![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
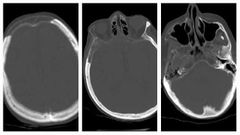
Finding Diagnosis |
Geographic areas of lucency (fat density, -20 HU) involving the skull, not constrained by sutures.Minimal bone expansion. Osteolysis circumscripta ( Pagets disease) |
|
|
What are the phases of Pagets? 3 |
Lytic Sclerotic Mixed |
|
|
Complications of skull bone Pagets? 4 |
Deafness Cranial nerve paresis Basilar invagination >> hydrocephalus >> brainstem compression Secondary high grade osteosarcoma |
|
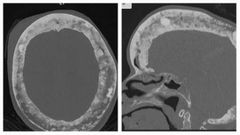
Finding Diagnosis Buzzword |
Paget involvement of the skull, with widening of the diploic space, typical "cotton wool" appearance and over-riding enlarged frontal bone (Tam o' Shanter sign). |
|
|
Differential diagnosis of clivus bone lesions? 2 |
Chordoma midline Chondrosarcoma off midline |
|
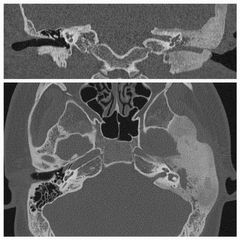
Finding Diagnosis |
Extensive sclerotic bony expansion with a groundglass appearance involving the left zygoma, sphenoid and petrous temporal bone.The bony expansion is centred on the medullary bone and has abrupt transition zones. Fibrous dysplasia |
|
|
Age of onset in each disease Fibrous dysplasia Pagets |
FD less than 30s Pagets 80s |
|
|
Fibrous dysplasia In the skull it spares ? Associated syndrome ? In the skull bone it affects ? |
Otic capsule ( blue arrow) McCune Albright syndrome( old French man drinking coffee and likes to molest young girls ) café u lait spots, Precocious puberty and multifocal fibrous dysplasia Outer table whereas Pagets likes the inner table. |
|
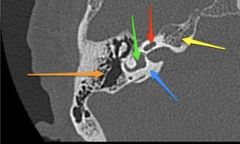
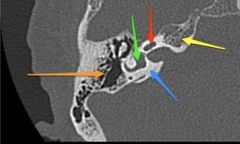
Name structures |
Annotated axial CT of the right petrous temporal bone:blue arrow: otic capsule (dense bone) yellow arrow: petrous apex orange arrow: mastoid air cells red arrow: cochlea green arrow: vestibule |
|
|
Which modality you prefer in assessing sinuses and fungal infections ? When? |
Orbit and sinus infections CT
Anterior 2/3 orbits better CT
Posterior 1/3 and to check for cavernous sinus involvement MRI Tumor progression, perineural spread and marrow involvement MRI
|
|
|
What are the 3 differential for hyperdense sinus? |
1- blood 2- inspissated secretions 3- fungus |
|
|
Differences between allergic fungal sinusitis and invasive fungal sinusitis ? |
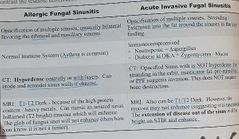
Allergic fungal Immnuocompetent ( asthma) Hyperdense in CT with bone remodelling and erosion No extension to the fat planes around it MRI T1and T2 dark, enhancing mucosa but the central fungal glob will not enhance Invasive Fungal Immunocompromised Neutropenia ( aspergillus) Diabetic DKA ( zygomycetes or mucor) CT not Hyperdense, extension to the mastocator fat space, PPF, orbital fat with fat stranding MRI dark T1 and T2, no enhancing mucosa, fat enhances with bright STIR images |
|
|
When you call sinusitis is chronic? |
After 12 weeks |
|
|
What are the 3 pattern of sinonasal disease? |
1- infundibular patter 2- osteomeatal complex pattern 3- polyposis pattern |
|
|
What is the most common pattern ? |
Infundibular pattern |
|
|
In infundibular pattern disease is limited to ? Due to? |
Maxillary sinus due to obstruction at the ipsilateral ostium/infundibulum |
|
|
Osteomeatal complex pattern Involves ? Reasons? 2 |
Involve the middle meatus and ipsilateral maxillary, ethmoid and frontal sinuses Hypertrophy of turbinates Anatomic variants ( concha bullosa , paradoxical middle turbinate and septal deviation) |
|
|
In sinonasal polyposis pattern Key feature is ? Associations? 2 |
Widening of the infundibulum Cystic fibrosis and aspirin hypersensitivity |
|
|
Features of sinus mucocele in MRI? 4 |
Airless sinus Expansion T1bright and T2 low ( proteinacious material) or water content T1 dark and T2 bright Peripheral enhancement due to inflamed mucosa |
|
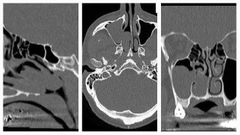
Finding Diagnosis |
There is a polypoidal soft tissue mass partially filling the right maxillary sinus and extending into the nasal cavity through the widened secondary maxillary ostium. posteriorly, the polyp protrudes through the choana into the nasopharynx. Antrochoanal polyp |
|
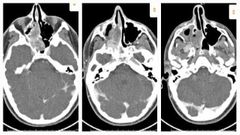
Finding Diagnosis |
There is a large mass extending from the posterior right nasopharynx extending posteriorly with osseous destruction to occupy a majority of the sphenoid sinus. The lesion enters and expands the right foramen rotundum. The superolateral margin of the right sphenoid sinus shows a subtle bony defect adjacent to the mass but there is no evidence of intracranial extension. The mass extends into, fills and expands the right pterygopalatine fossa. Laterally, it extends through the pterygomaxillary fissure into the masticator space. There is bowing of the medial wall of the right orbit and the mass erodes portions of the posterior and medial wall of the right maxillary sinus Juvenile nasal angiofibroma |
|
|
Classic history for juvenile nasal angiofibroma ? Management ? |
Teenage boy with nasal bleed Pre- surgical embolization ( internal maxillary and ascending Pharyngeal artery) |
|
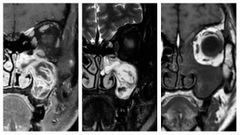
Finding Diagnosis |
MRI with contrast through the paranasal sinuses demonstrates a mass occupying the left maxillary antrum and widening the ostiomeatal complex. On non-contrast T1 images, it is somewhat heterogeneous in intensity ranging from isointense to hypointense compared to muscle.On T2 weighted images, the mass demonstrates a striking convoluted appearance with alternating bands of markedly hyperintense tissue separated by low-intensity tissue. Following administration of contrast a similar appearance is noted, again with the so-called convoluted cerebriform . . Inverted papilloma |
|
|
What are the features of inverted papilloma in MRI ? Risk of ? |
Like a Brain on T1 and T2 ( cribriform pattern) Squamous cell carcinoma in 10 % |
|
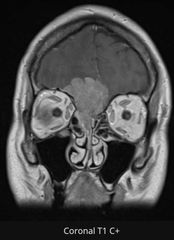
Finding Diagnsois |
Enhancing soft tissue mass centred on the floor of the anterior cranial fossa extending into the nasal cavity and with infiltration of the right frontal lobe. The mass is clearly extra-axial with involvement of the upper nasal cavity. Differential includes A) meningioma, likely high cellularity/mitotic and/or WHO II or III, with brain invasion is a distinct possibility; B) olfactory neuroblastoma - usually more substantial nasal component and peritumoral cysts intracranially. Metastasis, lymphoma and haemangiopericytoma are all less likely differentials. |
|
|
Classic appearance of esthesioneuroblastoma ? Which radiotracer will show uptake in this case ? |
Dumbell shape * waist at the cribriform plat
Octerio scan |
|
|
Commonest location for sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma? Appearance in MRI ? |
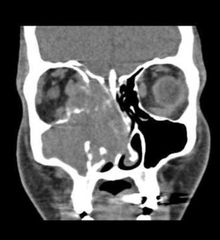
Maxillary antrum Highly cellular T2 low and less enhancement |
|
|
Types if epistaxis? Common location for epistaxis? Treatment? |
Anterior common at Kiesselbach plexus easy to stop it Posterior from sphenopalatine artery 5% Which is atetminal branch for internal maxillary artery Angio embolism ( check anastamotic variant like ophthalmic artery from ECA) |
|
|
Causes of nasal septal perforation ? 5 |
Surgical Cocaine use > 3 months Wegener granulomatosis Too much nose picking 🤧 Syphilis ( affecting bony septum more) |

