![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Skin type: - sallow complexion - thick epidermis - shiny appearance - open pores - comedones - papules/pustules |
Oily |
|
|
|
Causes of oily skin |
Onset of puberty Hormone imbalance Ethnic background |
|
|
|
Papules |
Small inflamed elevation, containing no pus |
|
|
|
What are open comedones? |
Blackheads |
|
|
|
Describe how an open comedone is formed |
Excess sebum & dead skin cells partially block a pore The sebum solidifies, filling the follicle The sebum & dead skin cells reach the pore opening Upon exposure to air, the melanin will oxidize, resulting in a black/brown discolouration
|
|
|
|
Skin type: Drier Loss of firmness/elasticity Dilated capillaries Thinning epidermis Uneven pigmentation Lines around north/eyes Underlying bone structure becomes more evident Underlying fat begins to disappear Muscle tone begins to disappear |
Mature skin |
|
|
|
What are the 5 layers of the epidermis |
Corneum Lucidum Granulosum Spinosum Germinativum |
|
|
|
What is the epidermis |
Outermost layer of skin |
|
|
|
What do Sebaceous glands do |
Secrete oily matter (sebum) into hair follicles & lubricate skin |
|
|
|
Papule |
A red lesion, typically less than 1 cm around. May be domed or flat on top |
|
|
|
Characteristics of dry skin |
Pale in colour Thin epidermis Tight after washing Flaky Under active sebaceous glands Fine lines around eyes prematurely Dilated capillaries |
|
|
|
What skin types should you not use Bio cream on? |
Severe rosacea Hypersensitive |
|
|
|
What is lactic acid made from |
Sour milk |
|
|
|
What effect can lactic acid have |
Lightening Increase skins water holding capacities Reduce appearance of fine lines Improves skin’s texture Stimulation of collagen & elastin |
|
|
|
What is tartaric acid from |
Grapes |
|
|
|
What effect can tartaric acid have on the skin? |
Anti inflammatory Anti oxidant Acne |
|
|
|
Where does glycolic acid come from? |
Sugar cane |
|
|
|
What benefits does glycolic acid have? |
Lightens pigmentation Helps premature aging |
|
|
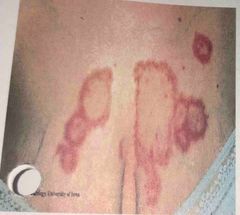
Front (Term) |
Tinea corpus (ringworm) |
|
|
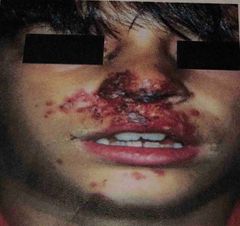
Front (Term) |
Impetigo |
|
|
|
What is the most common and recognizable effect of rosacea? |
The “butterfly effect” of redness across the cheeks and nose that extends to the forehead |
|
|
|
What causes the skin in rosacea conditions to appear shiny? |
Lymphodoema - fluid retention and tissue swelling that is localized on the face; caused by a compromised lymphatic system |
|
|
|
What do you see in the beginning of stage 2 rosacea? |
Dilated blood vessels that form a web like pattern over one or more areas of the face |
|
|
|
What can eventually develop in stage 2 rosacea? |
Acne like lesions, papules and pustules |
|
|
|
What occurs in stage 3 rosacea? |
Nose enlargement, redness and severe swelling |
|
|
|
What are 6 sensations a person with sensitive skin may feel? |
Stinging Burning Tightness Itching Slight dryness Redness |
|
|
|
T/F : someone with sensitive skin has an impaired acid mantle |
False |
|
|
|
Which skin tones are more likely to develop rosacea? |
Fair/ pale |
|
|
|
Who is more likely to develop rosacea, women or men? |
Women |
|
|
|
What are the 4 main triggers that can cause sensitivity? |
▪️ climate ▪️ psychological ▪️ mechanical ▪️ external |
|
|
|
What are some external triggers for sensitivity? |
Fragrance (artificial) Detergents Hard water Preservatives |
|
|
|
What should you avoid during a facial on a person with rosacea? |
▪️ most exfoliant ▪️ massage ▪️ any products that are drying (such as an enzyme peel) ▪️ excessive warmth (blankets, bed warmer, hot towels) ▪️ steaming |
|
|
|
What should you do during a facial on a person with rosacea? |
Multiple rounds of lymph drainage Use #2 oil Keep towels cooler Use products with high moisture properties Use cold stones to soothe redness |
|
|
|
Acne is an inflammatory disease of ______________ |
The pilosebaceous unit |
|
|
|
Acne begins at ___________ |
Puberty |
|
|
|
What does the pilosebaceous unit consist of |
Follicle Sebaceous gland Hair shaft Arrector Pilli |
|
|
|
What are contraindications for facial steaming? |
Highly vascular conditions Sunburn Acne rosacea Highly nervous client Claustrophobia Aggravated asthma Severe infection/ inflammation Hyper sensitive skin |
|
|
|
What are 3 key points to maintaining safety with a steamer? |
Never allow steamer to run dry When turning on, ensure it is pointed away from both client and yourself - ensure it is steaming smoothly before administering treatment
Maintain in good working order, using only distilled water to prevent calcium and mineral deposits |
|
|
|
What are 5 benefits to facial steaming? |
Stimulates the sebaceous glands, helping to lubricate the skin
Softens comedones for easier extraction
Germicidal effect if using ozone
aids desquamation by softening dead skin cells
Stimulates the sudoriferous glands, producing sweat, helping to eliminate toxins
|
|
|
|
What effect does steaming have on dry skin? |
Deep cleansing Desquamation of dead skin cells Improves colour |
|
|
|
What effect does steaming have on sensitive skin? |
Gently cleanses Hydrates skin |
|
|
|
What effect does steaming have on oily skin? |
Unlocks and softens congestion Deep cleanses Improves skin colour |
|
|
|
What effect does steaming have on mature skin? |
Increases cellular regeneration Increases desquamation Hydrates skin Improves colour |
|
|
|
What does the reticular layer do? |
Protects and repairs injured tissue |
|
|
|
Which glands are located in the regular layer? |
Sweat & sebaceous |
|
|
|
What does the reticular layer consist of? |
Dense, coarse branching collagen fiber bundles |
|
|
|
What do the collagen fibres do? |
Allow the skin to bend and fold over underlying muscle activity |
|
|
|
What does collagen do for the skin? |
Gives it its strength and youthful plump appearance |
|
|
|
What does elastin do for the skin? |
Allowed skin to stretch easily but quickly regain its shape |
|
|
|
What does over extension of elastin do? |
Can rupture the elastin fibres and allows collagen to overstretch or tear; causing stretch marks |
|
|
|
What are reticulin fibres? |
Fibres that run through and between other fibres and structures in the dermis;? Supporting everything and keeping it in place |
|
|
|
T/F: fibroblast cells are located in the dermis |
True |
|
|
|
What accounts for 75% of the dermis’ weight? |
Collagen |
|
|
|
Production of what decreases as the skin ages? |
Collagen |
|
|
|
The skin loses its ability to retain _______ as it ages |
Water |
|
|
|
Hyaluronic acid holds how much of it’s weight in water? |
600-1000 |
|
|
|
What are fibroblast cells? |
Cells in the dermis that absorb amino acids and convert them to polypeptide chains of collagen which are secreted into the dermis to help form structural integrity of the dermal region |
|
|
|
What are mast cells filled with? |
Heparin, histamine and hyaluronic acid |
3 H |
|
|
What do mast cells do |
Release histamine when triggered - producing an allergic reaction |
|
|
|
What is cytoplasm? |
Cellular material in a cell, excluding the nucleus |
|
|
|
What are histiocyte cells? |
Cells that interest foreign particles in an effort to protect the body from infection |
|
|
|
What are eosinophil cells job? |
To fight parasitic infections |
|
|
|
What is the main purpose of neutrophils? |
To kill as many bacteria that are invading the body as possible - they are the body’s natural antibiotic |
|
|
|
What are the two layers of the dermis? |
Papillary & reticular |
|
|
|
What does the reticular layer do? |
Protects and repairs injured tissue |
|
|
|
What does the reticular layer contain? |
Collagen fibre bundles |
|
|
|
T/F: there are many veins and arteries in the reticular layer that link up with the papillary capillaries |
True |
|
|
|
What does collagen do for the skin? |
Gives skin strength and resilience
Provides a youthful, plump appearance |
|
|
|
What does elastin do for the skin? |
Allows skin to stretch easily and regain its shape |
|
|
|
What happens when elastin gets overextended |
The elastin fibres will rupture - causing the collagen to become overstretched and even tear - causing stretch marks |
|
|
|
What do reticulin fibres do? |
Run through and in between the other fibres and structures in the dermis to help keep everything in place. |
|
|
|
How does steaming aid the desquamation of dry skin? |
Softens dead skin cells |
|
|
|
Which layer of skin becomes hydrated with steaming? |
Stratum corneum |
|
|
|
What is acne? |
An inflammatory skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit |
|
|
|
What does the pilosebaceous unit consist of? |
Follicle Sebaceous gland Hair shaft Arrector Pilli |
|
|
|
What does hyaluronic acid do for the skin? |
Protects collagen and elastin fibres
Provides essential hydration through its water binding properties |
|
|
|
What are 4 potential causes of destruction to the dermis? |
Improper diet Illness Poor lifestyle Sun exposure Stress |
|
|
|
What can happen to the skin when there is a reduction in the amount of hyaluronic acid in the dermis? |
Inability to retain water (drier skin)
Skin becomes thinner (unable to restore itself Collagen level drops & elastin becomes loose (wrinkles) |
|
|
|
What are 3 main components of the dermis that fibroblast cells make? |
Collagen Elastin Hyaluronic acid |
|
|
|
What are free radicals? |
Atoms that have an unpaired electron; making them unstable They attack fully charged electrons to make themselves stable but end up damaging the cell they stole from |
|
|
|
Which UV Rays penetrate the dermis? |
UVA |
|
|
|
What are 5 visible changes you can see and feel with the skin as it ages? |
Thinner epidermis Dehydration Age spots Dilated capillaries Bone structure more evident Sallow complexion Fine lines abs wrinkles |
|
|
|
What can be seen in acne stage one? |
Minor papules - in small amounts Open and closed comedones - especially in t zone area
|
|
|
|
What can you see in acne stage two? |
Open and closed comedones Papules and pustules Mild inflammation |
|
|
|
What can be seen during acne stage 3? |
Red, inflamed areas Larger papules and pustules Modules Scarring Spreading to back, chest and shoulders |
|
|
|
Describe Acne stage for |
Considered cystic/ noduled Present on back, chest, shoulders and begins to form on upper arm region Numerous comedones, papules, pustules, nodules and cysts Infection and inflammation is deeply rooted and scarring is inevitable Can lead to psychological and emotional issues
|
|
|
|
What is the Ph of the acid mantle? |
5.5 |
|
|
|
What is P.Acne? |
A facultative anaerobic bacteria |
|
|
|
What does P.Acne thrive on? |
Lack of oxygen and sebum in abundance |
|

