huge arms with mirrors at the end -can change laser to make constructive/destructive interference -so gravitational waves affect light, see change in pattern -need to keep mirrors stable -multiple observatories -on 14/9/15, observed black holes colliding, fit exactly with general relativity theory |
|
|
Black hole masses we now know from LIGO |
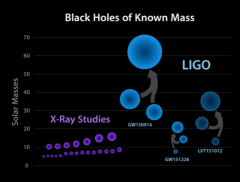
|
|
|
Black hole mass ranges? |
-stellar mass: 1.5 to 70 Msun -supermassive: 10^5 to 10^10 Msun -intermediate???? 100 to 10^5 Msun? - active field of research - multiple scenarios for formation proposed but not observed yet, globular clusters might be best chance to search for them |
|
|
How do you grow a supermassive black hole? |
-do their seeds have intermediate mass/stellar mass? -direct collapse of gas? ???? gravitational wave observations will help find out |

