![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
t(X;17)(p11.2;q25) - ASPL-TFE3 fusion gene
|
Alveolar soft parts sarcoma
|
|
|
t(12;16)(q13;p11) - FUS-ATF1 fusion gene
|
Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma
|
|
|
t(9;22)(q22;q12) - CHN-EWS fusion gene
|
Chondrosarcoma, myxoid, extraskeletal
|
|
|
t(12;22)(q13;q12) ATF1/EWS
|
Clear cell sarcoma
|
|
|
t(11;22)(p13;q12) EWS/WT1
|
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor
|
|
|
t(11;22)(q24;q12) FLI1/EWS
|
Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET, extraosseous
|
|
|
t(2;13)(q37;q14) PAX3/FKHR
t(1;13)(p36;q14) PAX7/FKHR |
Rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar
|
|
|
t(X;18)(p11.23;q11) - SYT-SSX1
|
Synovial sarcoma
|
|
|
t(1;2)(p11;q35-37)
|
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor
|
|
|
|
|
A two year old child had an abdominal mass, which was excised.
Molecular: 1p36.33 deletion, N-myc amplification, 14p deletion |
Neuroblastoma
Positive: chromogranin, synaptophysin, neurofilament and neuron-specific enolase, as well as vimentin and ALK negative: keratin, CD45, CD99 and desmin |
|
|
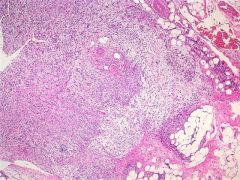
Nodular fasciitis
It is highly cellular and composed of plump, immature fibroblasts or myofibroblasts, with a feathery pattern due to the abundance of ground substance. The tumor cells usually have prominent nucleoli. There is often a myxoid stroma, frequent mitotic figures but no atypical forms, a lymphocytic infiltrate and red blood cell extravasation. The vasculature is usually prominent. There may be bands of collagen similar to keloid scars, or metaplastic bone |
|
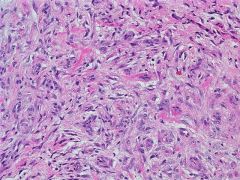
The spindle cells had diffuse cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for CD68 and calponin, and were negative for S100 and pan-keratin. CD34 highlighted the blood vessels.
|
Nodular fasciitis
|
|
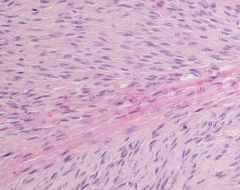
Fascial tissue with infiltrates of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
|
Palmar fibromatosis (Dupuytren's contracture)
|
|
|
Deep fibromatosis (musculoaponeurotic)
vague fascicles of (myo)fibroblasts. Infiltrative borders separated by abundant amount of collagen |
|
|
33 year old woman had a 2.4 cm. soft tissue mass of the cheek. Her past medical history was remarkable only for a remote mitral valve replacement. The mass had been present for a while, but recently grew in size
Immunohistochemistry: CD34 positive; negative for Factor XIIIa and CD68 |
Solitary fibrous tumor of the dermis
|
|
|
herringbone growth pattern
compact fascicles of spindled cells with uniform nuclear features. minimal intervening stroma. variably immunoreactive for smooth muscle actin. |
Fibrosarcoma
|
|
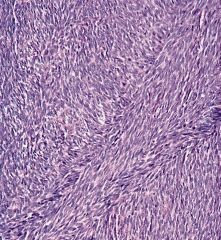
|
Fibrosarcoma
|
|
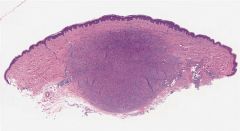
|
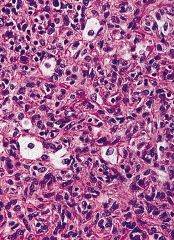
Benign fibrous histiocytoma: Polymorphous population of histiocytoid and spindled
cells, Touton giant cells and chronic inflammatory cells. |
|
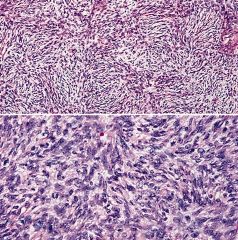
Positive stains: CD34 (strong in 95%), vimentin; also actin (focal), ApoD, bcl2, NKI-C3 (AJCP 1992;97:478), CD99
Negative stains: Factor XIIIa (usually), keratin, EMA, S100, HMB45, desmin, CD117 |
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP):
prominent storiform pattern of monomorphic fibroblast-like cells that invade into subcutis Bednar’s tumor: 5-10% of cases; pigmented variant due to dendritic cells with melanin, S100+ only in pigmented cells, HMB45 negative; associated with black patients |
|
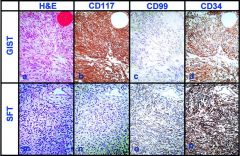
|
Hematoxylin-eosin stained sections of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) (a) and solitary fibrous tumors (SFT) (m). The tumor cells in GIST were immunoreactive for CD117 (b), but tumor cells in SFT were nonimmunoreactive (n). All SFT were immunoreactive for CD99 (o), but some GIST were nonimmunoreactive for this marker (c). Strong immunoreactivity for CD34 was present in most of SFT (p) and GIST (d) (a–p, original magnification ×40)
|
|
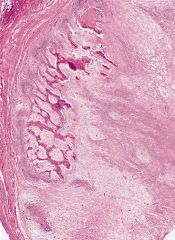
|
Myositis ossificans is a benign, ossifying soft-tissue lesion typically occurring within skeletal muscle. Patients are usually adolescents and young adults; myositis ossificans is rare in children under 10 years of age. The most frequent symptoms and signs are pain and tenderness with a soft tissue mass. Approximately 80% of cases arise in the large muscles of the extremities.
|
|
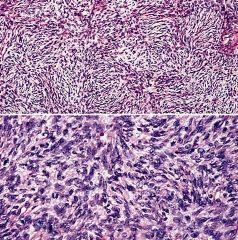
Positive stains: CD34 (strong in 95%), vimentin; also actin (focal), ApoD ,bcl2, NKI-C3 (AJCP 1992;97:478), CD99
Negative stains: Factor XIIIa (usually), keratin, EMA, S100, HMB45, desmin, CD117 |
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
|
|
|
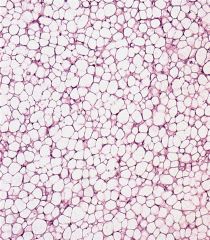
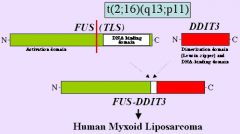
Myxoid liposarcoma
|
t(12;16)(q13;p11) TLS/CHOP
|
|
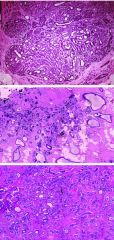
|
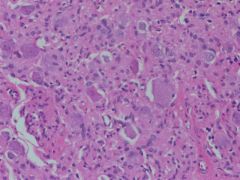
Paraganglioma.
Nests of polygonal tumor cells with nuclear atypia and eosinophilic cytoplasm create a Zellballen pattern. |

