![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do you classify a soil? |
By their; Composition- mineralogy and proportions Grain size and grain size distribution Structure (cracks) Physical properties |
|
|
How do you classify fine sand? |
-Individual particles visible -Exhibit dilatancy (reaction to shaking, releases water) -Easy to crumble -Falls of hands when dry -Feels gritty -No plasticity |
|
|
How would you classify silt? |
-No particles visible -Exhibits dilatancy -Easy to crumble -Dusted off hands when dry -Feels rough -Some plasticity |
|
|
How would you classify clay? |
-No particles visible -No dilatancy (absorbs water) -Hard to crumble -sticks to hands when dry -Feels smooth (even in mouth) -Plasticity |
|
|
How would you identify organic silts/clays? |
-Dark grey to blue-black -May smell if fresh sample |
|
|
How would you identify loam? |
-Soft deposit -Equal sand/silt/clay |
|
|
Properties of a narrow/uniformly graded soil |
-Little compaction -Lower density -Higher pore space -Faster compaction -Water drains -Roots space |
|
|
Properties of of a well/graded soil |

-More compaction -Higher density -Lower pore space -Slower compaction -Less permeable -Less root space |
|
|
Name some microstructures in soil |
-Fissures (not as strong) -Roots (hold soils together) -Bedding -Sand/silt layers These properties control how water infiltrates through soil Also controls pathways roots are able to grow |
|
|
What are granular soils? |
-Gravel, sand, or silt (coarse grained) -Little or no clay content -No cohesive strength -Some moist granular soils exhibit slight apparent cohesion -Granular soil cannot be molded when moist and crumbles easily when dry |
|
|
What are cohesive soils? |
-Clay (fine grained) -Has cohesive strength and does not crumble -Can be excavated with vertical side slopes -Is plastic when moist -Cohesive soil is hard to break up when dry and exhibits significant cohesion when wet |
|
|
How are cohesive soils classified? |
By their plastic behaviour and liquid behaviour (as properties unrelated to particle size) |
|
|
Effect of increasing water content on cohesive soils at Wp and Wl |
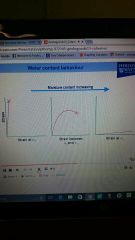
|
|
|
What is the liquid limit? Wl or LL |
The point at which soil stops acting as a plastic solid |
|
|
Define the plastic limit ( Wp or PL) |
-When soil can resist large shearing stress -Exhibits no plastic deformation -Acts as a brittle solid |
|
|
Define the plastic limit ( Wp or PL) |
-When soil can resist large shearing stress -Exhibits no plastic deformation -Acts as a brittle solid |
|
|
What is the plasticity index? Ip |
Range of water content when soil is plastic (bigger range for finer soils) Ip = Wl - Wp |
|
|
What is the liquidity index? Il |
Compares a soils plasticity with its natural moisture content Il = (W - Wp) /Ip If = 1.0 soil at liquid limit If = 0 soil at plastic limit |
|
|
Name the 3 methods of finding the liquid limit |
-Cone penetrometer - definitive method (best) -Cone penetrometer - one point method -Casagrande test |

