![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
(A) A
(B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E |
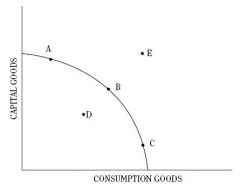
An economy that is fully employing all its productive
resources but allocating less to investment than to consumption will be at which of the following positions on the production possibilities curve shown above? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E |
|
|
Assume that land can be used either for producing grain or for grazing cattle to produce beef. The opportunity cost of converting an acre from cattle grazing to grain production is the
(A) market value of the extra grain that is produced (B) total amount of beef produced (C) number of extra bushels of grain that are produced (D) amount by which beef production decreases (E) profits generated by the extra production of grain |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following will occur as a result of an improvement in technology?
(A) The aggregate demand curve will shift to the right. (B) The aggregate demand curve will shift to the left. (C) The aggregate supply curve will shift to the right. (D) The aggregate supply curve will shift to the left. (E) The production possibilities curve will shift inward. |
x
|
|
|
Increases in real income per capita are made possible by
(A) improved productivity (B) a high labor/capital ratio (C) large trade surpluses (D) stable interest rates (E) high protective tariffs |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following is an example of “investment” as used in economics?
(A) A schoolteacher purchases 10,000 shares of stock in an automobile company. (B) Newlyweds purchase a previously owned home. (C) One large automobile firm purchases another large automobile firm. (D) A farmer purchases $10,000 worth of government securities. (E) An apparel company purchases 15 new sewing machines. |
x
|
|
|
The United States Department of Labor defines an individual as unemployed if the person
(A) does not hold a paying job (B) has been recently fired (C) works part time but needs full-time work (D) is without a job but is looking for work (E) wants a job but is not searching because he or she thinks none is available |
x
|
|
|
8. Which of the following workers is most likely to be classified as structurally unemployed?
(A) A high school teacher who is unemployed during the summer months (B) A recent college graduate who is looking for her first job (C) A teenager who is seeking part-time employment at a fast-food restaurant (D) A worker who is unemployed because his skills are obsolete (E) A person who reenters the job market after relocating |
x
|
|
|
Assume that a country with an open economy has a fixed exchange-rate system and that its currency is currently overvalued in the foreign exchange market. Which of the following must be true at the official exchange rate?
(A) The quantity of the country’s currency supplied is less than the quantity demanded. (B) The quantity of the country’s currency supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. (C) The demand curve for the country’s currency is horizontal. (D) The supply curve for the country’s currency is horizontal. (E) There is an excess demand for the country’s currency. |
x
|
|
|
According to the classical model, an increase in the money supply causes an increase in which of the following?
I. Real gross domestic product II. Nominal gross domestic product III. Nominal wages (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III |
x
|
|
|
x
|

The diagram above shows aggregate supply curves AS1, AS2, and AS3. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) AS2 reflects wage and price rigidity. (B) AS1 reflects greater wage and price flexibility than AS2. (C) AS2 reflects greater wage and price flexibility than AS1 and AS3. (D) The shift from AS1 to AS3 is due to a decrease in nominal wages. (E) The shift from AS3 to AS1 is due to an increase in oil prices. |
|
|
An increase in which of the following would cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the right?
(A) Corporate income tax rates (B) Aggregate demand (C) Labor productivity (D) The average wage rate (E) The price level |
x
|
|
|
As income level increases from $500 to $1,000, consumption increases from $700 to $1,100. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to
(A) 1.10 (B) 0.80 (C) 0.70 (D) 0.50 (E) 0.10 |
x
|
|
|
In the circular flow diagram of an economy, which of the following is true?
(A) Businesses pay wages, rent, interest, and profits to households in return for use of factors of production. (B) Businesses purchase goods and services from households in return for money payments. (C) Households pay wages, rent, interest, and profits to businesses in return for use of factors of production. (D) The relationship between households and businesses exists only in a traditional society. (E) The relationship between households and businesses exists only in a command economy. |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following would most likely lead to a decrease in aggregate demand?
(A) A decrease in taxes (B) A decrease in interest rates (C) An increase in household savings (D) An increase in household consumption (E) An increase in business firms’ purchases of capital equipment from retained earnings |
x
|
|
|
According to the Keynesian model, equilibrium output of an economy may be less than the full-employment level of output because at full employment
(A) sufficient income may not be generated to keep workers above the subsistence level (B) there might not be enough demand by firms and consumers to buy that output (C) workers may not be willing to work the hours necessary to produce the output (D) interest rates might not be high enough to provide the incentive to fi nance the production (E) banks may not be willing to lend enough money to support the output |
x
|
|
|
If the Federal Reserve lowers reserve requirements, which of the following is most likely to happen to interest rates and nominal gross domestic product?
Interest Rates : Nominal Gross Domestic Product (A) Increase : Decrease (B) Increase : Increase (C) Decrease : Decrease (D) Decrease : Increase (E) No change : No change |
x
|
|
|
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.9, what is the maximum amount that the equilibrium gross domestic product could change if government expenditures increase by $1 billion?
(A) It could decrease by $9 billion. (B) It could increase by $0.9 billion. (C) It could increase by $1 billion. (D) It could increase by $9 billion. (E) It could increase by $10 billion. |
x
|
|
|
Expansionary fiscal policy will be most effective in increasing real gross domestic product when
(A) the aggregate supply curve is horizontal (B) the economy is at or above full-employment output (C) transfer payments are decreased, while taxes remain unchanged (D) wages and prices are very flexible (E) the Federal Reserve simultaneously increases the reserve requirement |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following would increase the value of the simple spending multiplier?
(A) An increase in government expenditure (B) An increase in exports (C) A decrease in government unemployment benefits (D) A decrease in the marginal propensity to consume (E) A decrease in the marginal propensity to save |
x
|
|
|
Assume that the reserve requirement is 25 percent. If banks have excess reserves of $10,000, which of the following is the maximum amount of additional money that can be created by the banking system through the lending process?
(A) $2,500 (B) $10,000 (C) $40,000 (D) $50,000 (E) $250,000 |
x
|
|
|
The principal reason for requiring commercial banks to maintain reserve balances with the Federal Reserve is that these balances
(A) provide the maximum amount of reserves a bank would ever need (B) give the Federal Reserve more control over the money-creating operations of banks (C) ensure that banks do not make excessive profits (D) assist the Treasury in refinancing government debt (E) enable the government to borrow cheaply from the Federal Reserve’s discount window |
x
|
|
|
The purchase of securities from the public in the open market by the Federal Reserve will
(A) increase the supply of money (B) increase the interest rate (C) increase the discount rate (D) decrease the number of Federal Reserve notes in circulation (E) decrease the reserve requirement |
x
|
|
|
To counteract a recession, the Federal Reserve should
(A) buy securities on the open market and raise the reserve requirement (B) buy securities on the open market and lower the reserve requirement (C) buy securities on the open market and raise the discount rate (D) sell securities on the open market and raise the discount rate (E) raise the reserve requirement and lower the discount rate |
x
|
|
|
Total spending in the economy is most likely to increase by the largest amount if which of the following occur to government spending and taxes?
Government Spending : Taxes (A) Decrease : Increase (B) Decrease : No change (C) Increase : Increase (D) Increase : Decrease (E) No change : Increase |
x
|
|
|
According to the Keynesian model, an increase in the money supply affects output more if
(A) investment is sensitive to changes in interest rates (B) money demand is sensitive to changes in interest rates (C) the unemployment rate is low (D) consumption is sensitive to the Phillips curve (E) government spending is sensitive to public opinion |
x
|
|
|
Supply-side economists argue that
(A) a cut in high tax rates results in an increased deficit and thus increases aggregate supply (B) lower tax rates provide positive work incentives and thus shift the aggregate supply curve to the right (C) the aggregate supply of goods can only be increased if the price level falls (D) increased government spending should be used to stimulate the economy (E) the government should regulate the supply of imports |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following policies would most likely be recommended in an economy with an annual inflation rate of 3 percent and an unemployment rate of 11 percent?
(A) An increase in transfer payments and an increase in the reserve requirement (B) An increase in defense spending and an increase in the discount rate (C) An increase in income tax rates and a decrease in the reserve requirement (D) A decrease in government spending and the open market sale of government securities (E) A decrease in the tax rate on corporate profits and a decrease in the discount rate |
x
|
|
|
According to the monetarists, inflation is most often the result of
(A) high federal tax rates (B) increased production of capital goods (C) decreased production of capital goods (D) an excessive growth of the money supply (E) upward shifts in the consumption function |
x
|
|
|
An expansionary fiscal policy would most likely cause which of the following changes in output and interest rates?
Output : Interest Rates (A) Increase : Increase (B) Increase : Decrease (C) Decrease : Increase (D) Decrease : Decrease (E) No change : Decrease |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following would result in the largest increase in aggregate demand?
(A) A $30 billion increase in military expenditure and a $30 billion open market purchase of government securities (B) A $30 billion increase in military expenditure and a $30 billion open market sale of government securities (C) A $30 billion tax decrease and a $30 billion open market sale of government securities (D) A $30 billion tax increase and a $30 billion open market purchase of government securities (E) A $30 billion increase in social security payments and a $30 billion open market sale of government securities |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following measures might be used to reduce a federal budget defi cit?
I. Increasing taxes II. Decreasing federal spending III. Decreasing interest rates (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and III |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following would most likely be the immediate result if the United States increased tariffs on most foreign goods?
(A) The United States standard of living would be higher. (B) More foreign goods would be purchased by Americans. (C) Prices of domestic goods would increase. (D) Large numbers of United States workers would be laid off. (E) The value of the United States dollar would decrease against foreign currencies. |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following policies is most likely to encourage long-term economic growth in a country?
(A) An embargo on high-technology imports (B) A decrease in the number of immigrants to the country (C) An increase in government transfer payments (D) An increase in the per capita savings rate (E) An increase in defense spending |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following would occur if the international value of the United States dollar decreased?
(A) United States exports would increase. (B) More gold would flow into the United States. (C) United States demand for foreign currencies would increase. (D) The United States trade deficit would increase. (E) United States citizens would pay less for foreign goods. |
x
|
|
|
If exchange rates are allowed to fluctuate freely and the United States demand for Indian rupees increases, which of the following will most likely occur?
(A) The dollar price of Indian goods will increase. (B) The rupee price of United States goods will increase. (C) The United States balance-of-payments deficits will increase. (D) The dollar price of rupees will fall. (E) The dollar price of Indian goods will fall. |
x
|
|
|
The replacement of some portion of the federal personal income tax with a general sales tax would most likely result in
(A) greater overall progressivity in the tax structure (B) smaller overall progressivity in the tax structure (C) stronger automatic stabilization through the business cycle (D) a larger budget deficit (E) a smaller federal budget deficit |
x
|
|
|
A deficit in the United States trade balance can be described as
(A) an excess of the value of commodity imports over the value of merchandise exports (B) an excess of the value of merchandise exports over the value of commodity imports (C) an excess of payments to foreigners over receipts from foreigners (D) an almost complete depletion of the gold stock (E) an excess of receipts from foreigners over payments to foreigners |
x
|
|
|
Problems faced by all economic systems include which of the following?
I. How to allocate scarce resources among unlimited wants II. How to decentralize markets III. How to decide what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce IV. How to set government production quotas (A) I only (B) I and III only (C) II and III only (D) I, II, and III only (E) I, II, III, and IV |
x
|
|
|
An increase in which of the following will cause an increase in the demand for a certain good?
(A) The price of the good (B) The number of sellers of the good (C) The price of a complementary good (D) The cost of purchasing the good (E) The number of buyers of the good |
x
|
|
|
x
|
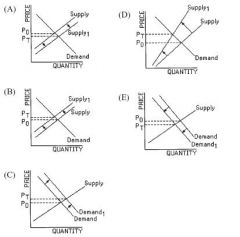
Assume that the government imposes a per unit tax on the production of a certain good. In the graphs below, P0 indicates the price before the implementation of the tax and PT indicates the price after the implementation of the tax. Which of the following is a graphical representation of this situation?
|
|
|
Which of the following groups is most likely to experience losses if infl ation increases unexpectedly?
(A) Lenders (B) Borrowers (C) Workers with variable-wage contracts (D) Owners of real estate (E) People who hold noncash assets |
x
|
|
|
Assume that last year the consumer price index (CPI) was 150 and a household’s nominal income was $30,000. If the CPI this year is 160, to be as well off as last year, the household should have an increase in nominal income of
(A) $1,800 (B) $1,875 (C) $2,000 (D) $3,000 (E) $4,800 |
x
|
|
|
The natural rate of unemployment can be defined as the unemployment rate that exists when the economy
(A) is neither growing or shrinking (B) has zero inflation (C) has only cyclical and structural unemployment (D) has no trade deficit or government deficit (E) produces at the full-employment output level |
x
|
|
|
A fully anticipated expansionary fiscal policy will cause the price level and real output to change in which of the following ways in the long run?
Price Level : Real Output (A) Increase : Increase (B) Increase : Not change (C) Not change : Not change (D) Decrease : Increase (E) Decrease : Decrease |
x
|
|
|
If the nominal gross domestic product is $8trillion and the money supply is $2 trillion, the velocity of money is
(A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 10 (E) 16 |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT true of the Federal Reserve?
(A) It serves as a lender of last resort for member banks. (B) It supervises member banks. (C) It provides check-clearing services. (D) It issues traveler’s checks. (E) It controls the money supply. |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes crowding out?
(A) Competition between the government and private borrowers for loanable funds results in an increase in interest rates. (B) Increases in the costs of inputs lead to decreases in domestic production. (C) The Federal Reserve’s open-market operations decrease the amount of funds banks have available for lending. (D) Reductions in the government’s budget defi cit lead to fewer Treasury bonds being issued. (E) The scarcity of funds forces Congress to decrease spending on critical public works programs. |
x
|
|
|
Suppose that the economy is operating at full employment. If the government wants to discourage consumption spending, stimulate investment spending, and maintain full-employment output, which of the following combinations of monetary and fiscal policies would most likely achieve these goals?
Monetary Policy : Fiscal Policy (A) Increase money supply : Increase government spending (B) Increase money supply : Increase personal income taxes (C) Decrease money supply : Increase government spending (D) Decrease money supply : Increase personal income taxes (E) Decrease money supply : Decrease personal income taxes |
x
|
|
|
If the Federal Reserve suddenly increases the growth rate of the money supply from 4 percent to 8 percent per year, interest rates, aggregate demand, and nominal gross domestic product (GDP) will most likely change in which of the following ways in the short run?
Interest Rates : Aggregate Demand : Nominal GDP (A) Increase : Increase : Increase (B) Increase : Decrease : Increase (C) Decrease : Increase : Increase (D) Decrease : Increase : Decrease (E) Decrease : Decrease : Increase |
x
|
|
|
The United States federal government budget deficits tend to be large when which of the following is low?
(A) The interest rate on government bonds (B) The growth rate of the economy (C) The unemployment rate (D) The infl ation rate (E) The international value of the United States dollar |
x
|
|
|
Using the same amount of resources, Beeland can produce 80 tons of corn or 80 tons of wheat and Eland can produce 40 tons of corn or 20 tons of wheat. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) The opportunity cost of producing a ton of corn in Beeland is two tons of wheat. (B) The opportunity cost of producing a ton of corn in Beeland is a ton of wheat. (C) The opportunity cost of producing a ton of corn in Eland is two tons of wheat. (D) Beeland has both the absolute and comparative advantage in producing corn. (E) Eland has the comparative advantage in producing wheat. |
x
|
|
|
If the required reserve ratio is 0.20 and the Federal Reserve buys $200 worth of securities, the maximum increase in the money supply will be
(A) $ 200 (B) $ 400 (C) $ 600 (D) $ 800 (E) $ 1,000 |
x
|
|
|
Assets : Liabilities
Reserves $4,000 : Demand deposits $10,000 Loans $6,000: The table above shows the T-account entries of a bank. If the required reserve ratio is 0.20, what is the maximum amount of additional loans that this bank can make? (A) $ 0 (B) $ 2,000 (C) $ 2,500 (D) $ 4,000 (E) $ 10,000 |
x
|
|
|
Hyperinflation is usually associated with which of the following?
(A) An increase in labor productivity (B) An increase in exports (C) A decrease in total spending (D) Appreciation of the domestic currency (E) Rapid growth of the money supply |
x
|
|
|
According to the short-run Phillips curve, which of the following will occur when the Federal Reserve increases the money supply?
(A) Both the unemployment rate and the inflation rate will increase. (B) Both the unemployment rate and the inflation rate will decrease. (C) The unemployment rate will increase, and the inflation rate will decrease. (D) The unemployment rate will decrease, and the inflation rate will increase. (E) The inflation rate will increase, but the unemployment rate will remain constant. |
x
|
|
|
Which of the following is true if there is a current account deficit in the United States balance-of-payments accounts?
(A) There is a corresponding deficit in the capital account. (B) There is a corresponding surplus in the capital account. (C) There is an offsetting surplus in the government’s budget. (D) There is an offsetting increase in net exports. (E) The United States dollar appreciates in the foreign exchange market. |
x
|
|
|
An increase in national saving will cause real interest rate and investment spending to change in which of the following ways?
Real Interest Rate : Investment (A) Increase : Increase (B) Increase : Decrease (C) Increase : Not change (D) Decrease : Increase (E) Decrease : Not change |
x
|
|
|
To raise its long-run rate of economic growth, a country should design and implement policies that do which of the following?
(A) Encourage current consumption over saving (B) Encourage saving and investment (C) Increase the price level and profits (D) Promote equity through income redistribution (E) Limit business activities to protect the environment |
x
|
|
|
With a constant money supply, an increase in the demand for money will affect interest rates and bond prices in which of the following ways?
Interest Rates : Bond Prices (A) Increase : Increase (B) Increase : Decrease (C) Increase : Not change (D) Decrease : Increase (E) Not change : Increase |
x
|
|
|
According to the quantity theory of money, an increase in the money supply results in an increase in which of the following?
(A) Interest rate (B) Unemployment (C) Nominal gross domestic product (D) The government’s budget deficit (E) The value of the dollar on the foreign exchange market |
x
|

