![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
180 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Contains catechol nucleus |
Catecholamines |
|
|
Another name for catechol nucleus |
1,2 dihydroxybenzene |
|
|
Receptor for catecholamines |
Type 2/ G-protein linked receptors |
|
|
Alpha 1 Blood vessels?? Smooth muscle?? Pupil?? Pilomotor muscle?? Bladder sphincter?? Prostate?? |
Gq Vasoconstriction Contraction Mydriasis Hair erection Contraction Contraction |
|
|
Opening of an organ |
Sphincter |
|
|
Alpha 2 Pre synapse? Post synapse? |
Negative feedback effect = decreased synthesis of catecholamines Vaso constriction |
|
|
Example of beta 2 agonist |
Clonidine (Catapres) -for HPN •pre-synapse Decreased catecholamine level = decreased BP •post-synapse Transient increase in BP |
|
|
Beta 1 Cardiac muscle?? Juxtaglomerular cells?? |
Inotropism, dromotropism, chronotropism Renin release |
|
|
Force of heart contraction |
Inotropism |
|
|
Time of heart contraction |
Chronotropism |
|
|
Conduction of heart cells |
Dromotropism |
|
|
Beta 3 Adipose cells? |
Lipolysis |
|
|
Another name for lipolysis |
Fat metabolism |
|
|
Use of beta 3 agonists |
Investigational drug for the management of obesity |
|
|
Location of beta 2 receptors? |
Smooth muscles |
|
|
Effects on smooth muscles of beta 2 receptor |
DUMBELS |
|
|
Uses of beta 2 agonist |
For broncial asthma Tocolytic |
|
|
Prevents premature labor |
Tocolytic |
|
|
Drugs that are beta 2 agonist |
Salbutamol/ terbutarine |
|
|
D1 location and effect? |
Vasodilation in the renal and sphlanchnic blood vessels |
|
|
Loss of response due to prolonged administration / tolerance |
Desensitization |
|
|
Another names for tolerance |
refractoriness / tachyphylaxis |
|
|
Loss of responsiveness because of repeated activation by the drug |
Homologous desensitization |
|
|
Loss of responsiveness of some cell surface receptors that have been DIRECTLY activated by a drug |
Heterologous desensitization |
|
|
Major mechanism of desensitization |
Phosphorylation |
|
|
Drugs that mimic the action of epi or norepi |
Symphatomimetic Agents |
|
|
Another name for sympathomimetic agents |
Adrenomimetic/adrenergic/adrenoceptor agonists |
|
|
Pharmacophore for adrenergic agents |
Phenyethylamine |
|
|
Parent compound from which sympathomimetic drugs are derived |
Phenylethylamine |
|
|
What happens in the substituion in the terminal amino group? |
Increased beta receptor activity- decreased alpha receptor activity |
|
|
Substitution on the benzene ring |
Maximal alpha and beta activity |
|
|
Substitution on the alpha carbon |
Resistant to mao enzyme |
|
|
Substitution on beta carbon |
Direct or indirect acting Direct if OH group is present on benzene ring Indirect if no OH group |
|
|
Hydroxyl group on benzene ring - drug is metabolized by?? |
COMT (catechol-o-methyl transferase) |
|
|
When resistant to COMT? Oral or parenteral? |
Oral |
|
|
Obtained from Ma huang |
Ephedrine |
|
|
SN of ephedrine |
Ephedra silica |
|
|
Stimulates more than 1 receptor |
non-selective |
|
|
Example of non-selective |
NE EPI Isoproterenol |
|
|
Stimulates only one receptor |
Selective |
|
|
Examples of non-selective natural catecholamines |
Epi Norepi Dopamine (in concentrations) |
|
|
Example of non-selective synthetic catecholamine |
Isoproterenol |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of catecholamines |
Poor oral absorption due to the degradation of COMT |
|
|
Catecholamines are vasoconstrictors.. |
Decreases blood flow = decreased absorption |
|
|
Other name of epinephrine |
Adrenaline |
|
|
Use of epinephrine |
•vasoconstrictor (alpha 1) •cardiac stimulant (beta 1) |
|
|
Clinical uses of epinephrine |
Bronchospasm (sq, inhalation) For glaucoma (Dipevefrin) -pivalic ester For anaphylactic shock Adjunct in anesthetics -minimizes systemic absorption and toxicity First line cardiac stimulant |
|
|
Another name of norepinephrine |
Levarterenol or noradrenaline |
|
|
Alternative for dopamine for the management of septic shock |
Norepinephrine |
|
|
SBP of a person with septic shock |
<90 mmHg |
|
|
Intermediate precursor of norepinephrine |
Dopamine |
|
|
Clinical uses of dopamine |
DOC for septic shock Given in acute oliguric renal failure Management of cardiogenic shock |
|
|
Synthetically prepared dopamine |
Docard |
|
|
Concentration of dopamine in D1 |
1-3 mcg/kg |
|
|
Concentration of dopamine in beta 1 |
2-5 mcg/ kg |
|
|
Concentration of dopamine in alpha 1 |
>5 mcg /kg |
|
|
Assures delivery of blood in the body |
Blood pressure |
|
|
Another name of isoproterenol |
Isoprenaline |
|
|
Very potent non selective, beta receptor agonist |
Isoproterenol |
|
|
Drug that produces tachyphylaxis |
Isoproterenol |
|
|
Clinical uses of isoproterenol |
Management of bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Management of shock states and acute heart failure |
|
|
Use of selective alpha 1 agonists |
Nasal decongestant Vasoconstrictor |
|
|
CI for selective a1 agonists |
Patients with severe HPN |
|
|
MOA of a1 agonists |

|
|
|
Pure alpha agonist Not a catecholamine =longer duration of action |
Phenylephrine (Neo-synephrine) |
|
|
Uses of phenylephrine |
Nasal decongestant Used to raise BP and to terminate episodes of supraventricular tachycardia |
|
|
Direct acting a1 agonist Increases BP |
Methoxamine |
|
|
Uses of Methoxamine |
Relieves attacks of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia Used to overcome hypotension during surgery caused by halothane anesthetics |
|
|
Inhaled anesthesia |
Halothane anesthetics |
|
|
Adverse effect of halothane anesthesia |
Hypotension |
|
|
Clinical uses of a1 agonist |
Nasal decongestan Local vasoconstrictor Local anesthesia Management of acute hypotension Used to terminate supraventricular tachycardia |
|
|
Adverse effects of a1 agonists |
Tolerance (USE FOR NMT 5 DAYS) Exacerbation of HPN Urinary retention Topical effect: rebound hyperemia (upto 3 days use only) |
|
|
Another name for rebound hyperemia |
Rhinitis medicamentosa/ Rebound nasa congestion |
|
|
Effects of a2 agonist in pre-synapse |
Vasodilation Sedation Depression |
|
|
Effect of a2 agonist in post-synapse |
Transient vasoconstriction |
|
|
Analogues of Clonidine |
Brimonidine Apraclonidine |
|
|
Uses of Clonidine (Catapres) |
Management of HPN Alternative in the management of ADHD for clonidine withdrawal induced HPN |
|
|
DOC for ADHD |
Methylprenidate (Ritalin) |
|
|
Another name for methyldopa |
Alpha-methyldihydroxyphenylalanine |
|
|
ADHD stands for? |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |
|
|
True or false: is methyldopa a prodrug? |
True |
|
|
A false neurotransmitter that produces transient vasoconstriction and long term vaso dilation |
Methyldopa |
|
|
Another term for HPN during pregnancy |
Gestational HPN |
|
|
Alternative drugs used for the management of gestational HPN |
Methyldopa Nifedipine Hydralazine Labetalol |
|
|
Adverse effects of methyldopa |
Sedation Hepatotoxicity (>2g/day) False positive coomb's test |
|
|
Test used to detect antibody which causes hemolysis |
Coomb's test |
|
|
Used as inotropic agent For pharmacologic stress testing |
Dobutamine |
|
|
Reliever meds for asthma |
Short-Acting Beta Agonists |
|
|
Administration of albuterol |
Thru metered dose inhalers |
|
|
Another name of Albuterol |
Salbutamol |
|
|
Administration of Terbutaline |
Subcutaneous |
|
|
Controller meds for asthma |
Long-acting beta agonists |
|
|
Clinical uses of B2 agonists |
Management of BA &COPD Management of symptomatic bradycardia Tocolytic agent Adjunct in the management of hyperkalemia |
|
|
Manages symptomatic bradycardia |
Terbutaline |
|
|
Adverse effects of b2 agonists |
Tremor -contraction of skeletal muscles Muscle weakness -hypokalemia Tachycardia -at high doses |
|
|
D1 agonist that selectively leads to peripheral vasodilation |
Fenoldopam |
|
|
IV for the Tx of severe HPN |
Fenoldopam |
|
|
Increases the conc of catecholamines |
Indirect acting sympathomimetic agents |
|
|
2 mechanisms of indirect sympathomimetic |
•increase catecholamine release •inhibition of reuptake |
|
|
Plant alkaloid found in Ma huang |
Ephedrine |
|
|
Uses of ephedrine |
Nasal decongestant Tx for asthma Mgt. Of hypotension |
|
|
Marked as CNS stimulant (schedule 1 drug) |
Amphetamine |
|
|
Used in therapy of depression, hyperactivity, narcolepsy, appetite control |
Amphetamine |
|
|
Tendency to fall asleep |
Narcolepsy |
|
|
Production of ephedrine to amphetamine |
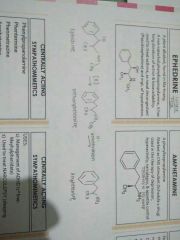
|
|
|
Found in fermented foods |
Tyramine |
|
|
Normal by-product of tyrosine metabolism Oxidized by MAO |
Tyramine |
|
|
Can precipitate vasopressor episode when taken with MAOI |
Tyramine |
|
|
MOA of tyramine + MAOI |

|
|
|
DOC for HPN crisis |
Na nitroprusside |
|
|
Stimulates release of catecholamines |
Centrally acting sympatholmimetic agents |
|
|
Uses of centrally acting sympathomimetic agents |
Mgt. of ADHD Tx for narcolepsy Appetite suppresant Nasal decongestant Tx for pulmonary HPN |
|
|
Tx for pulmonary HPN |
Sildenafil 20 mg (Revation) Sildenafil 40 mg (Viagra) |
|
|
Adverse effects of centrally acting sympathomimetic agents |
CNS stimulant Hemorrhagic stroke Primary pulmonary HPN |
|
|
What kind of antagonism are sympatholytic agents? |
Pharmacologic antagonism |
|
|
Another name for sympatholytic agents |
Adrenergic/adrenoceptor antagonists |
|
|
Adverse effect of apha receptor antagonist |
Orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
CI for beta receptor antagonists |
Patients with BA |
|
|
DOC for Pheocromocytoma |
Phenoxybenzamine Phentolamine |
|
|
Prototype non selective beta antagonist |
Propranolol |
|
|
Long half-life beta antagonist |
Nadolol -1x a day |
|
|
Short half-life if taken orally |
Esmolol (IV) |
|
|
Most cardioselective beta antagonist |
Nebivolol |
|
|
Tumor in adrenal glands |
Pheocromocytoma |
|
|
A1 antagonist use |
For benign prostatic hyperplasia |
|
|
A2 antagonist use |
For erectile dysfunction |
|
|
Management for orthostatic hypotension |
Administer at bedtime |
|
|
Decreases peripheral vascular resistance |
Apha blockers |
|
|
MOA of alpha blocker for pheocromocytoma |

|
|
|
MOA of alpha blocker for BPH |

|
|
|
Causes irreversible antagonist of alpha receptor |
Phenoxybenzamine |
|
|
Causes reversible antagonist of alpha receptor |
Phentolamine |
|
|
Has Ach, 5-HT, histamine effect |
Phenoxybenzamine |
|
|
A2 antagonists for erectile dysfuntion ; injected in the penile shaft |
Yohimbine Rauwolsine |
|
|
Uses of alpha blockers |
Mgt. of HPN, pheocromocytoma, bph Mgt. of Reynaud's phenomenon Mgt. of urinary retention / diuretic Mgt. of carcinoid syndrome (phenoxybenzamine, octreotide) Mgt. of erectile dysfunction °oral -sildenafil, tadalafil °inj- phentolamine, yohimbine, rauwolsine |
|
|
Diagnosis for pheocromoctoma |
VMA assay in serum /urine Imaging studies |
|
|
Management for pheocromocytoma |
Initial control °alpha blockers- phenoxybenzamine, phentolamine °beta blockers- lobetalol Surgical intervention |
|
|
Tumor caused by the hypersecretion of NE and EPI |
Pheocromocytoma |
|
|
Manifestations of pheocromocytoma |
Agitation Confusion Tachycardia Palpitation Paroxysmal HPN |
|
|
Digital vasospasm in a cold environment |
Raynaud's syndrome |
|
|
Management for Reynaud's syndrome |
Alpha blockers Calcium channel blockers |
|
|
Cyanosis or whitish discoloration in the hands |
Raynaud's syndrome |
|
|
Neuroendocrine tumor ; hypersecretion of 5-HT |
Carcinoid syndrome |
|
|
Manifestations of carcinoid syndrome |
Severe headache, watery diarrhea, flushing |
|
|
Beta blockers with Intrinsic Sympathomimetic Activity (ISA) partial agonist effect |
P-indolol; Penbutolol A-cebutolol;Acarteolol L-abetalol |
|
|
Advantage of beta blockers w/ ISA |
less associated with rebound HPN upon withdrawal |
|
|
Beta blockers with Membrane Stabilizing Activity (MSA) quinidine-like effect or anesthetic effect |
P-indolol A-cebutolol L-abetalol M-etoprolol P-ropranolol |
|
|
Beta blockers with mixed alpha and beta-blocking effect |
L-abetalol C-arvedilol |
|
|
Obstruction of the coronary artery |
Angina pectoris |
|
|
Supplies blood |
Coronary artery |
|
|
Another name for angina pectoris |
Coronary Artery Disease |
|
|
Symptoms of myocardial infarction/ischemia |
Chest pain / angina pectoris |
|
|
Reasons for angina pectoris |
Atherosclerosis (lipid) Blood clot (embolus) Inflammation Vasoconstriction |
|
|
Non-selective agent with no local anesthetis effect For glaucoma Excellent ocular hypitensive effects |
Timolol (opthalmic) |
|
|
Non-selective agent for glaucoma |
Levobunolol (opthalmic) |
|
|
Beta 1-blocker used for glaucoma |
Betaxolol (opthalmic) |
|
|
Partial agonist effect Effective for glaucoma |
Carteolol (opthalmic) |
|
|
Alternative to hydralazine in Tx for pregnancy-induced HPN |
Labetalol |
|
|
Angina pectoris from physical activities |
Stable |
|
|
Severe/ deadly kind of angina pectoris |
Unstable |
|
|
Digital vasospasm Continous vasoconstriction Prinzmetal's |
Vasospastic angina pectoris |
|
|
Clinical uses of beta blockers |
Mgt of HPN in Px with CAD Mgt of arrythmia Manage chronic stable angina pectoris Mgt of stable heart failure Mgt of glaucoma Manage sympathetic symptoms of hyperthyroidism Prophylaxis of migraine Mgt of stage fright |
|
|
Management of stage fright |
Propranolol 10 mg |
|
|
Adverse effects of beta blockers |
Bronchospasm Decreased exercise tolerance Bardycardia Heart block Dyslipidemia Decreased sexual activity |
|
|
Can mask symptoms of diabetes mellitus |
Beta blockers |
|
|
CI of beta blockers |
Anaphylaxis Bradycardia Active BA Unstable heart failure Patients taking non-dihydropyridine CCBs Diabetes mellitus |
|
|
The only beta blocker for Px with DM |
metoprolol |
|
|
Acebutolol |
Sectral |
|
|
Atenolol |
Tenormin |
|
|
Betaxolol |
Kerlone |
|
|
Bisoprolol |
Zebeta |
|
|
Carteolol |
Cartrol |
|
|
Carvedilol |
Coreg |
|
|
Labetalol |
Normodyne |
|
|
Metoprolol |
Lopressor |
|
|
Nadolol |
Corgard |
|
|
Penbutolol |
Levatolol |
|
|
Pindolol |
Visken |
|
|
Propranolol |
Inderal |
|
|
Timolol |
Blocarden |

