![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What’s in the solar system? |
-sun is at centre of solar system -8 planets orbit the sun+ 1 dwarf planet (Pluto) -natural satellites |
|
|
satellites |
Celestial body that orbits a planet either natural (moon) or artificial (communications) |
|
|
How was the sun formed ? |
Formed from a cloud of dust and gas (nebula) pulled together by gravitational attraction |
|
|
Dwarf planet |
Object orbiting a star that is massive enough to be rounded by gravity -but has not ‘cleared the neighbourhood’ |
|
|
Asteroids |
Rock in space that orbits the sun but some may cross the earths orbit producing a risk of collision. |
|
|
Comets |
A ball of icy rock that follows an elliptical orbit around sun. -vaporises as it approaches the sun turning it into a gas. |
|
|
Life cycle of a star |
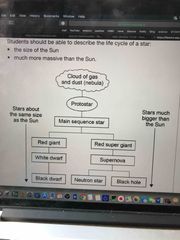
Nebula>Protostar>main sequence star |
|
|
Protostar |
As the mass falls together it gets hot. A star is formed when a hydrogen nuclei fuse together to make helium |
|
|
Red giant star |
The hydrogen has been used up in the process. Larger nuclei begin to form and star may expand to become a red giant. |
|
|
White dwarf |
Star may begin to contract under the pull of gravity. The star becomes a white dwarf which fades and changes colour as it cools. |
|
|
White dwarf |
Star may begin to contract under the pull of gravity. The star becomes a white dwarf which fades and changes colour as it cools. |
|
|
Supernova |
Larger star with more mass will go on making nuclear reactions, getting hotter and expanding until it explodes . |
|
|
Main sequence star criteria |
-forced caused by gravitational attraction and fusion energy are balanced -radiation pressure from fusion reactions tend to expand the star -gravitational attraction tends to collapse the star |
|
|
What does a supernova do? |
When it explodes, all the elements produced are thrown out into the universe. |
|
|
What must happen for a stable orbit? |
The radius must change if the speed changes. |
|
|
How do planets stay in orbit? |
Gravitational attraction provides the centripetal force needed to keep planets and all types of satellite in orbit. |
|
|
Red shift |
The increase in the wavelength of light from most distant galaxies. The further away a galaxy, the faster they are moving and the bigger observed increase in wavelength |
|
|
What suggests there is an expanding universe? |
The change of each galaxy’s speed with distance |
|
|
Big bang |
The starting point of the expanding universe when it was smaller and more dense |

