![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Asterism |
group of easily recognizable stars (a distinctive pattern of stars) i.e.. big dipper |
|
|
Asteroids |
are minor planets (irregular shapes) located between orbits of Mars and Jupiter composed of rock and minerals. There are 5000 identified. |
|
|
Astrology |
a psuedoscience, which is based on belief NOT evidence. |
|
|
Astronomical Unit |
symbol (AU). Scale used for distance measurement in the universe. The distance from the Earth to the sun is 149 599 000 km and was designated as 1 AU |
|
|
Astronomy |
the study of the universe; the study of celestial bodies (sun, moon, and stars) |
|
|
Aurora Australanis |
caused by collisions of charged particles and molecules in the upper atmosphere. Appears as shifting patterns of coloured light that are visible in the night sky in southern latitudes. |
|
|
Aurora Borealis |
caused by collisions of charged particles and molecules in the upper atmosphere. Appears as shifting patterns of coloured light that are visible in the night sky in northern latitudes. |
|
|
Big Bang Theory |
A theory used to describe the formation of the universe. theory states that there was a big explosion some 15 - 20 billion years ago that spread out and formed the first matter (atomic particles) |
|
|
Back hole |
An object in space that has such a strong pull of gravity that nothing, not even light, can escape it. |
|
|
Celestial bodies |
refers to the Sun, Moon, stars and planets |
|
|
Comet |
small celestial bodies that orbit the Sun. (billions of these exist). They have bright bodies and tails that always point away from the sun. Composed of dust (carbonaceous or silicate rock) and/or ice. |
|
|
Constellation |
a group of stars that form a pattern that is officially recognized. The sky is divided into 88 regions each associated with a constellation. ie. Gemini |
|
|
Dwarf planets |
Pluto, Xena and Ceres are our 3 dwarf planets. A dwarf planet is a celestial body that is in orbit around the Sun; has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body farces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape; but has NOT cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit; and is not a satellite |
|
|
Galaxy |
a huge accumulation of stars, gas and dust belt together by gravity. The Sun and Earth (etc.) resides in the Milky Way galaxy seen as a hazy white band in the sky. |
|
|
Geocentric |
based on theory proposed by Aristotle which presented a model of the solar system where the Earth was the centre of the solar system. (everything else revolved around the Earth) |
|
|
Heliocentric |
based on theory proposed by Copernicus which presented a model of the solar system where the Sun was the centre of the solar system. (everything else revolved around the Sun) |
|
|
Inner planets |
designated given to planets close to a star. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars in our solar system |
|
|
Inter-stellar medium |
the space between the stars and the material it contains |
|
|
Light Year |
used for distance past our solar system. the distance that a beam of light travels in a vacuum in one year. 300 000 km/s Approximately 9.46 trillion km = 1 light year 63 240 = 1 light year |
|
|
Luminous |
an object which emits its own light i.e.. sun, stars |
|
|
Luminosity |
a measure of the total amount of energy a star radiates per second |
|
|
Lunar Eclipse |
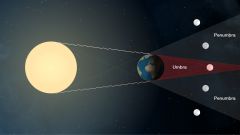
occurs when the Earth passes between the Moon and the Sun. The Moon is plunged into darkness as Earth's shadow moves across it. |
|
|
Magnetosphere |
the space surrounding a celestial body such as the Earth, where a magnetic field exists. |
|
|
Meteors |
solid body that enters the Earth's atmosphere from outer space, becoming hot and bright because of friction with the atmosphere. aka "shooting stars" |
|
|
Meteorites |
remnants of meteors that don't burn up completely and fall to earth. They are made of mainly stone or iron. |
|
|
Nebula |
a vast cloud of gas and dust which may be the birth place of a star. (i.e. The Ant Nebula) |
|
|
Nonluminous |
an object which does not emit light i.e.. planet, Moon |
|
|
Outer planets |
designation given to planets father away from a star. They are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. |
|
|
Planet |
A celestial body that orbits a star and does not produce its own light. A planet is a celestial body that is self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape; and has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit; and is not a satellite |
|
|
Parallax |
the apparent shift in the position of a nearby object when it is viewed from two different points |
|
|
Retrograde motion |
Planets usually move in an east to west direction as the orbit around the sun, but in retrograde motion the planet appears to orbit in a westward direction before resuming its usual E to W direction |
|
|
Satellite |
a small body that orbits a larger one. (i.e.. the Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth) (i.e. a communication satellite is an artificial satellite) |
|
|
SETI |
Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence project which is searching for radio signals from intelligent life. |
|
|
Spectrum |
the series of coloured coloured bands visible when white light is passed through a prism. A prism separates white light into its component wavelengths. A spectroscope is used to see the spectrum. |
|
|
Solar Eclipse |
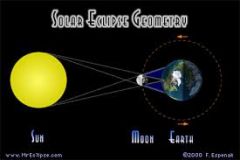
occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun. (shadow falls on the Earth). WE can't see the Sun = solar eclipse |
|
|
Star |
a celestial body that is a huge ball of gas which has an ongoing fusion retain at its core.
Types of stars a) Neutron Star: A supernova of a star results in the crushed remnant. It is small, super dense star. b) Cepeid variable star: a star that pushes, chafing its brightness in a regular cycle. c) Binary stars: two single stars that orbit one another |
|
|
Quasar |
celestial objects that LOOK LIKE a star, but they emit much more energy. They are believed to be the result of galaxies colliding and their gasses explosively erupting. |
|
|
Solar System |
the family of the Sun, the planets, their moons, dwarf planets, asteroids and comets. |
|
|
Sun |
the star of our solar system. We use its mass to measure others tars and assign its mass to be 1 solar mass. |
|
|
Super nova |
a huge explosion constituting the death of a star. Stars of more than 3 solar masses will result in the formation of a black hole; 3 or less solar masses and a neutron will result. |

