![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The socioeconomic status is determined by what type of status? |
Ascribed Status and Achieved Status |
|
|
|
Type of middle class that includes successful business and professional people. |
Upper-middle |
|
|
|
Type of middle class that includes those who are skilled and semi-skilled workers with fewer luxuries |
Lower-middle |
|
|
|
Type of middle class that includes thos who are unable to step above the class due to economic and educational shortcomings. |
Middle-middle |
|
|
|
Refers to the amount of positive regard (high levels of respect) has for a given person or idea. |
Prestige |
|
|
|
It can be described as the ability to affect other’s behavior through real or perceived rewards and punishments and is based on the unequal distribution of valued resources. |
Power |
|
|
|
It proposes that have-nots called proletariat could overthrow the haves called the bourgeoisie as well as the entire capitalist economy by developing class consciousness. |
Marxist Theory |
|
|
|
It refers to the organization of the working class around shared goals and recognition of a need for collective political action. |
Class Consciousness |
|
|
|
A misperception of one’s actual position within society. Members of the proletariat do not see just how bad conditions are, do not recognize the commonalities between their experiences and others. |
False consciousness |
|
|
|
This type of economy led to an increase in social inequality, a reduction in social cohesion, and a warning of social capital. |
Capitalists |
|
|
|
It refers to a lack of social norma, or the breakdown of aocial bonds between an individual and society. |
Anomie |
|
|
|
It focuses on how anomic conditions can lead to deviance. |
Strain theory |
The reaction is mainly due to the disconnect between social goals and social structure. |
|
|
It is the peaceful inclusion or movement into the mainstream society |
Social Integration |
|
|
|
It is considered the investments people make in their aociety in return for economic or collective rewards. |
Social Capital |
|
|
|
What is the idea behind the investment or the social capital of an individual in a society? |
The greater the investment, the higher the level of social integration or inclusion The lesser the social capital leads to greater social inequality The fewer you have in weak ties the harder the acces to social capital |
|
|
|
Two types of social inequality in social networks: |
Situational - socioeconomic advantage Positional-based on how connected one is within a network and one’s centrality within that network |
|
|
|
Difference between social capital and cultural capital. |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What are strong ties? |
Peer group and kinship contacts which are smaller in size but powerful. |
|
|
|
These are social connections that are personally superficial such as associates but that are large in number and provide connections to wide range of individuals. |
Weak Ties |
|
|
|
The compounding of disadvantage seen in individuals who belong to more than one oppresed groups. |
Intersectionality |
|
|
|
Social inequality is more pronounced in what? |
Racial and thnic minorities |
|
|
|
Social inequality that is passed down from one generation to the next. |
Social reproduction |
|
|
|
This theory says about holes in the structure of society rather than poverty due to the actions of individuals. |
Structural poverty theory |
The percentage of a society that falls under the poverty line stats relatively constant due to their existence |
|
|
Types of poverty |
Absolute and relative |
|
|
|
Difference of absolute and relative poverty |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
5 ethnicities model |
Asian, Black, white, latino and Native American |
|
|
|
It is typically the result of an economic and occupational structure that allowd one to acquire higher level employment opportunities given proper credentials and experience requirements. |
Social Mobility |
|
|
|
This changes are from parents to children |
Intergenerational |
|
|
|
Intragenerational |
Happens within person’s lifetime |
|
|
|
It is based on intellectual talent and achievement and is means for a person to advance up the sociAl ladder |
Meritocracy |
|
|
|
Plutocracy us |
A rule by the upperclasses |
|
|
|
Examples of upward mobility is seen in |
Professional athletes and musicians |
|
|
|
It is a change in occupation or lifestyle that remains within the same social class |
Horizontal mobility |
|
|
|
Difference of absolute and relative poverty |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
How does social capital affect social cohesion? |
The less social capital a person has ( reduced network equality and equality of opportunity ) the more social inequality. This, in turn, decreases social cohesion. |
|
|
|
Arise from this sense of powerlessness when poor individuals feel segregated and isolated from society. |
Social exclusion |
|
|
|
It focuses on social stratification across territories and their populations. Also how social processes affected by geography. |
Spatial inequality |
|
|
|
These people tend to have more career options to choose from and can more easily improve their SES through such avenues as education, marriage and career choice. |
People living in urban areas |
|
|
|
The migration pattern of the middle classes to suburban communities |
Suburbanization |
|
|
|
Urban decay |
Previously functional portion of a city deteriorates and becomes decreipt over time |
|
|
|
Opposited of urban decay |
Urban renewal where land is reclaimed and renovated for public or private use |
|
|
|
Displacement of low SES populations by purchasing and renovating deteriorated neighborhoods |
Gentrification |
|
|
|
It |
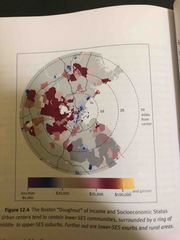
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
It categorizes countries and emphasizes the inequalities of the division of labor at the global level |
World system theory |
|
|
|
It focuses on higher skills and higher paying productions |
Core nations |
|
|
|
It refers to an uneven distribution of environmental hazards in communities |
Environmental injustice |
|

