![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sebaceous Glands |
Saclike structures create sebum which lubricates skin and hair and prevents drying |
|
|
|
Papule |
Surface lesions,nodule firm raise area |
Example pimple |
|
|
Impetrgo |
An acute contagious staphylococcal infection resulting in blister like lesions filled with puss Treat with antibiotic. |
|
|
|
Dermis |
True skin, deepest layer, made up of elastic tissue, Rich blood supply and nerve cells |
|
|
|
Macule |
Surface lesions, spot that is neither raised nor depressed |
Example measles or freckles |
|
|
Subcutaneous layer |
Hypodermis or superficial fascia Connects skin to deep fascia muscles Consists of areolar connective tissue and various amounts of adipos tissue |
|
|
|
Meibomian glands |
Modified sebaceous glands Associated with eyelashes and produce secretions that lubricate the eyes |
|
|
|
Eczema |
Atopic dermatitis |
|
|
|
Modifed sweat glands |
Ceruininous glands- produce cerumen (ear wax) in ear canal Ciliary Glands-Glands ay the edge of the eye lids Mammary glands-produce milk |
|
|
|
Superficial partial thickness |
Involves epidermis and portions of dermis Tissue is red and blissteted,painful |
Ex sunburn or scalding |
|
|
Dermal papillae |
Seen on sur r ace of thick skin (feet and hands) Tips of fijgers and toes Portions of dermis extending upwards into epidermis ,all8wing blood vessels to getbcloser to the superficial cells |
|
|
|
Exfoliation |
Loss of surface cell Helps prevent infection |
|
|
|
Melanin |
Protects skin from uv rays Substance that colors "tans" skin Produced by melanocytes- irregular patches are freckles Located in the deepest layer of the skin |
|
|
|
Sudoriferous glands |
Sweat glands Coiled tubelike structures located in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue Main function is to cool the body |
|
|
|
Sebum |
Oily secretions that prevents hair and skin from drying Made in sebaceous glands |
|
|
|
Melanocytes |
Add pigment to developing hair composed mainly of keratin |
|
|
|
Arrector pili |
Muscles contract raising the hair forming "goosebumps " or "chicken skin" Form with chills or frightened |
|
|
|
Nail structure |
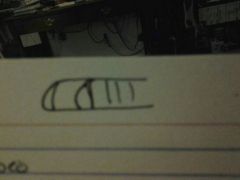
Nail plate Nail bed Lunula Cuticle Nail root Growth region and nail matrix |
|
|
|
Eccrine glands |
Typeof sweat glands located throughout the body Opens via pores |
|
|
|
Fissure |
Deeper lession Crack in the skin |
Example Athletes foot |
|
|
Erythematous |
Reddened skin |
|
|
|
Cyanosis |
Bluish discoloration due to oxygen levels |
|
|
|
Apocrine glands |
Mainly located in groin and axille (armpit) Not avtive until puberty Released through hair fallicles BO when sexuually or emotionally stimulated |
|
|
|
Jaundice |
Yellowish discoloration caused by excessive amounts of bile,pigment, and bilirubin in the blood |
|
|
|
Pruritus |
Medical term for itching |
|
|
|
Superficial burn |
First degree burn Involves only the epidermis Skin red and dry |
Example Sun burn |
|
|
Vernix caseosa |
Cream cheese like substance that covers new born babies Sebaceous glands preoduced |
Put it on a bagel |
|
|
Vesicle |
Surface lession Bulla Blister or small sac filled with fluids |
Example shingles or chicken pox |
|
|
Pustule |
Surface lesions Vesicle filled with pus |
|
|
|
Deep partial thickness |
Second degree burn Involves epidermis and dermis Tissue may blister, weeping surface or dry sweat glands damaged Less painful because of nerve damage |
|
|
|
Laceration |
Deeper lesion Rough jagged wound made by tearing the skin |
|
|
|
Excoriation |
Deeper lesions Scratch into the skin |
|
|
|
Full thickness |
Third degree burns Involves full skin and subcutaneous tissue Tissue dry, broken, pale, charred May require skin grafts or amputation |
|
|
|
Psoriasis |
Chronic overgrowth of epidermis Red flat areas covered with silver scales |
|
|
|
Herpes Zoster |
Common cold sores |
|
|
|
Ulcer |
Deeper lesion A sore associated with disintegration and death of tissue |
|
|
|
Epidermis |
Outer most layer Divided into 4/5 layers Top layer stratum corneum Bottom layer stratum basale All epithelial cells No blood cells |
|
|
|
Stratum corneum |
Top layer of epidermis |
|
|
|
Stratum basale |
Bottom layer of epidermis |
|

