![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what are the layers of the skin and what is found in each layer
|
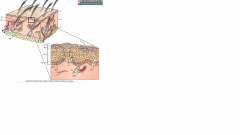
outer to inner....
epidermis- ( CRAIG GREW SEVERAL BALLS!!)- cornificed, granular, spinous and basal. dermis-cells fibres, matrix, vasculature and innervation hypodermis- fat and fibrous tissue |
|
|
|
what are the skins functions
|
Functions of the skin:
Protective barrier Immunity [Skin Immune System] Plus: Thermoregulation Blood Pressure regulation Sensory perception Secretion (Communication) Storage Vitamin D production (esp. herbivores) |
|
|
|
what is the function of the stratum corneum and what are its main components
|
a barrier. like a brick wall.
The corneocytes (made of tough protein) form the bricks and between these a double layer of lipids (fatty materials) and water make up the mortar. Some lipids have a hard crystal-like structure and are impermeable to water. Others lipids do not have this structure and they allow water to percolate through. So, the barrier is semi-permeable. The elasticity, firmness and correct functioning of the stratum corneum depends on its moisture content. Retention of water is aided by substances in the skin called natural moisturising factors (NMFs). If the moisture content is too high or too low, it can affect the skin’s barrier properties. |
brick wall!! ( motar + bricks)
|
|
|
define intertrigo
|

skin fold dermatitis eg in bulldog
|
|
|
|
when might you see alopecia which is symmetrical
|
oestrogen production by sertoli cell tumor
|
|
|
|
how is flea allergic dermatitis affected by climate
|
more common in temperate climates and seasonal in cooler climates
|
|
|
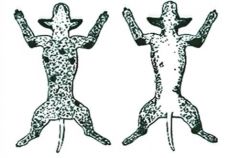
what type of Mange is this
|
Sarcoptic mange
|
|
|
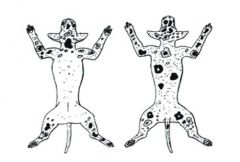
what type of mange is this
|
demodectic mange
|
|
|
|
what is a primary and secondary skin legion
|
primary- has developed spontaneously due to a disease. ( more useful to determine underlying cause ).
secondary- from primary legion or self trauma or external factors ( complicate the diagnosis ). |
|
|
|
define Macule and draw it
|
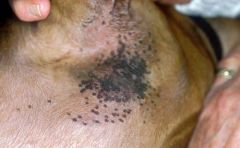
A primary legion.
a circumscribed, non palpable spot, which is change in the colour of the skin. (< 1cm) if > than 1cm it is called a patch. http://www.rvc.ac.uk/review/Dermatology/Lesions/macules.htm |
big mac burger bap!!
|
|
|
define a papule and draw it
|
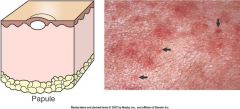
A primary legion.
a small solid elivation of the skin < 1cm in diameter. usually a build up of inflammatory cells. http://www.rvc.ac.uk/review/Dermatology/Lesions/papules.htm |
its palpable !!
|
|
|
define plaque and draw it
|
A primary legion.
a large > 1cm flat topped formed by extension of palpules |
|
|
|
define a nodule and draw it
|
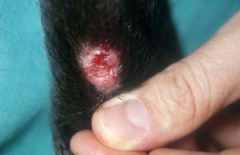
A primary legion.
a circumscribed, solid elevation that is > 1cm in diameter. usually due to massive cell infiltration that may be inflammatory or neoplastic and usually extends into the deeper layers http://www.rvc.ac.uk/review/Dermatology/Lesions/nodules1.htm |
|
|
|
define a tumor and draw it
|
A primary legion.
a large mass > 2cm involving skin structures( neoplastic or non eg inflammation ) |
|
|
|
define a pustule and draw it
|
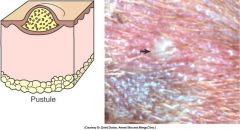
a small elevation. intra-epidermal, sub-epidermal or follicular. contains puss. (usuually neutrophis and bac. but may have eosinophils and be sterile) epi is thin so tend to burst.
usually caused by pyoderma in dogs but may be caused by immumn mediated disease and be sterile. http://www.rvc.ac.uk/review/Dermatology/Lesions/pustules.htm |
p for pyoderma ( usually ) in dogs!!
|
|
|
define an abcess and draw it
|
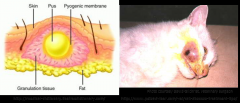
a localised collection of puss surrounded by inflammation. ( usually deeper than a pustule )
|
think pus!
|
|
|
define a visicle and bulla and draw them
|
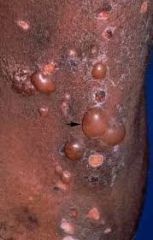
Vesicle-sharply circumscribed elivation filled with clear fluid ( rather than puss). (intra- epidermal / subepidermal) <1cm in diameter. also fragile. Bulla > 1cm in diameter.
http://www.rvc.ac.uk/review/Dermatology/Lesions/vesicles1.htm |
Vitalise WATER Bottle!!
|
|
|
define a wheal and draw it
|
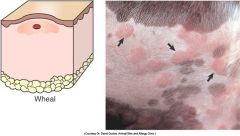
aka a hive. ( the hive!). A circumscribed raised oedema. Often transient. eg nettle sting.
( angio-oedema is deeper) |
|
|
|
define a cyst and draw it
|
a cavity with a epi lining. (fluid or solid contents , smooth and wells circumscribed. Usually moveable ( fluctuant)).
http://www.rvc.ac.uk/review/Dermatology/Lesions/tumours.htm |
|
|
|
what are the 5 differentials of a mass
|
abcess/cyst/granuloma/neoplasia/haematoma.
|
|
|
|
which of the following are secondary skin legion descriptions and which are primary ....
Epidermal collarette Excoriation Tumour Pustule abcess Wheal (or Angioedema) Fissure Bulla Nodule Erosion or Ulcer Scar Cyst plaque Callus Macule Papule Lichenification Vesicle |
primary-Macule or (>1cm) Patch
Papule or (>1cm) Plaque Vesicle or (>1cm) Bulla Pustule (or Abscess) Wheal (or Angioedema) Cyst Nodule (1-2cm); Tumour (>2cm) secondary-Epidermal collarette Excoriation Erosion or Ulcer Fissure Scar Lichenification Callus |
|
|
|
define collarette and draw it
|
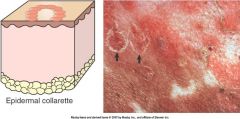
a secondary skin legion.
a circular rim of loose scale ( keratin ) that began life as a pustule/vesicle/bulla |
like a collar!!
|
|
|
define excoriation and draw it
|
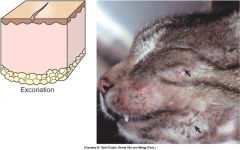
a secondary skin legion.
erosions or ulcers caused by self trauma. usually linear. ( by -scratch/rub/bite generally shows there is pruritis or pain ) |
I drew that x myself!
|
|
|
define erosion and draw it
|
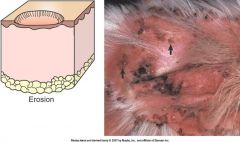
a secondary skin legion.
shallow epi defect which does not go into the BM and so can heel by regeneration without scarring. |
|
|
|
define an ulcer and draw it
|
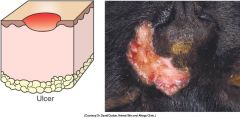
a secondary skin legion.
epidermal damage which exposes the underlying dermis- so heel by scarring. |
|
|
|
define a fissure and draw it
|
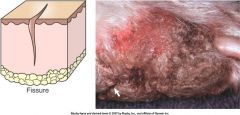
a secondary skin legion.
a linear cut which includes the epidermis +/- dermis. A sharply defined cleft or many small cracks. Seen especially in dry skin http://www.rvc.ac.uk/review/Dermatology/Lesions/excoriation.htm |
|
|
|
define a scar and draw it
|

a area of fibrous tissue reparing a injury (ulcer!) which goes into the dermis
|
just what I already know
|
|
|
define lichenification and draw it
|

The skin becomes thicker and harder with exagerated skin markings, like elephant skin. Usually due to friction areas may be hyperpigmented.
|
think of tree bark!!
|
|
|
define callus and draw it
|
localised lichenification. it is caused by long term friction and is commonly seen on the elbows
|
|
|
|
name 6 legions which may be primary or secondary
|
Alopecia (hair loss)/Scale/Crust/Follicular Casts/Comedo/Pigment alteration
chesley football clyb alway score plenty!! |
chesley football clyb alway score plenty!!
|
|
|
define scale and draw it
|
primary or secondary lesions
a visible build up of keratinised cells. ( normally loss of cornified cells is not visible to the naked eye). May be thin/thick/dry/oily. |
|
|
|
define crust and draw it
|
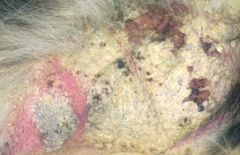
primary or secondary lesions
crust is formed from dried exudate which sticks to the skins surface. ( serum/blood/cells/scale) eg from erosions /ulcers/pustules |
think of how the crust on your pie forms!!
|
|
|
define comedones ( sing. comedo) and draw`
|
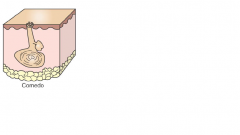
Blackheads!! primary or secondary lesions
a dialted hair folicicle which is filled with cornifided cells and sebatious material. (It is not someone who makes other people laugh, as previously suggested by an intrepid undergraduate.!!) |
|
|
|
define a folicular cast and draw it
|

a build up of keratinous debris that sticks to the hair shaft and sticks out from the follicle
|
|

