![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
229 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the cause of Albinism?
|
Albinism
Autosomal recessive melanin synthesis protein gene defects Type I: Tyrosinase -/- Type II: P Gene/P Protein -/- Type III: Tyrosinase Related Protein 1 -/- |
|
|
What is the cause of Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
Autosoma dominant STK11 tumor suppressor gene defect Bluish, brown, and/or black macules on the lips, perioral skin, buccal mucosa |
|
|
Which two genodermatoses are associated with colon polyps? Which are benign? Which are pre-malignant?
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
-benign colon polyps -increased risk of ovarian, breast, pancreatic CA Gardner Syndrome -pre-malignant colon polyps -very high risk of adenocarcinoma of the colon, increased risk of thyroid cancer -treat with prophylactic colectomy |
|
|
Bluish, brown, and/or black macules on the lips, perioral skin, and buccal mucosa are associated with what syndrome?
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
Autosomal dominant STK11 gene defect |
|
|
What is the cause of Gardner Syndrome? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Gardner Syndrome
Autosomal dominant APC tumor suppressor gene defect Multiple epidermal cysts, fibromas, osteomas, congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) |
|
|
Multiple epidermal cysts, fibromas, osteomas, and congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) are associated with what syndrome?
|
Gardner Syndrome
Autosomal dominant APC tumor suppressor gene defect |
|
|
What is the cause of Xeroderma Pigmentosa? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Xeroderma Pigmentosa
Autosomal recessive XPA, B, C, D, E, F, or G nucleotide excision repair gene defect Acute sun sensitivity, pigmented macules, telangiectasias, actinic keratoses, 1000x increased risk for basal and squamous cell carcinomas and malignant melanomas |
|
|
Acute sun sensitivity, pigmented macules, telangiectasias, actinic keratoses, and 1000x increased risk for basal and squamous cell carcinomas and malignant melanomas are associated with what syndrome?
|
Xeroderma Pigmentosa
Autosomal recessive XPA, B, C, D, E, F, G nucleotide excision repair gene defect |
|
|
What is the cause of Neurofibromatosis Type I? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Neurofibromatosis Type I (NF I)
Autosomal dominant neurofibromin gene defect on chromosome 17 Cafe-au-lait macules, neurofibromas, axillary freckling (Crowe's sign), Lisch nodules, optic glioma, sphenoid wing dysplasia, pseudoarthrosis |
|
|
Cafe-au-lait macules, neurofibromas, and axillary freckling (Crowe's sign) are associated with what syndrome?
|
Neurofibromatosis Type I
Autosomal dominant neurofibromin gene defect on chromosome 17 |
|
|
What is Crowe's sign? What is it associated with?
|
Axillary freckling
Neurofibromatosis Type I |
|
|
Lisch nodules, optic glioma, sphenoid wing dysplasia, and pseudoarthrosis are associated with what syndrome?
|
Neurofibromatosis Type I
Autosomal dominant neurofibromin gene defect on chromsome 17 |
|
|
What is the cause of Neurofibromatosis Type II? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Neurofibromatosis Type II
Autosomal dominant scwannomin or merlin gene defect on chromosome 22 Bilateral acoustic neuromas on CN VIII, neurofibromas |
|
|
Bilateral acoustic neuromas on CN VIII and neurofibromas are associated with what syndrome?
|
Neurofibromatosis Type II
Autosomal dominant schwannomin or merlin gene defect on chromosome 22 |
|
|
What is the cause of Tuberous Sclerosis? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Tuberous Sclerosis
Autosomal dominant TSC-1 (hamartin, ch9) or TSC-2 (tuberin, ch16) gene defect Adenoma sebaceum/angiofibromas, mental retardation, epilepsy, Shagreen patch, Koenen's tumors, hypomelanotic papules, fibrous plaques |
|
|
What are adenoma sebaceum/angiofibromas? What are they associated with?
|

1-3mm red-brown papules on cheek, nose, and forehead
Tuberous Sclerosis |
|
|
What are Shagreen patches? What are they associated with?
|

Connective tissue nevi commonly located in the lumbosacral area
Tuberous Sclerosis |
|
|
What are Koenen's tumors? What are they associated with?
|

Small periungual fibromas
Tuberous Sclerosis |
|
|
Adenoma sebaceum/angiofibromas, shagreen patches, koenen's tumors, hypomelanotic macules, and fibrous plaques are associate with what syndrome?
|
Tuberous Sclerosis
Autosomal dominant TSC-1 (hamartin, ch9) or TSC-2 (tuberin, ch16) gene defect |
|
|
What is the cause of Marfan Syndrome? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Marfan Syndrome
Autosomal dominant fibrillin gene defect Tall stature, lankiness, arachnodactyly, loose-jointedness, ascending aoritc aneurysm, mitral valve prolapse |
|
|
Tall stature, lankiness, arachnodactyly, loose-jointedness, ascending aortic aneurysm, and mitral valve prolapse are associated with what syndrome?
|
Marfan Syndrome
Autosomal dominant fibrillin gene defect |
|
|
Those with Dystrophic EB are at high risk of developing which form of cancer? Where?
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma in scars by age 20
|
|
|
What is the cause of Ehler-Danlos Disease? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|
Ehler-Danlos Disease
Several genetically distinct connective tissue disorders Excessive stretchability and fragility of the skin, hyperextensibility of the joints, paper-thin scarring, "fish-mouth" wounds, molluscum pseudotumors |
|
|
Excessive stretchability and fragility of the skin, hyperextendibility of the joints, paper-thin scarring, "fish-mouth" wounds, and molluscum pseudotumors are associated with what syndrome?
|
Ehler-Danlos Disease
Several genetically distinct connective tissue disorders |
|
|
What is the cause of Fabry's Disease? What are the associated clinical symptoms?
|

Fabry's Disease
X-linked recessive a-galactosidase A gene defect leading to an accumulation of neutral glycosphingolipids Angiokeratomas, painful crises, acroparethesias, angina, myocardial infarction, proteinuria (maltese crosses) |
|
|
Angiokeratomas, painful crises, acroparathesias, angina, myocardial infarction, and proteinuria are associated with what syndrome?
|
Fabry's Disease
X-linked recessive a-galactosidase A gene defect to an accumulation of neutral glycosphingolipids |
|
|
What are maltese crosses? What are they associated with?
|
Birefringent characteristic lipid globules seen with polarized light in urine samples
Fabry's Disease |
|
|
Diffuse hyperpigmentation is associated with what endocrine syndrome? What is the mechanism of action?
|
Addison's Disease
Adrenal cortex insufficiency causes the pituitary to release excessive ACTH which is cleaved into MSH |
|
|
Addison's Disease is associated with what cutaneous feature? What is the mechanism of action?
|
Hyperpigmentation
Adrenal cortex insufficiency causes the pituitary to release excessive ACTH which is cleaved into MSH |
|
|
Yellow-orange nodules, often on the elbows, are associated with what disorder? What are they?
|
Hyperlipidemia
Xanthomas |
|
|
Hyperlipidemia is associated with what cutaneous feature?
|
Xanthomas
|
|
|
What are seborrheic keratoses? Are they malignant?
|
Darkly pigmented macules-->papules-->nodules which are benign
|
|
|
What are actinic keratoses? Are they malignant?
|
Erythematous, sandpapery, scaly macules which are pre-cancerous
|
|
|
From which embryological layer are melanocytes derived?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
From which embryological layer are Merckel cells derived?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
From which embryological layer are Langerhans cells derived?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
Which UV radiation penetrates to the dermis?
|
UVA
|
|
|
Which UV radiation does not penetrate past the epidermis?
|
UVB
|
|
|
What mineral is required for the function of tyrosinase?
|
Copper
|
|
|
What are melanosomes?
|
Tyrosinase-containing organelles which produce melanin
|
|
|
What is TODA stage I?
|
Clear, spherical membrane containing tyrosinase
|
|
|
What is TODA stage II?
|
Oval membrane with filament periodicity
|
|
|
What is TODA stage III?
|
Oval membrane with filament periodicity with some melanin
|
|
|
What is TODA stage IV?
|
Electron opaque organelle containing melanin
|
|
|
What is the difference between melanosomes in whites and blacks?
|
Melanosomes in whites are smaller, fragmented, and naked while melanosomes in blacks are larger, unified, and enveloped
|
|
|
Each melanocyte is arborized to how many keratinocytes?
|
35
|
|
|
What is the immediate skin response to UV light?
|
Immediate Pigment Darkening
-Occurs in seconds -Dislocation of melanosomes to dendrites -No increase in melanocyte # |
|
|
What is the delayed skin response to UV light? When does it occur?
|
Delayed Pigment Formation (tanning)
-Occurs in 2-3 days -Increased melanosomes in melanocytes -Increased melanosomes in keratinocytes -Increase in melanocyte numbers |
|
|
How does MSH lead to increased pigment?
|
MSH activates adenyl cyclase which causes an increase in cAMP which activates tyrosinase and melanosome synthesis
|
|
|
What is the role of MMP-9 in wound healing?
|
Activated by inflammation, delays wound healing
|
|
|
What is the role of TNFa in wound healing?
|
Decreases activity in order to organize collagen
|
|
|
What is the activity of TGFb in wound healing?
|
Stimulates fibroblasts
|
|
|
Which organism is responsible for infections from cat bites?
|
Pasteurella multocida
|
|
|
Which organism is responsible for infections from dog bites?
|
Pasteurella canis
|
|
|
Which organism is responsible for infections from human bites?
|
Eikenella corrodens
|
|
|
What is the treatment for bite wounds if occuring 8 hours after the injury?
|
Fillet open wound, give antibiotics
|
|
|
Edema extending beyond erythema, vesicles or bulla, subcutaneous gas, and an absence of lymphangitis or lymphadenitis could be what infection?
|
Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection
|
|
|
Is lymphangitis or lymphadenitis present in cellulitis or necrotizing soft-tissue infections?
|
Yes in cellulitis
No in necrotizing soft-tissue infections |
|
|
What is Type 1 Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection?
|
polymicrobial infection (including S. aureus)
|
|
|
What is Type 2 Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection?
|
monomicrobial Group A Strep infection
|
|
|
What is Fournier's Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection?
|
Scrotal infection
|
|
|
What is Necrotizing Cellulitis? What is the causative agent?
|
Infection with Vibrio vulnifus from raw oysters, mixture of aerobic and anaerobic/enterics from IV drug use
|
|
|
What causes erysipelas? What are the features?
|
Group A Strep
Bright red, edematous, indurated lesion (peau d'orange) with sharp raised border |
|
|
What causes folliculitis? What are the features?
|
S. aureus or P. aeruginosa from hot tubs
Small erythemtous papules with a central pustule |
|
|
What causes cellulitis? What are the features?
|
Group A Strep (sometimes S. aureus)
Subcutaneous tissue involvement with lymphadenitis and lymphangitis |
|
|
What causes Impetigo? What are the features?
|
Group A Strep
Vesicopustular lesions with golden crusts |
|
|
What causes bullous impetigo? What are the features?
|
S. aureus
Vescles become bullae which become light brown crusts |
|
|
Which skin infections are caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Strep)?
|
Impetigo
Erysipelas Cellulitis (more often) Type II Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection |
|
|
Which skin infections are caused by Staphylococcus aureus?
|
Bullous impetigo
Folliculitis Abscesses Type I Necrotozing Soft-Tissue Infection |
|
|
Which layer of the skin do superficial mycoses infect?
|
Stratum corneum
|
|
|
What is tinea versicolor? What is the causative agent?
|
White macules caused by M. furfur
|
|
|
What is tinea negra? What is the causative agent?
|
Black macules caused by Hortaea werneckii
|
|
|
What does M. furfur cause?
|
Tinea versicolor
|
|
|
What does Hortaea werneckii cause?
|
Tinea negra
|
|
|
What is White Piedra? What is the causative agent?
|
White hair nodules caused by Trichosporon beigelii
|
|
|
What is Black Piedra? What is the causative agent?
|
Black hair nodules caused by Piedraia hortae
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of Tinea?
|
Trichophyton rubrum
|
|
|
What is tinea pedis?
|
Dermtophytosis of the foot
|
|
|
What is tinea cruris?
|
Dermatophytosis of the groin caused by trichophyton rubrum
|
|
|
What is tinea corporis?
|
Dermatophytosis of the body caused by Triychophyton rubrum
|
|
|
What is tinea manuum?
|
Dermatophytosis of the hands by Trichophyton rubrum
|
|
|
What is tinea capitis?
|
Dermatophytosis of the scalp by trichophyton rubrum
|
|
|
What is onchyomycosis?
|
Dermatophytosis of the nails
|
|
|
What is intertrigo? What is the causative agent?
|
Intertrigo often affects skin folds and begins as vesciopustues that rupture into maceration and fissuring, evolving into an erythematous base with scalloped border and white rim of necrotic epidermis. This is a cutaneous Candida infection.
|
|
|
What does Trichophyton rubrum cause?
|
Tinea
|
|
|
What does Candida cause?
|
Intertrigo
|
|
|
Which amino acid is melanin derived from?
|
Tyrosine, an <i>aromatic</i> amino acid
|
|
|
What causes Cowden's Disease? What are the clinical symptoms?
|
PTEN gene defect
Cobblestone appearance, benign polyps |
|
|
A cobbestone appearance and benign polyps are associated with what syndrome?
|
Cowden's Disease
PTEN gene defect |
|
|
Ehlers-Danlos Disease patients are at risk for what type of cancer?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Which UV light causes photo-aging?
|
UVA
|
|
|
What blocks UVA?
|
ecamsule
avobenzene zinc oxide |
|
|
What blocks UVB?
|
ecamsule
oxygenzone zinc oxide |
|
|
What is SPF?
|
Time to burn with product/Time to burn without product
|
|
|
What are erythematous, sandpapery, scaly macules often on sun damaged skin? Are they malignant or benign?
|
Actinic keratoses
Pre-malignant |
|
|
What is the most common skin cancer?
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of basal cell carcinomas?
|
Pearly papule/nodules with telangiectasias and a central indentation or crater, sometimes evolving into a "rodent" ulcer nodule
|
|
|
Where are basal cell carcinomas often found?
|
Upper lip and higher
|
|
|
What are pearly papules/nodules with telangiectasias and a central indentation or crater, sometimes evolving into a "rodent" ulcer nodule?
|
Basal cell carcinomas
|
|
|
Which skin cancers have a high propensity for metastasis? Which have a low propensity for metastasis?
|
Melanomas = high
Squamous Cell Carcinoma = low-med Basal Cell Carcinoma = low |
|
|
What are the clinical features of sqamous cell carcinomas?
|
Ill-defined erythematous papule with rough, scaly surface
|
|
|
Where are squamous cell carcinomas often found?
|
Lower lip and lower
|
|
|
Transplant patients are prone to what form of skin cancer?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What is an ill-defined erythematous papule with a rough, scaly surface?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What is the most common type of melanoma?
|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma
|
|
|
What is a junctional nevus?
|
Proliferation of slightly altered melanocytes within the epidermis
|
|
|
What is a compound nevus?
|
Migration of slightly altered, proliferating melanocytes to the dermis
|
|
|
What is an intradermal nevus?
|
Loss of nevus cells in the epidermis, all are in the dermis
|
|
|
Describe a superficial spreading melanoma? On what skin does it occur?
|
Mixture of brown/tan, pink/white, irreguar borders, and biphasic growth occurring on intermittently sun damaged skin in the 4th to 5th decade
|
|
|
What is a lentigo maligna melanoma?
|
Dark, irregular ink spot arising on chronically sun damaged skin such as the head and neck with a very long radial growth phase
|
|
|
What is a nodular melanoma? What sort of skin does it occur on?
|
Aggressive dark nodule with monophasic growth, lacking a radial phase, on sun-exposed and non-exposed areas
|
|
|
What is an acral lentiginous melanoma?
|
Dark macule on non-sun-exposed skin common in non-white skin toned individuals
|
|
|
What are ephelides?
|
Freckles
|
|
|
What is a solar lentigo?
|
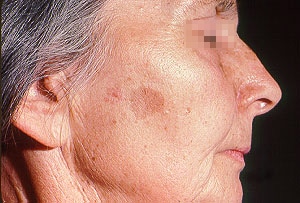
Liver spots, tan macues that develop due to sun exposure that are benign
|
|
|
What is the best predictor of prognosis with melanomas? From where is it measured?
|
Vertical tumor thickness measured from the stratum granulosum
|
|
|
Nail clubbing is a sign of what clinical syndrome?
|
Hypoxia
|
|
|
What is koilonychia? What is it a sign of?
|
Spoon nails
Sign of Fe deficiency |
|
|
What is the worrisome diameter for melanomas?
|
<u>></u>6mm
|
|
|
What are Terry's Nails? What are they a sign of?
|
Proximal 2/3 white nails
Sign of cirrhosis |
|
|
What are Lindsay's Nails? What are they a sign of?
|
Distal white half-and-half nails
Sign of renal failure |
|
|
What are Muehrcke's lines? What is it a sign of?
|
Paired, transverse, narrow white bands parallel to the lunula
Hypoalbuminemia |
|
|
What are blue nails a sign of?
|
Wilson's disease
|
|
|
What are proximal splinter hemorrhages a sign of?
|
Endocarditis
|
|
|
How many hairs are there on the human head?
|
100,000
|
|
|
What is the growth rate of nails?
|
.1mm/day
1mm/10days 3mm/month |
|
|
What does overactivation of Wnt cause? Inhibition?
|
Overactivation: tumor formation
Inhibition: hairloss and small hair follicles |
|
|
What occurs when BMP is on? When BMP is off?
|
On: Telogen, hair regeneration, tumor formation
Off: Anagen |
|
|
What are the phases of hair growth?
|
Anagen: growth (2-8y, 80-90%)
Catagen: destruction (2-3w, 1-3%) Telogen: resting (3mo, 10-15%) |
|
|
What is patchy hair loss with exclamation point hairs?
|
Alopecia areata
|
|
|
What is typical male-pattern baldness?
|
Androgenic alopecia
|
|
|
What is a psychiatric condition of pulling hairs out?
|
Trichotillomania
|
|
|
What is diffuse shedding often due to systemic insult or injury?
|
Telogen effluvium
|
|
|
What is generalized and complete hair loss affecting 90% of scalp hair? What is it caused by?
|
Anagen effluvium
Caused by chemotherapy |
|
|
What is moth-eaten hair?
|
Syphilitic alopecia
|
|
|
What is hair loss due to hair braiding?
|
Traction alopecia
|
|
|
What is cicatricial alopecia with tufted hair and follicular based pustules with erythema and scaling in which S. aureus is often cultured?
|
Folliculitis decalvans
|
|
|
What is chronic suppurative nodules which undermine to form communicating sinuses often affecting adult black males and causing scarring alopecia?
|
Dissecting cellulitis
|
|
|
What is follicular papules/pustules which progress to firm nodules/plaques often on the occipital scalp of black males?
|
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
|
|
|
What is PASTE (plugging, atrophy, scale/sclerosus, telangiectasia, and erythema) on the scalp?
|
Discoid Lupus Erythematous
|
|
|
What is polygonal patches of alopecia with pinpoint hyperkeratotic follicular papules commonly affecting women of 30-70 years of age?
|
Lichen Planopilaris
|
|
|
What is a large, boggy, erythematous plaque with papules, pustules, and crust found in the scalp? What is the causative agent?
|
Kerion
Trichophyton mentagrophtes |
|
|
What hair disease is present when the hairs have intersections of splintery hair?
|
Trichorrhexis nodosa
|
|
|
What hair disease is present when the hairs have intersections of a hair shaft into another?
|
Trichorrhexis invaginata
|
|
|
What is twisted hair?
|
Pili torti
|
|
|
What is beaded hair? How does it appear on the scalp?
|
Monilethrix
Hair remains short |
|
|
What is uncombable hair syndrome?
|
Pili trianguli et canaliculi
|
|
|
Geometric pitting in nails is a sign of what hair syndrome?
|
Alopecia areata
|
|
|
Longitudinal, subungual, red and/or white streaks are associated with what disease?
|
Darier's disease
|
|
|
Dorsal pterygium, anonychia, and thinning, fragility, and ridging of the nails are associated with what disease?
|
Lichen planus
|
|
|
What are the components of sebum?
|
triglycerides, squalene, cholesterol and esters
|
|
|
What sort of secretions do sebaceous cells perform?
|
Holocrine
|
|
|
What are the three mechanisms of pathogenesis of acne vulgaris?
|
Sebum overproduction - estrogen treatment
Abnormal differentiation of follicular epithelium (accutane/isotretinoin/vitamin A derivative) Bacterial infection by P. acnes - abx (tetracycline) |
|
|
How do retinoids exert their effect on target cells?
|
Retinoids are lipid soluble and therefore cause nuclear signaling
|
|
|
What are crusty, greasy lesions in oily areas of the skin that cause dandruff?
|
Seborrheic dermatitis
|
|
|
What is a non-pruritic, scaly, well-demarcated rash on extensural surfaces? Increased risk of what morbidities is this condition associated with?
|
Psoriasis
Arthritis and increased risk of heart disease |
|
|
Oil-spots are the single greatest predictor of what skin disease?
|
Psoriasis
|
|
|
What are the three pathogenetic mechanisms (genetic, cellular, and immunological) of psoriasis?
|
Genetic disposition (HLA-B)
Hyperproliferation of keratinocytes Sustained Th1 immune response |
|
|
What sort of T cell response is induced in psoriasis?
|
Th1
|
|
|
What are linear lesions caused by psoriasis and trauma?
|
Koebnerization
|
|
|
What is purple, polygonal, papular, plaque, pruritic, and related to psorisis?
|
Lichen planus
|
|
|
When eczema is chronically scratched, it becomes what?
|
Lichen simplex chronicus
|
|
|
What is lichen simplex chronicus?
|
Chronically scratched eczema
|
|
|
T cells express which adhesion molecules to bind to which adhesion molecules on APCs?
|
LFA-1 and CD2 to bind to ICAM-1 and LFA-3, respectively
|
|
|
What surface marker targets T cells to the skin?
|
CD45RO
|
|
|
What is the prevalence of psoriasis?
|
2%
|
|
|
How many new cases of psoriasis are there per year?
|
150,000
|
|
|
Family history is positive in what percentage of psoriasis cases?
|
30-50%
|
|
|
Which form of psoriasis is related to strep throat?
|
Guttate psoriasis
|
|
|
Keratinocyte cell cycles in psoriasis exhibit what differences from normal keratinocytes?
|
Greatly reduced cell cycle
Doubled proliferative cell population |
|
|
How many more keratinocytes are produced per day in psoriasis than in normal individuals?
|
30
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Efalizumab?
|
MAB against LFA-1 on T-cells which inhibits binding of T-cells to APC ICAM-1
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Alefacept?
|
Fusion protein (LFA-3:IgG Fc)bocks CD2 on T cells, activating NK cells to kill this population
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Infliximab?
|
MAB to TNF-a neutralizes free and bound TNF-a
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Adalimumab?
|
MAB to TNF-a neutralizes free and bound TNF-a
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Etanercept?
|
MAB to TNF-a neutralizes only free TNF-a
|
|
|
From which embryonic layer are keratinocytes derived?
|
Ectoderm
|
|
|
From which embryonic layer are Langerhans cells derived from?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
From which embryonic layer are Merckel cells and Melanocytes derived from?
|
Neural Crest
|
|
|
In which layer is keratohyalin present?
|
Stratum granulosum
|
|
|
In which layer is eleidin present?
|
Stratum lucidum
|
|
|
In which layer are membrane-coating granules known as lamellar bodies found?
|
Stratum spinosum
|
|
|
In which layer is filaggrin found?
|
Stratum granulosum
|
|
|
In which layer is the glycolipid coating that serves as the water barrier for the epidermis formed?
|
Stratum granulosum
|
|
|
What is the cell surface marker associated with Langerhans cells?
|
CD1a
|
|
|
What is the cause of Bullous Pemphigoid? In which BMZ layer does it occur?
|
IgG against BPAG-1/BP-230 or BPAG-2/BP-180/Collagen XVII in the plasma membrane layer
|
|
|
What is the cause of EB Simplex? In which BMZ layer does it occur?
|
Gene defects in Keratin 5 or 14 or Plectin in the plasma membrane layer
|
|
|
What is the cause of Junctional EB? In which BMZ layer does it occur?
|
Gene defects in Integrin or Laminin 5 in the lamina lucida
|
|
|
Where is nidogen found?
|
Lamina lucida
|
|
|
What is the cause of Cicatricial Pemphigoid? In which BMZ layer does it occur?
|
IgG against Laminin 5 IgG in the lamina lucida
|
|
|
Where is heparan sulfate found?
|
Lamina densa
|
|
|
What is the cause of Dystrophic EB? In which BMZ layer does it occur?
|
Gene defect in laminin VII in the sublamina densa
|
|
|
What is the cause of EBA? In which BMZ layer does it occur?
|
IgG against Collagen VII in the sublamina densa
|
|
|
In which layer is fibrillin found?
|
Sublamina densa
|
|
|
In which layer is linkin found?
|
Sublamina densa
|
|
|
What is the cause of Cicatricial Pemphigoid? In which BMZ layer does it occur?
|
IgG against Laminin 5 in the lamina lucida
|
|
|
What is the cause of Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis?
|
IgA against Collagen VII in the sublamina densa
|
|
|
What is the cause of Dermatitis Herpetiformis?
|
IgA against transglutaminase in the lamina lucida
|
|
|
What is the cause of Pemphigus Vulgaris? Where is it found?
|
IgG against desmoglein-III in the deep epidermis, often found in the mouth
|
|
|
What is the cause of Pemphigus Foliaceus? Where is it found?
|
IgG against desmoglein-I in the superficial epidermis, not found in the mouth.
|
|
|
In which layer are Meissner's corpuscles found? What is their purpose?
|
Dermal papillary layer
Fine-touch receptors |
|
|
In what layer are Paccinian Corpuscles found? What is their purpose?
|
Dermal reticular layer
Pressure receptors |
|
|
In what layer are Krause end-bulbs found? What is their purpose?
|
Dermal reticular layer
Cold and Pressure receptors |
|
|
What results from increased collagen formation without an accompanying increase in fibroblasts?
|
Keloids
|
|
|
A Th1 response is mediated by what cytokines? Which disease is it associated with?
|
TNF-b, IFN-g, IL-2
Psoriasis |
|
|
A Th2 response is mediated by what cytokines? Which disease is it associated with?
|
IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10 Atopic Dermatitis
|
|
|
What does IL-5 do?
|
Stimulate eosinophil production
|
|
|
What form of IgE receptors do eosinophils have? Is it strong or weak-affinity?
|
FceRII
Weak |
|
|
What form of IgE receptors do basophils have? Is it srong or weak-affinity?
|
FceRI
Strong |
|
|
What form of IgE receptors do mast cells have? Is it strong or weak affinity?
|
FceRI
Strong |
|
|
What is the triad of atopy?
|
Allergic rhinits (hay fever)
Atopic dermatitis Atopic asthma |
|
|
Where does positive selection of T cells occur?
|
Cortex
|
|
|
Where does negative selection of T cells occur?
|
Medulla
|
|
|
Which immunoglobulin is the most potent activator of the classical complement pathway?
|
IgM
|
|
|
Which immunoglobulin is the most potent activator of the alternative complement pathway?
|
IgA
|
|
|
Which IgG immunoglobulins can activate the classical complement pathway?
|
IgG1, IgG3
|
|
|
Which immunoglobulins are often associated with autoimmunity?
|
IgG4
|
|
|
Which immunoglobulin is responsible for immediate allergic and anaphylactic reactions?
|
IgE
|
|
|
Which UV light suppresses the immune system?
|
UVB
|
|
|
What type of hypersensitivity reaction is Atopic Dermatitis/Eczema?
|
Type I IgE mediated hypersensitivity
|
|
|
What type of hypersensitivity reaction is Allergic contact dermatitis?
|
Type IV Memory T Cell mediated delayed type hypersensitivity
|
|
|
What histological spongiosis associated with?
|
Eczema/Atopic Dermatitis
|
|
|
Where does Atopic Dermatitis present during the infantile phase? When is this phase?
|
0-2 years
Extensor surfaces |
|
|
Where does atopic dermatitis present during the childhood phase? When is this phase?
|
2-12 years
Flexor regions |
|
|
Where does atopic dermatitis present during the adult phase? When is this phase?
|
12+ years
Lichenified eczema in periorbital region and upper body |
|
|
Eosinophilia and IgE overproduction are associated with what skin condition?
|
Atopic dermatitis
|
|
|
What gene mutation is associated with atopic dermatitis?
|
Filaggrin
|
|
|
Which skin condition leads to a decrease in anti-microbial peptides? What organism is often found?
|
Atopic dermatitis
Often colonized by S. aureus |
|
|
Which Th cell response is humoral?
|
Th2
|
|
|
Which Th cell response is cell-mediated?
|
Th1
|

