![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the functions of soil? |
-Medium for plant growth. -Recycling system for nutrients and organic wastes. -Habitat for organisms. -Engineering medium. -System for water supply and purification. |
|
|
Define the hydrological cycle? |
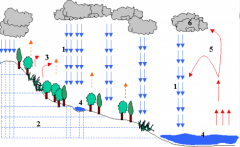
As much as 10% of rainfall is transpired by plants uptakes owing to the soils water holding capacity. 1 = precipitation. 2 = infiltration and through-flow. 3 = transpiration. 4 = surface run-off and erosion. 5 = evaporation. 6 = condensation. |
|
|
What are the basic requirements for crop growth? |
Anchorage.
Water - cooling, nutrient transport, turgor and photosynthesis. Air, particularly oxygen - respiration for energy. Nutrients - ions in soil solution. Insulation - e.g., bare soil = 35 degrees whereas at 5cm depth = 25 degrees. Phytotoxin control - metals such as Pb, Zn and Cu. |
|
|
What management factors influence crop growth? |
-Cultivation. -Drainage. -Irrigation. -Nutrient input. -Organic matter. |
|
|
What factors influence long term soil quality? |
-Acidification. -Salinity. -Erosion. -Compaction. -Water logging. -Desertification. -Chemical pollution (pesticides, PAH's, PCB's and heavy metals). |
|
|
What factors influence water and air pollution? |
-Nitrates and ammonia. -Phosphorous. -Pesticides. -Heavy metals. -Radionuclide's. -Erosion. -Surface run-off. |
|
|
What are the initial soil formation inputs? |
Rocks: Igneous - solidification of molten lava. Sedimentary - weathering products of other rocks; transport and deposition as a result of geological processes. Metamorphic - formed by the action of heat or pressure on pre-existing rocks resistant to weathering. Organic: 1) Bare rock surface. 2) Initial colonization by lichen. 3) Lichen growth. 4) Lichen residues lead to build up of organic matter. 5) Colonization by plants. |
|
|
What are the main organic inputs during soil formation? |
-Fats and waxes. -Lignin. -Sugars and starches. -Cellulose. -Protein. -Hemicellulose. |
|
|
Draw a glucose and a cellulose particle. |
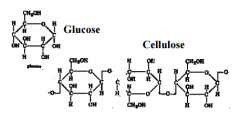
|
|
|
What are the organic compounds in plant tissues and how quickly do they decompose? |
Decreasing in rates of decomposition: -Sugars (eg glucose) -Starches. -Simple proteins. -Crude proteins. -Hemicelluloses. -Celluloses. -Fats and waxes. -Lignins. |
|
|
How do organic inputs transform within the soil? |
-Organic residues are slowly altered by micro-organisms to new material called 'humus' which is both chemically and physically different from the chemicals that make up plant and animal remains. -Organic residues persist in the soil for a few years whilst humus is very stable and can be > 1000 years old. -Humus is intimately mixed with the mineral fraction and imparts a dark brown colour to soil. |
|
|
How is material moved and then finally lost from the soil? |
-The movement and accumulation of different materials in the 'soil profile' is determined largely by the rate of water movement. -Some parts of the soil profile become enriched, others become depleted of certain materials (e.g., clay minerals) especially in high rainfall areas. |

