![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does a black hole form? Why is it black? |
-collapse of a massive star core into a single point because gravity is too great for any pressure to balance it -spacetime continuum is torn - singularity is created -20Msun star creates a 5Msun black hole -black because gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape |
|
|
Tell me about orbital speeds for satellites (circular orbit) |
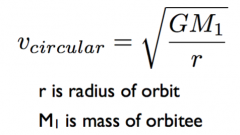
-higher orbits orbit at lower speeds |
|

|
D - formula says it only depends on orbitee mass and radius all orbiters have same speed |
|
|
What is the escape velocity formula? |
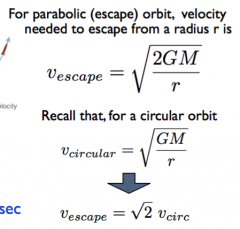
|
|
|
What is the relationship between escape velocity and black holes? |
-decreasing radius at constant central mass increases escape velocity -eventually not even light can escape |
|
|
What is the Schwarzschild radius? |
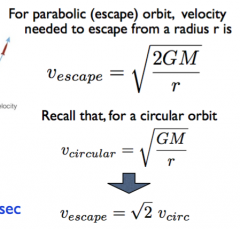
distance from a black hole where nothing can escape - event horizon because no idea what happens inside it |
|
|
How big is a black hole? |
-subbing into the Schwarzschild equation, 3km per solar mass which is tiny -need to really really compress (won't happen to our sun - need way more gravity) |
|

|
D because black holes aren't vacuums cleaners - just act like normal things, unless you get really close -but without sun's energy, earth would freeze and we die |
|
|
What happens if you are really close to the event horizon? |
-tidal force is really strong for a stellar black hole - spaghettification into a thin, long string -star/humans get shredded -supermassive black holes are gentler near the event horizon because Schwarzschild radius is bigger - stars fall in without getting shredded |
|
|
Why do small black holes spaghettify their food? |

mass is smaller, therefore more tidal force |
|
|
What happens to time near the event horizon? |
-time passes more slowly because of strong gravitational field (general relativity) |
|
|
How do you observe black holes if light can't even escape from it? |
-watch things move near them (dynamical mass) -watch matter fall into them (and emit light) |
|
|
How do you infer black holes? |
-look for black hole binaries -more massive star evolves faster, may become black hole -look for remaining star orbiting something invisible --> stellar mass black hole |
|
|
What happens in black hole binary systems? |
-gravity of black hole can peel off layers of companion star, creates accretion disc -very hot accretion disc - bright in UV, x-ray -huge doppler shift as material gets close to black hole |
|
|
Tell me about supermassive black holes |
-orbit speeds become very large for stars at centre of some galaxies -must be something very massive and very small down there - SMBHs are 10^6 to 10^9 Msun -lurk at the centres of most massive galaxies |
|
|
Tell me about Sagittarius A* |
-the Milky Way's black hole -have been watching stars move around it for 20 years -star S0-2 has a period of 15.2 years, pericentre of only 17 hours -require M=4.3x10^6 Msun inside a 17 light-hour radius -has to be a black hole |

