![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 layers that skin consists of?
|
Epidermis
Dermis Hypodermis (subcutis) |
|
|
Where do each of the skin layers originate from?
|
Epidermis - ectoderm
Dermis and hypodermis - mesoderm |
|
|
What are 10 functions of skin?
|
Enclosing barrier - for internal organs
Water and nutrient barrier Environmental barrier (chemical, microbial and physical) Provides shape and form Produces keratinised structures Produces sebum - antimicrobial Camouflage Temperature regulation Sensory perception Vitamin D |
|
|
Which type of glands are found on the digital pads of carnivores?
|
Merocrine
(apocrine found all over body) |
|
|
What are the 3 types of hair?
|
Guard hair
Wool hair - soft undercoat, thin, shorter, more numerous than guard hairs, lack medulla Tactile hair - thicker, protrude beyond guard hairs, form whiskers |
|
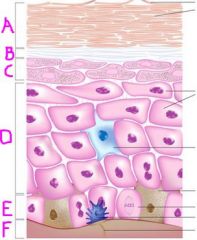
Name labels A to F
|
A- stratum corneum
B- stratum lucidum C- stratum granulosum D- stratum spinosum E- stratum basale F- dermis |
|
|
Describe the stratum corneum
|
Made up of dead keratinocytes, continually replaced, cells surrounded by lipids in interC space. Contains keratin fibres in cells, keratin lies in keratohyalin
|
|
|
Describe the stratum granulosum
|
Cells have flattened, they produce keratohyalin, contain keratohyalin granules
|
|
|
Describe the stratum spinosum
|
Enlarged, keratin fibres produced, lipid secreted into intercellular space.
|
|
|
Describe the stratum basale
|
Single layer of cells, contains keratinocytes and melanocytes
|
|
|
What is the structure at the end of a hair follicle called?
|
Papilla - connective tissue and capillary loop
|
|
|
What is a hair made up of?
|
Medulla, cortex and cuticle
|
|
|
What surrounds the hair?
|
Internal and external root sheath
|
|
|
What happens in the 3 stages of hair growth?
|
Anagen - hair produced by mitosis in hair bulb, cells undergo keratinisation
Catagen - hair bulb is constricted, CT sheath thickens and pushes club hair externally Telogen - dermal papilla separates, a secondary hair germ forms |
|
|
What is the function of a Merkel cell?
|
Touch receptor
|
|
|
What are Langerhans cells?
|
Dendritic cells, antigen-presenting cells, prominant in s.spinosum
|
|
|
What are functions of hair?
|
Camouflage
Warmth Communication to other animals Protection (hedgehog) Detection of dirt (eyelashes) |

