![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
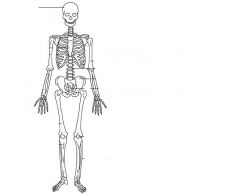
What bone is this?
|
Frontal Bone (skull)
|
|
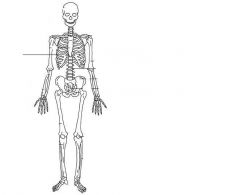
|
Ribs (thoracic cage)
|
|
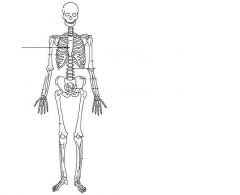
|
Sternum (Thoracic cage)
|
|
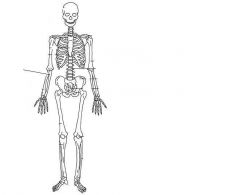
|
Ulna
|
|
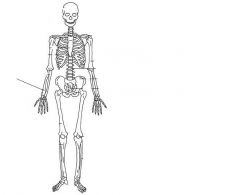
|
Radius
|
|
|
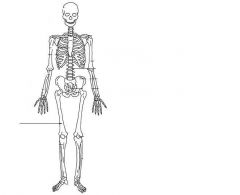
Femur
|
|
|
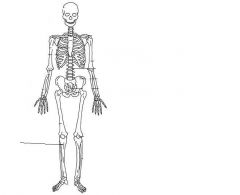
Tibia
|
|
|
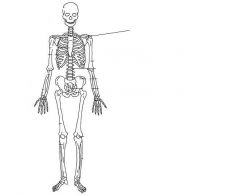
Clavicle (pectoral girdle)
|
|
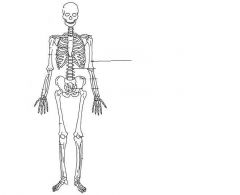
|
Humerus
|
|

|
Vertebral Column
|
|
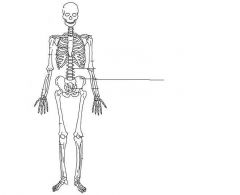
|
Hip bone (pelvis)
|
|

|
Sacrum (Pelvis)
|
|

|
Patella
|
|

|
Fibula
|
|

|
Coronal Suture
|
|

|
Parietal Bone Lambdoid Suture
|
|

|
Parietal Bone Sagittal Suture
|
|
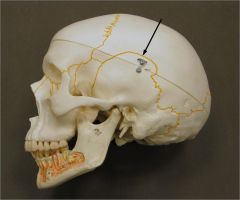
|
Parietal Bone Squamous Suture
|
|
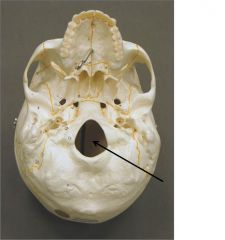
|
Occipital Bone Foramen Magnum
|
|
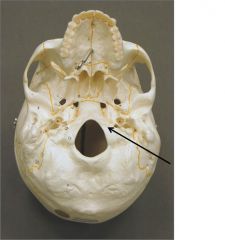
What Bone/Marking is this, And what does it Articulate with
|
Occipital Bone, Occipital Condyles, superior facets of the atlas vertebra
|
|
|
Fill. The cranial Bones are held together by joints called what?
|
Sutures
|
|
|
Fill. Cranial nerves and blood vessels pass through openings in the skull called, What?
|
Foramina
|
|
|
Fill. The bony palate is composed of two (what) Bones and the palatine processes of the (what)
|
Palatine, Maxillae
|
|
|
Fill. The pituitary gland lies in a depression of the (what) bone, a complex cranial bone with great and lesser wings.
|
Sphenoid
|
|
|
Fill. The space on the posterior surface of the scapula inferior to the scapular spine is called the (what)
|
Infraspinours Fossa
|
|
|
Fill. The medial one of the forearm is the (What)
|
Ulna
|
|
|
Fill. The cartilaginous pads between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae called the (what)
|
Intervertebral discs
|
|
|
Fill . Spinal nerves pass through gaps between adjacent vertebrae called the (what)
|
interertebral foramina
|
|
|
Fill. At the inferior end of the sternum is a small, pointed bone call the (what)
|
xiphoide process
|
|
|
Fill. The ape of your shoulder if formed by a plate-like extension of the scapular spine called the (what)
|
acromion
|
|
|
Fill. The pelvic girdle is made up of the (what)
|
Sacrum, and Hip Bones
|
|
|
Fill. The right and left hip bones are held together anteriorly by a fibrocartilage pad called the (what)
|
Pubic Symophysis
|
|
|
Fill. When you are sitting, your body weight is supported on the right and (what), which are thick, rough areas of the hip bones.
|
ischial tuberosities
|
|
|
Fill. The bony prominences on the sides of your ankles, just above the top of a dress shoe, are the lateral and medial (what)
|
Malleoli
|
|
|
Fill. The bones of the giners and toes are called the (what)
|
Phalanges
|
|
|
Has a unique structure called the dens or odontoid process
|
Axis
|
|
|
The point of your elbow where you rest it on a table
|
Olecranon
|
|
|
Bone that contains the stylomastoid formen
|
Temproal
|
|
|
Suture named for the greek Letter /l
|
Lambdoid
|
|
|
Knobs on an inferior bone of the skulls that articulate with the atlas
|
occipital condyles
|
|
|
vertebras whose superior articular processes face medially
|
lumbar
|
|
|
consists of a manubrium, gladiolus, and xiphoid process
|
sternum
|
|
|
its distal end has a capitulm and a trochlea
|
humerus
|
|
|
The thumb
|
Pollex
|
|
|
Contains the acetabulum, greater sciatic notch, and iliac crest
|
hip bone
|
|
|
The bone contains numerous air cells, contributes the upper half of the nasal septum and has pores for the passage of olfactory nerves:
A. Frontal B. Vomer C Ethmoid D Sphenoid E Nasal |
C: Ethmoid
|
|
|
All of the following can be palpated on a living person except the
A. Mastoid process B. Mental Protuberance C Suprasternal Notch D. Sella Turcica E. Olecranon |
D Sella Turcica
|
|
|
The squamous Suture surrounds
A. A squamous epithelium B. the pariteal bone C. the temporal bone D. The sphenoid bone E. the ethmoid bone |
C Temoral Bone
|
|
|
The fetal skull has a small gap where the frontal, parital, temporal, and sphenoid bones meet called the
A. anterior fontanel B posterior fontanel C. Mastoid Fontanel D.Pariefrontal Fontanel E. Sphenoid Fontanel |
E Mastoid Fontanel
|
|
|
The distal end of the femur, where is meets the tibia, is covered with
A. Spongy bone B synovial membrane C a synostosis D.The periosteum E Articular Cartilage |
E Articular Cartilage
|
|
|
The jelly-like center of an intervertebral disc is called
A.the gelatinus centralis B the nucleus Puplosus C synovial fluid D vitreous humor E Tissue Gel |
B: The nucleus
|
|
|
Costal Facets are found on
A. cervial vertebrae B the thoracic vertebrae C all vertebrae D true ribs E all ribs |
B Thoracic Vertebrae
|
|
|
The spinal column has all of the following curvatures except A
A, cervical curvature B. Thoracic curvature C. Lumbar Curvature D. Sacral Curvature E Pelvic Curvature |
D Sacral Curvature
|
|
|
9. The linea Aspear is uniqure to the
A ulna B atlas C Femur D. Fibula E Hip bone |
C Femur
|
|
|
10. The sesmoid bone embedded in the quadriceps femoris tendon is the
A. Patella B. Hamate C. Medial Malleolus D. Parital E. Navicular |
A Patella
|
|
|
What Articulates with acetabulum?
|
Femoral Head
|
|
|
What Articulates with Atlas, superior articulating facet
|
Occipital Condyles
|
|
|
What Articulates with Clavicle, Sternal End
|
Manubrium
|
|
|
What Articulates with Femoral Condyles
|
Proximal Tiba
|
|
|
What Articulates with Lateral Sacrum
|
Hip Bone
|
|
|
What Articulates with Humerus, Head
|
Glenoid Cavity, Scapula
|
|
|
What Articulates with Mandibular Condyle
|
Mandibular fossa
|
|
|
What Articulates with Inferior Manubrium
|
Gladiolus
|
|
|
What Articulates with Radius, Proximal Head
|
Capitulum, Humerus
|
|
|
What Articulates with Radial Notch, Ulna
|
Lateral edge, radial head
|
|
|
What Articulates with Rib, Tubercle
|
Transverse Process, Thoracic Vertebrae
|
|
|
What Articulates with Talus (distal)
|
Navicular
|
|
|
What Articulates with Talus (superior)
|
Distal Tibia
|
|
|
What Articulates with Trochlear notch, Ulna
|
Trochlea, Humerus
|
|
|
What Articulates with Vomer (superior)
|
Perpendicular plate, ethmoid bone
|
|
|
Acetabulum
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Hip Bone
|
|
|
Acromion
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Femur
|
|
|
Anterior Superior iliac Spine
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Hip Bone
|
|
|
Axilliary border
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Scapula
|
|
|
capitulum
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Humerus
|
|
|
Coracoid Process
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Scapula
|
|
|
Coronoid Process
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Ulna
|
|
|
Glenoid Cavity
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Scapula
|
|
|
Gluetal Lines
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
C Hip Bone
|
|
|
Greater Trochanter
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
Femur
|
|
|
Greater Tubercle
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
A Humerus
|
|
|
Intercondylar Notch
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
B Femur
|
|
|
Intertrochanteric crest
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
B Femur
|
|
|
intertubercular Sulcus
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
A Humerus
|
|
|
Inferior public Ramus
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
C Hip Bone
|
|
|
Infraspinous fossa
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
E Scapula
|
|
|
Linea Aspera
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
B Femur
|
|
|
Paterllar Surface
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
B Femur
|
|
|
Obturator foramen
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
C Hip Bone
|
|
|
Olecranon
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
F Ulna
|
|
|
Olecranon fossa
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
A Humerus
|
|
|
Sciatic Notches
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
C Hip Bone
|
|
|
Trochlea
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
A Humerus
|
|
|
Trochlear notch
A. Humerous B. Femur C. Hip Bone D. Radius E. Scapula F. Ulna |
F Ulna
|

