![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
250 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy |
Science of the structure of the body |
|
|
Physiology |
Study of the function of the body |
|
|
Osteology |
Detailed study of the body of knowledge related to the bones of the body |
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
Divides the body into right & left segments |
|
|
Midsagittal Plane |
Divides the body into equal right & left halves |
|
|
Coronal Plane |
Divides the body into anterior & posterior segments |
|
|
Midcoronal Plane |
Divides the body into equal anterior & posterior halves; also called midaxillary plane |
|
|
Horizontal Plane |
Divides the body into superior & inferior parts; also called transverse, axial, or cross-sectional plane |
|
|
Oblique Plane |
Passes through the body at an angle between the other 3 planes |
|
|
Anterior (Ventral) |
Forward or front part of body or organ |
|
|
Posterior (Dorsal) |
Back part of body or organ |
|
|
Caudal |
Away from the head of the body |
|
|
Cephalic |
Toward the head of the body |
|
|
Superior |
Nearer the head or situated above |
|
|
Inferior |
Nearer the feet or situated below |
|
|
Central |
Midarea or main part of an organ |
|
|
Peripheral |
Parts at or near the surface, edge, or outside another body part |
|
|
Medial |
Toward the median plane of the body or toward the middle of another body part |
|
|
Lateral |
Parts away from the median plane of the body or away from the middle of another body part to the right or left |
|
|
Superficial |
Parts near the skin or surface |
|
|
Deep |
Parts far from the surface |
|
|
Distal |
Farthest from the point of attachment |
|
|
Proximal |
Parts nearer the point of attachment |
|
|
External |
Outside of an organ or the body |
|
|
Internal |
Within or on the inside of an organ |
|
|
Parietal |
Wall or lining of body cavity |
|
|
Visceral |
Covering of an organ |
|
|
Ipsilateral |
Part or parts on the same side of the body |
|
|
Contralateral |
Part or parts on the opposite side of the body |
|
|
Palmar |
Palm of hand |
|
|
Plantar |
Sole of foot |
|
|
Dorsum |
Top of anterior surface of foot or back of posterior surface of hand |
|
|
True Anatomic Position |
Facing forward, head up, heels together with toes facing forward, arms extended by the sides with the palms of the hands facing forward |
|
|
Two great cavities of the torso |
Thoracic & Abdominal |
|
|
Thoracic Cavity divided into what? |
Pericardial segment & 2 pleural portions |
|
|
Pelvic Cavity |
Lower portion of abdominal cavity. |
|
|
Thoracic Cavity contents |
*Pleural membranes *Lungs *Trachea *Esophagus *Pericardium *Heart & Great Vessels |
|
|
Abdominal Cavity contents |
*Peritoneum *Liver *Gallbladder *Pancreas *Spleen *Stomach *Intestines *Kidneys *Ureters *Major Blood Vessels |
|
|
Pelvic Portion (Cavity) contents |
*Rectum *Bladder *Part of Reproductive System *Sigmoid Colon |
|
|
Integumentary System |
Protects organism from injury, disease, & infection; aids in regulation of temperature, excretion of wastes, & reception of senses; ex: skin, hair, nails, duct glands |
|
|
Skeletal System |
Provides framework for body & works to protect & support body; ex: bones, joints, cartilage, connective tissue |
|
|
Muscular System |
Provides for body movement & support; ex: skeletal, smooth, & cardiac muscle |
|
|
Nervous System |
Coordinates body activities by receiving, interpreting, & conducting messages to all other systems of the body; ex: brain, spinal cord |
|
|
Special Senses |
Function in receiving sensations such as sight, smell, hearing, & taste; ex: eyes, ears, nose, taste buds |
|
|
Digestive System |
Receives, breaks down, & absorbs food substances & excretes waste products; ex: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines |
|
|
Circulatory System |
Transports materials throughout the body by carrying oxygen & nutrients in the blood to all cells of body & carrying away waste products of cells; ex: heart, blood vessels, blood |
|
|
Respiratory System |
Takes in oxygen from the air & gives off carbon dioxide; ex: lungs, nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea |
|
|
Urinary System |
Serves in removing waste products from the blood & excreting waste as urine; ex: kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra |
|
|
Reproductive System |
Involved with reproduction & childbirth; ex: sex organs |
|
|
Endocrine System |
Serves to regulate various body functions through glands that secrete hormones directly into the blood to slow down or increase activity of cells; ex: ductless glands such as thyroid & pituitary |
|
|
Immune System |
Provides protection against disease & infection; ex: white blood cells, antibodies |
|
|
Body Habitus |
Variations in the shape of the body which determines size, shape, & position of organs |
|
|
Some organs can _____ in position as much as ______ inches. |
vary, 8 |
|
|
4 types of body habitus |
Sthenic, hypersthenic, hyposthenic, asthenic |
|
|
Sthenic |
Average- 50% |
|
|
Asthenic |
Thin- 10% |
|
|
Hyposthenic |
35% |
|
|
Hypersthenic |
5% |
|
|
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ) |
*part of small intestine, including descending duodenum *upper ascending colon *most of liver *gallbladder *bile ducts *head of pancreas *right adrenal gland *right kidney *upper part of right ureter |
|
|
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ) |
*ascending part of duodenum *upper descending colon *left half of transverse colon *spleen *small part of liver *left adrenal gland *left kidney *upper part of left ureter *stomach |
|
|
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ) |
*lower ascending colon *cecum *appendix *lower right ureter *terminal ileum *part of urinary bladder *sex organs |
|
|
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ) |
*lower descending colon *small intestine (part of ileum) *part of urinary bladder *sex organs |
|
|
Respiratory System contents |
Pharynx, trachea, bronchi, 2 lungs |
|
|
Hilum |
Mediastinal surface of lung that accommodates bronchi, pulmonary blood vessels, lymph vessels, & nerves |
|
|
Each lung is enclosed in a double-walled serous membrane sac called the _________. |
Pleura |
|
|
Visceral pleura |
Inner layer of pleura that adheres to surface of lung |
|
|
Parietal pleura |
Outer layer of pleura that lines wall of thoracic cavity & adheres to upper surface of diaphragm |
|
|
Pleural cavity |
Space between two pleural walls |
|
|
Oblique fissure |
Divides lungs into superior & inferior lobes |
|
|
Horizontal fissure |
Creates a right middle lobe |
|
|
Lingula |
Portion of left lung which corresponds to middle lobe of right lung (tongue-shaped process, fills space between chest wall & heart) |
|
|
Mediastinum structures |
*heart *great vessels *trachea *esophagus *thymus *lymphatics *nerves *fibrous tissue *fat |
|
|
Thymosin |
Hormone produces by thymus gland |
|
|
Trachea has ___-___ __________ cartilaginous rings. |
16-20, c-shaped |
|
|
Aspiration |
Inspiration of a foreign material into the airway |
|
|
Atelectasis |
Collapse of all or part of the lung |
|
|
Emphysema |
Destructive & obstructive airway changes leading to an increased volume of air in the lungs |
|
|
Hyaline membrane disease |
Underaeration of the lungs caused by lack of surfactant |
|
|
Pleural effusion |
Collection of fluid in the pleural cavity |
|
|
Pneumonia |
Acute infection in the lung parenchyma |
|
|
Pneumonia aspiration |
Pneumonia caused by aspiration of foreign particles |
|
|
Lobar pneumonia |
Pneumonia involving the alveoli of an entire lobe without involving the bronchi |
|
|
Pneumothorax |
Accumulation of air in the pleural cavity resulting in collapse of the lung |
|
|
Trachea lies in the midline of the body, _______ to the esophagus in the neck. |
anterior |
|
|
Trachea follows the curve of the vertebral column and extends from _____ to ______. |
C6 to T4-T5 |
|
|
Bronchial Tree after Trachea |
*primary bronchi *secondary bronchi *tertiary bronchi *bronchioles *terminal bronchioles |
|
|
Walls of alveolar sacs are lined with _______. |
alveoli |
|
|
Each lung had millions of alveoli, where ______ and ______ ________ are exchanged. |
oxygen, carbon dioxide |
|
|
Parenchyma |
light, spongy, highly elastic substance the lungs are composed of |
|
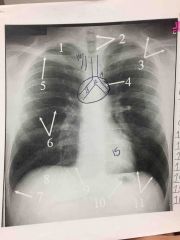
Routine Chest |

|
|
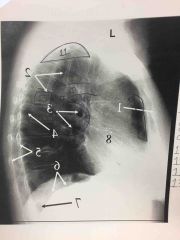
Routine Chest |

|
|
|
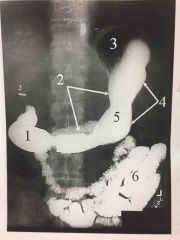
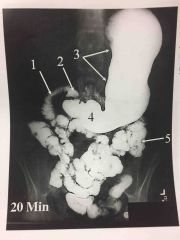
Primary organs of digestive system. |
*mouth *pharynx *esophagus *stomach *small intestine *large intestine |
|
|
Accessory organs of digestive system. |
*teeth *tongue *salivary glands *pancreas *liver *gallbladder |
|
|
4 parts of stomach |
*cardia *fundus *body *pyloric portion |
|
|
3 parts of small intestine |
*duodenum *jejunum *ileum |
|
|
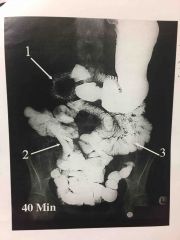
4 parts of colon |
*ascending colon *transverse colon *descending colon *sigmoid colon |
|
|
another name for right colic flexure |
hepatic flexure |
|
|
another name for left colic flexure |
splenic flexure |
|
|
5 bony positioning anatomical landmarks |
*xiphoid process *costal margin *iliac crest *greater trochanters *symphysis pubis |
|
|
Diaphragm located from ______ costal cartilage to level of _______ thoracic vertebrae. |
6-7, 9-10 |
|
|
gallbladder high/lateral, stomach high/transverse |
hypersthenic |
|
|
gallbladder mid-RUQ, stomach J-shaped & inferior |
sthenic |
|
|
gallbladder very low/medial, stomach in pelvis & very long |
asthenic |
|
|
types of abdominal pathology |
*visceral rupture *intestinal obstruction *intestinal perforation *free air due to post trauma/surgery |
|
|
peritoneum |
double walled serous membrane |
|
|
parietal peritoneum |
outer layer that adheres to abdominal wall |
|
|
visceral peritoneum |
inner layer that adheres to organs |
|
|
peritoneal cavity |
space between two layers of peritoneum |
|
|
mesentary |
double fold of visceral peritoneum connecting posterior abdominal wall to an organ |
|
|
omentum |
double fold of visceral peritoneum extending from stomach to another organ; layer of insulation |
|
|
retroperitoneal structures (BEHIND peritoneum) |
*kidneys *ureters *adrenal glands *pancreas *duodenum *large blood vessels |
|
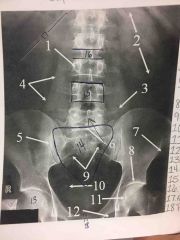
Supine Abdomen (KUB) |

|
|
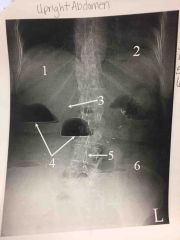
Upright Abdomen |

|
|
|
abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) |
localized dilation of abdominal aorta |
|
|
ascites |
fluid accumulation in the peritoneal cavity |
|
|
bowel obstruction |
blockage of bowel lumen |
|
|
ileus |
failure of bowel peristalsis |
|
|
metastasis |
transfer of a cancerous lesion from one area to another |
|
|
pneumoperitoneum |
presence of air in peritoneal cavity |
|
|
tumor |
new tissue growth where cell proliferation is uncontrolled |
|
|
pharynx |
passage for air & food |
|
|
oropharynx |
extends from soft palate to hyoid |
|
|
larynx |
organ of voice |
|
|
epiglottis |
above the laryngeal entrance, trap to prevent leakage into larynx between acts of swallowing |
|
|
thyroid cartilage |
forms laryngeal prominence, adams apple |
|
|
4 parts of pancreas |
*head *neck *body *tail |
|
|
Exocrine gland produces what? |
pancreatic juices |
|
|
Endocrine gland produces what hormones? |
insulin & glucagon |
|
|
What is the romance of the abdomen? |
pancreas head enclosed in C-loop of duodenum |
|
|
spleen functions |
produce lymphocytes & store and remove dead or dying RBC |
|
|
largest gland in body |
liver |
|
|
liver function |
produce bile |
|
|
falciform ligament |
divides liver into large right lobe and smaller left lobe |
|
|
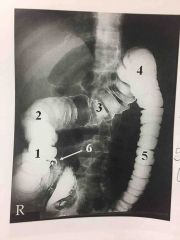
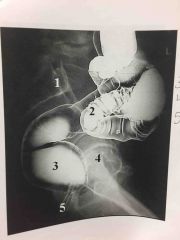
biliary system ducts in order with sphincters |
*R & L hepatic ducts *common hepatic duct *cystic duct *common bile duct *hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of vater) *sphincter of hepatopancreatic ampulla (sphincter of oddi) |
|
|
3 parts of gallbladder |
*neck *body *fundus |
|
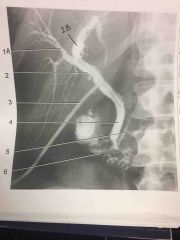
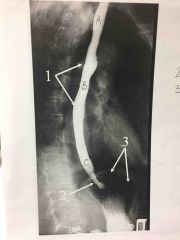
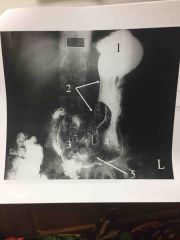
What procedure? |

T-tube Cholangiogram |
|
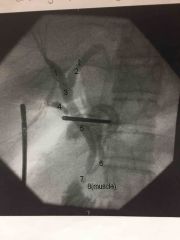
|

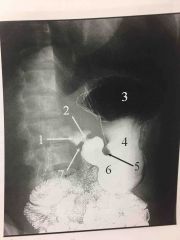
ERCP- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-pancreatography |
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
2 parts Digestive System |
Accessory glands & alimentary canal |
|
|
4 layers of esophagus, stomach, and small intestine |
Fibrous, muscular, submucosal, mucosal |
|
|
3 parts of Esophagus |
Cervical, thoracic, & abdominal |
|
|
Esophagus originates at what level? |
C6 |
|
|
Esophagus passes through diaphragm hiatus at ____. It joins the stomach at esophagogastric junction at level of _____ or xiphoid tip. |
T10, T11 |
|
|
Esophagus joins the stomach at the the esophagogastric junction through opening termed ________ ________. |
cardiac orifice |
|
|
Muscles controlling cardiac orifice are called ______ _______. |
cardiac sphincter |
|
|
Opening between stomach and small intestine is the ________ _________. |
pyloric orifice |
|
|
Muscle controlling pyloric orifice |
pyloric sphincter |
|
|
The mucosa of the small intestine contains a series of fingerlike projections called ______, which help facilitate the process of digestion and absorption. |
villi |
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
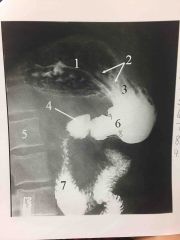
Barrett esophagus |
Peptic ulcer of lower esophagus, often with stricture |
|
|
Cholelithiasis |
Presence of gallstones |
|
|
Diverticulum |
Pouch created by herniation of the mucous membrane through the muscular coat. |
|
|
Gastroesophageal Reflux |
Backward flow of stomach contents into the esophagus |
|
|
Ileus |
Failure of bowel peristalsis |
|
|
Inguinal hernia |
Protrusion of the bowel into the groin |
|
|
Intussusception |
Prolapse of a portion of the bowel into the lumen of an adjacent part |
|
|
Polyp |
Growth or mass protruding from a mucous membrane |
|
|
Pyloric stenosis |
Narrowing of pyloric canal causing obstruction |
|
|
Crohn disease |
Inflammatory bowel disease, most commonly involving the distal ileum |
|
|
Ulcer |
Depressed lesion on the surface of the alimentary canal |
|
|
Volvulus |
Twisting of a bowel loop on itself |
|
|
Zenker diverticulum |
Diverticulum located just above the cardiac portion of the stomach |
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
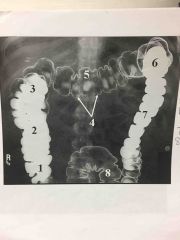
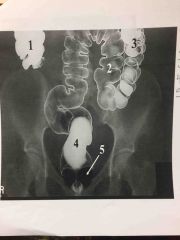
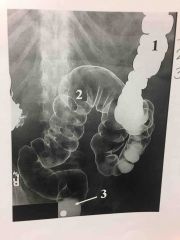
4 parts of large intestine |
*cecum *colon *rectum *anal canal |
|
|
How long is the large intestine? |
5 ft |
|
|
True or false. The 4 layers of the large intestine are the same as the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine? |
True |
|
|
Taeniae Coli |
External bands of muscle that form 3 thickened bands |
|
|
Haustra |
Series of pouches created by bands pulling muscle tone |
|
|
Large intestine function |
Reabsorption of fluids & elimination of waste |
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
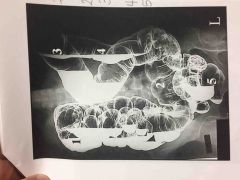
|

|
|
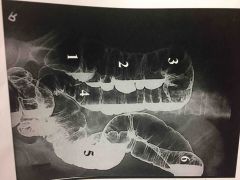
|

|
|
|
Urinary system contents |
*2 kidneys *2 ureters *1 urinary bladder *1 urethra |
|
|
Adrenal glands part of which System? |
Endocrine System |
|
|
Adrenal glands function |
Furnish epinephrine & cortical hormones |
|
|
Kidney weight |
About 150 grams |
|
|
REN |
Latin term for kidney |
|
|
Collecting tubules in renal pyramids converge medially to form a central tubule that opens at a ______ _______. |
Renal papilla |
|
|
Ureteropelvic Junction (UPJ) |
Renal pelvis connects to ureter here |
|
|
Nephron |
Essential microscopic structural & functional unit of kidney |
|
|
Make urethra length |
7-8” |
|
|
Prostate |
Surrounds proximal part of male urethra |
|
|
Glomerulus |
Cluster of blood capillaries |
|
|
Glomerulus function |
Filter for blood |
|
|
Kidneys extend from level of ____ to _____. |
T12-L3 |
|
|
Kidney functions |
*remove nitrogenous waste products *maintain/regulate fluid/water balance *maintain/regulate acid-base balance & electrolyte levels *secrete substances that affect blood pressure |
|
|
How much urine is excreted per day? |
1-2 L |
|
|
Ureter location in reference to peritoneum |
Behind |
|
|
Ureter curves anterior & medially to enter the ___________ urinary bladder. |
posterolateral |
|
|
Ureterovesical Junction (UVJ) |
Junction of ureter and urinary bladder |
|
|
Mucosa of trigone is smooth and the remainder contain folds called _______. |
Rugae |
|
|
Approximately how much fluid does the urinary bladder hold? |
500 mL |
|
|
Female urethra length |
1 1/2” |
|
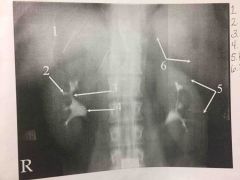
Front (Term) |
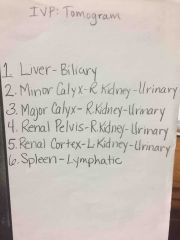
Back (Definition) |
|
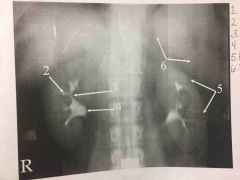
Front (Term) |
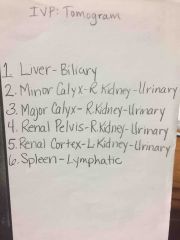
Back (Definition) |
|
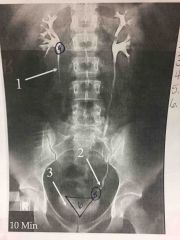
Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
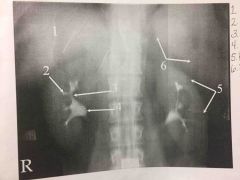
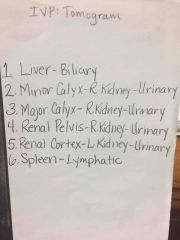
Front (Term) |
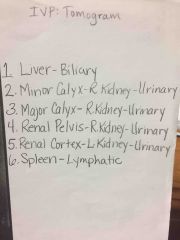
Back (Definition) |
|
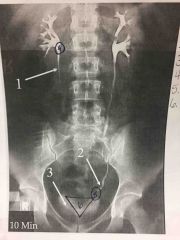
Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
How many bones are in the body? |
206 |
|
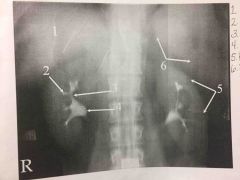
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
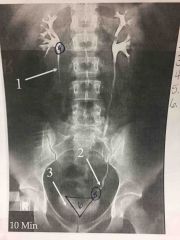
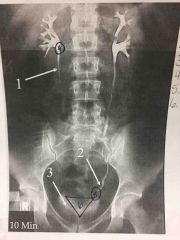
Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
How many bones are in the body? |
206 |
|
|
Functions of bones |
*attachment for muscles *basis for movement *frame to support body *storage for calcium, phosphorus, & other salts *produce red & white blood cells |
|
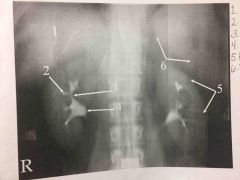
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
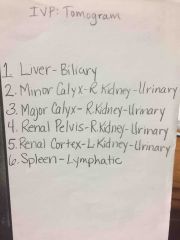
Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
How many bones are in the body? |
206 |
|
|
Functions of bones |
*attachment for muscles *basis for movement *frame to support body *storage for calcium, phosphorus, & other salts *produce red & white blood cells |
|
|
Compact bone |
Strong, dense outer layer; made up of compact bony tissue |
|
|
Trabeculae |
Speculated network of interconnecting spaces in spongy bone |
|
|
Medullary cavity |
Central cavity in long bones |
|
|
Ossification |
Development & formation of bones |
|
|
Bones begin to develop in the ___________________. |
2nd month of embryonic life |
|
|
Two stages of ossification |
*intermembranous *endochondral |
|
|
Intermembranous ossification produces _____ bones. |
Flat |
|
|
Endochondral ossification is where _______ bone formation begins. |
Long |
|
|
Once full ossification occurs, the ________ ________ becomes completely joined and becomes an _________ _________. |
Epiphyseal plate, epiphyseal line |
|
|
Classifications of bones by shape |
*long *short *flat *irregular *sesamoid |
|
|
Flat bones |
Two plates of compact bone |
|
|
Functional classification of joints |
*synarthroses- immovable *amphiarthroses- slightly movable *diarthroses- freely movable |
|
|
Fibrous joints |
3 types, virtually immovable |
|
|
Syndesmosis |
Immovable or slightly movable joint united by sheets of fibrous tissue |
|
|
Suture |
Immovable joint occurring only in the skull- held together by strong connective tissue |
|
|
Cartilaginous joints |
2 types, virtually immovable |
|
|
Symphysis |
Slightly movable bones separated by a pad of fibrocartilage |
|
|
Synchondrosis |
Immovable- rigid cartilage unite the bones |
|
|
Synovial joints |
6 types, freely movable |
|
|
Hinge |
Permits only flexion/extension |
|
|
Ellipsoid |
Permits movement in two directions at right angles to each other |
|
|
Nephrotosis |
Kidneys drop more than one lumbar vertebrae or any excessive downward displacement of kidneys |
|
|
Micturition |
Act of urinating |
|
|
Urination |
Act of voiding urine |
|
|
Extravasation |
Contrast leaking out of vein into tissue |
|
|
Vasovagal response |
Minor reaction response to fear; includes weakness, dizziness, sweating, and feeling faint |
|
|
Urticaria |
Hives |
|
|
Calculus |
Abnormal concretion of mineral salts, often called a stone |
|
|
Horseshoe kidney |
Fusion of kidneys, usually at lower poles |
|
|
Fistula |
Abnormal connection between two internal organs or between an organ and the body surface |
|
|
Ureterocele |
Ballooning of lower end of ureter into bladder |
|
|
axial bones- how many of each?
skull a) cranial b) facial c) auditory ossiclesneck d) hyoidthorax e) sternum f) ribsvertebral column g) cervical h) thoracic i) lumbar j) sacrum k) coccyx |
a) 8
b) 14 c) 6 d) 1 e) 1 f) 24 g) 7 h) 12 i) 5 j) 1 k) 1 |
|
|
appendicular bones- how many of each?
shoulder girdle a) clavicles b) scapulaeupper limbs c) humeri d) ulnae e) radii f) carpals g) metacarpals h) phalangeslower limbs i) femora j) tibias k) fibulae l) patellae m) tarsals n) metatarsals o) phalangespelvic girdle p) hip bones |
a) 2 b) 2 c) 2 d) 2 e) 2 f) 16 g) 10 h) 28 i) 2 j) 2 k) 2 l) 2 m) 14 n) 10 o) 28 p)2 |

