![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Axial Skeleton
-Skull |
1. cranium
2. facial bones 3. mandible -derived from gill arches 4. hyoid bone - derived from gill arches |
|
|
Axial Skeleton
-Vertebral Column |
1. Vertebra(e)
2. Intervertebral discs 3. intervertebral foramina - holes for spinal nerves that form once discs are together |
|
|
-Types of vertebrae
|
1. cervical
2. thoracic - articulate with ribs 3. lumbar - lower back 4. sacral - fuse to form sacrum, articulates with pelvis and ilium 5. coccygeal - fuse together to form coccyx |
|
|
Axial Skeleton
-Rib Cage -Sternum |
a. Ribs
b. Costal cartilage - hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
-Pectoral Region |
-Pectoral Girdle
* Clavicle * scapula -Pectoral Appendage * arm * hand |
|
|
Appendicular skeleton
- Pelvic Region |
a. Pelvic girdle - anchors leg & foot
1. left & right os coxa make up pelvic girdle * Ilium * Ischium - art. w/ ischial tuberosity * pubis |
|
|
Axial Skeleton
-Occipital bone features |
* occipital condyles - up and down and tilting head
* foramen magnum - spinal cord |
|
|
Vetebral column curvatures
Normal -Primary |
are convex
|
|
|
Vertebral Column Curvatures
Normal Secondary |
are concave
|
|
|
Vertebral Curvatures
Abnormal -Kyphosis |
excess thoracic curvature - hunchback
|
|
|
Vertebral curvatures
Abnormal -Lordosis |
excessive lumbar curvature - sway back
|
|
|
Vertebral curvatures
Abnormal Scoliosis |
lateral curvature
|
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral Region -Pectoral Girdle |
1. Clavicle-
* sternal end art. w/ manubrium of sternum * acromialend art. w/ acromium of scapula 2. Scapula * acromial proces art. w/ acromial end of clavicle * glenoid fossa art. w/ head of humerus |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral region -Pectoral appendage |
1. Humerus
* coronoid fossa - anterior * olecranon fossa - posterior |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral appendage -Ulna |
-on the side of the pinky
* coronoid process - anterior * olecranon process - posterior |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral appendage -Radius |
Radiates around ulna on the side of the thumb
|
|
|
Pelvic appendage
-Femur |
connects at acetabulum of os coxa
|
|
|
Pelvic Appendages
|
1. tibia - medial malleoulus, bump at ankle
2. fibula - lateral (attached to tibia at both ends) 3. tarsals - ankle bones * calcaneus - heel of foot * talus - art. with tibia & fibula 4. metatarsals 5. phalanges |
|
|
Types of bone
Shapes and size - LONG |
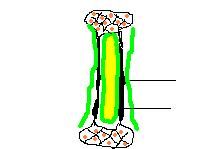
* diaphysis - shaft
* medullary cavity - filled with yellow bone marrow(adipose) * epiphysis (end) * endosteum * periosteum - dense irregular conn tiss. * compact bone * spongy (cancellous) bone with red bone marrow and trabeculae |
|
|
Types of bone
-Short |
include tarsals and carpals
|
|
|
Types of bone
- Flat |
* Tables of compact bone
* Diploe - type of spongy bone * include ribs and head bones |
|
|
Types of bone
-Irregular |
* vertebrae, some facial - same look as flat
|
|
|
Types of bone
|
* Osscles - tiny irregular bone such as auditary bone
* Sesamoid - bone in tendons ex. knee cap |
|
|
Functions of Skeletal System
|
1. Protection
2. Support 3. Lever for movement 4. hemopoiesis - RBM of spongybone, mostly erythropoieses 5. Mineral storage - calcium phosphorus |
|
|
Functions of Skeletal System
Hormones involved |
* Parathormone (parathyroid hormone) in thyroid - stimulates osteoclast to breakdown bone (osteoblasts make bone)
* Calcitonin - inhibits osteoclast (decreases Ca absorbtion and lowers blood Ca) * when osteoclast breakdown bone, it increases Ca reabsorbtion in blood and high blood Ca |
|
|
Bone Tissue
Cells |
* Osterblast - synthesize matrix
* osteocutes - sit in lacuna * osteoclast - breakdown bone |
|
|
Bone Tissue
Matrix |
Made up of:
* 2/3 organic salts - especially Ca salts * 1/3 organic collagen |
|
|
Ossification
- Intramenbranous |
* Flat bones of the skull
* mesenchyme - undifferentiated conn tissue will start making osteoblasts * osteoblasts - start making bone matrix as tuberculie |
|
|
Ossification
- Intracartilagionous or Endochondral |
* for most bones of the body
* hyaline cartilage * Primary ossification center - where bone 1st starts to form * epiphysis * epiphyseal discs - bands of cartilage, growth in this region is stimulated by growth hormone * diaphysis * secondary ossification center * epiphyseal lines - where epiphysis met diaphysis, no cartilage |
|
|
Ariculations
Fibrous Joints |
* dense conn. tissue btw the bones
* interms of movement, most are synarthroses(immovable) a. sysnostosis - sutures of the skull, as bones matures you loose most conn tissue in btw b. syndesmosis - held together by ligament, ex btw ulna & radius |
|
|
Articulations
Fibrous joints |
* Gomphosis - bolt shape
* the joint btw the root of the tooth and maxilla or mandible * periodontal membrane or ligament around tooth |
|
|
Articulations
Cartilaginous Joints |
* most are amphiarthroses (semi-movable)
A. synchondrosis - hyaline cartilage, ex. ribs to sternum B. symphysis - fibrocartilage, ex. centrum of vert. to other centrum, pubis to pubis |
|
|
Articulations
Synovial Joints |
* freely movable
* have synovial fluid that provides lubrication for movement |
|
|
Synovial Joints (diarthroses)
-Angular Movement |
a. flexion - to decrease the angle btw two bones
b. extension - to increase angle btw 2 bones c. abduction - move a body part away from midline d. adduction - moving toward midline of body |
|
|
Synovial Joints
- Circular movements |
a. circumduction - to discribe a circle with the distal end of an extremity
b. rotation - to twist on center axis * supination - lateral thumbs out * pronation - medial thumbs in |

