![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Vertebral Anomalies - Cervical Rib |
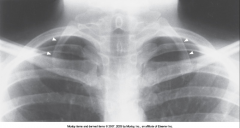
Has characteristics of vertebrae above and below
Can cause lack of blood flow to arms, numbness, and tingling - pressing on nerve/artery
Treated if symptoms |
|
|
Vertebral Anomalies - Transitional Vertebra |
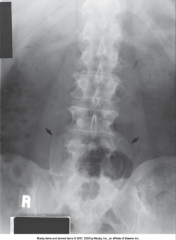
Has characteristics of vertebrae above and below
Can cause lack of blood flow to arms, numbness, and tingling
Treated if symptoms
|
|
|
Spina Bifida Occulta |
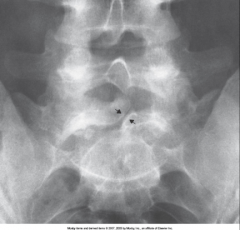
Image shows mild form in which there is a splitting of the bony neutral canal but no clinical symptoms
In this case often no treatment |
|
|
Meningocele |
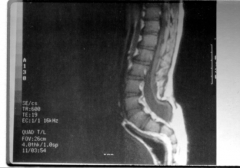
Protrusion of the meninges through the skin
*Spinal Cord not affected
Often no treatment |
|
|
Myelomeningocele |
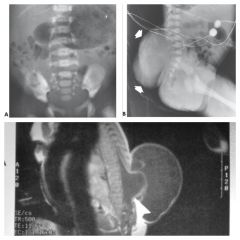
Herniation of the spinal cord & meninges through the skin
Hydrocephalus a frequent complication
Treatment: Surgery & Shunt |
|
|
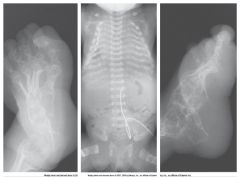
Osteopetrosis A.K.A. Marble Bone |
Rare hereditary bone dysplasia in which failure of the resporptive mechanism of calcified interferes with the normal replacement by mature bone
Results in extremely dense bones
Often Fatal
*Increase Exposure Factors* |
|
|
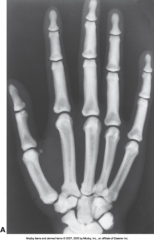
Osteogenesis Imperfecta A.K.A. Brittle Bone Disease |
Inherited generalized disorder of connective tissue characterized by multiple fractures & an unusual blue color to sclera of eye
Appears with very thin cortical density, brittle bones, multiple fractures, & various healing states
Treatment: Fracture alignment, external/internal fixators, & stem cell research
Adult pts often wheelchair bound
*Decrease exposure factors* |
|
|
Achondroplasia |
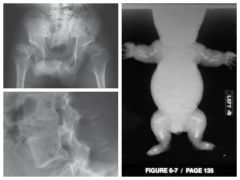
Most common form of dwarfism
Results from diminished proliferation of cartilage in growth plate - bones can't grown in length b/c of missing cartilage
Characterized by short limbs & normal trunk
Posterior scalloping of vertebral bodies
No cure - can surgically lengthen bones |
|
|
Congenital Hip Dysplasia |
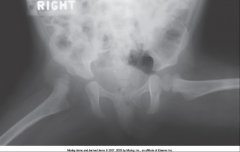
Incomplete formation of acetabulum
More common in Females
Hip may "pop" out of joint & a "click" may be felt/heard during exam with flexion & abduction
Treatment: Pelvic cast or immobilization of femoral head - must be done prior to walking |
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis - Early Stage |
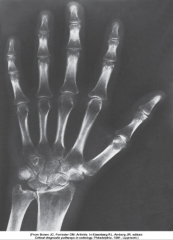
Early stage - Presents with soft tissue swelling
Mid stage - joint space narrowing
Late Stage- bone destruction
Chronic systemic disease with unknown cause - appears as nonsuppurative inflammation of synovial membrane (synovium) in hands & feet - synovium gets thickened with granulation tissue
Causes erosion of articular cartilage, boney cortex, and scarring
Treatment: aspirin, steriods, ibprofen, penicillin & surgery (last resort)
*women affect 3x more than men
|
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis - Late Stage |
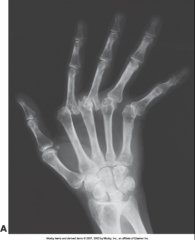
Early stage - Presents with soft tissue swelling
Mid stage - joint space narrowing
Late Stage- bone destruction
Chronic systemic disease with unknown cause - appears as nonsuppurative inflammation of synovial membrane (synovium) in hands & feet - synovium gets thickened with granulation tissue
Causes erosion of articular cartilage, boney cortex, and scarring
Treatment: aspirin, steriods, ibprofen, penicillin & surgery (last resort)
*women affect 3x more than men
|
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis - Severe bone-end erosion/subluxation |
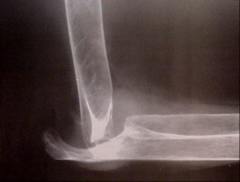
Early stage - Presents with soft tissue swelling
Mid stage - joint space narrowing
Late Stage- bone destruction
Chronic systemic disease with unknown cause - appears as nonsuppurative inflammation of synovial membrane (synovium) in hands & feet - synovium gets thickened with granulation tissue
Causes erosion of articular cartilage, boney cortex, and scarring
Treatment: aspirin, steriods, ibprofen, penicillin & surgery (last resort)
*women affect 3x more than men
|
|
|
Ankylosing Spondylitis - A.K.A. Bamboo Spine (Variation of RA) |
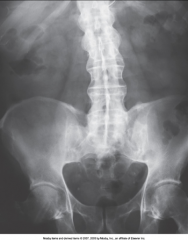
Chronic Inflammation of the spine - Narrowing of joint space and may lead to complete fibrous and bony ankylosis - ossification of paravertebral tissue & ligaments
Usually begins in SI Joints (bilateral) then progresses to lumbar region and upward
|
|
|
Reiter's Syndrome (Variation of RA) |
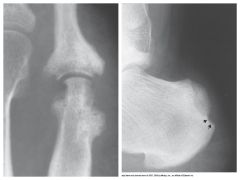
Reactive Arthritis - characterized by arthritis, urethritis, & conjunctivitis - reacts to other diseases/infections
Appears after venereal/GI infections
Seen in SI joints, calcaneus, toes
Most common in young men |
|
|
Psoriatic Arthritis (Variation of RA) |
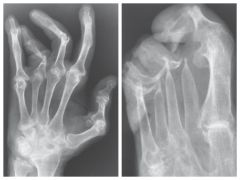
Destructive Process of peripheral joints that develops in pts with psoriasis
Involves distal IP joints of hands and feet
|
|
|
Osteoarthritis - A.K.A. Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD) |
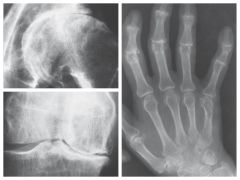
Common disorder characterized by loss of joint cartilage w/ increased bone formation
Able to visualize joint space narrowing, bone spurs, & increased density
primarily affects weight bearing bones & IP Joints
Common in aging process
Treatment: Steriods & Ibprophen
|
|
|
Degenerative Disk Disease (DDD) (Variation of DJD) |
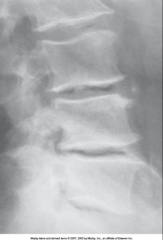
|
|
|
Bursitis |
Inflammation of the bursae - very small synovial sac - can cause "frozen joint"
Able to visualize calcified tendons on x-ray (especially above greater tuberosity of humerus)
*Best seen in ultrasound |
|
|
4 Muscles of Rotator Cuff |
Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Minor Subscapularis |
|
|
Rotator Cuff Tear |
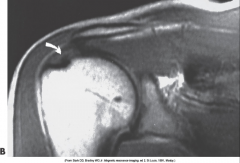
|
|
|
Meniscal Tear |
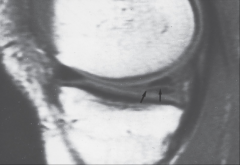
|
|
|
Bacterial Osteomyelitis |
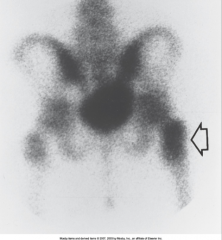
Inflammation of bone and bone marrow, reaches bone b/c spread hematogenously (through the blood) - cause bone absess (pyogenic)
Starts in medullary cavity spreads to periostinum
First signs soft tissue swelling - later ragged edge of bone
Shows in long bones high in red marrow of children and in vertebra or bone associated with decubitus ulcer in adults
Treatment: Antibiotics, amputation, placement of drain (abscess), bone grafts
Nuclear Med Scan best for early detection |
|
|
Staphylococcal Osteomyelitis (Variation of Bacterial Osteomyelitis) |
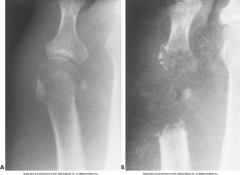
|
|
|
Chronic Osteomyelitis (Variation of Bacterial Osteomyelitis) |
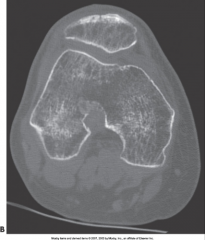
|
|
|
Bacterial Osteomyelitis (Variation of Bacterial Osteomyelitis) |
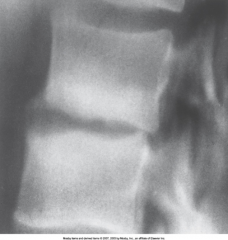
|
|
|
Tuberculous Osteomyelitis
|
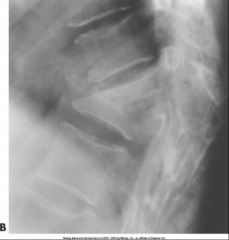
Most commonly involves the thoracic & lumbar spine
Very Rare
Appears as collapsed vertebra w/ kyphosis
Treatment: antibiotics, spinal fusion |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
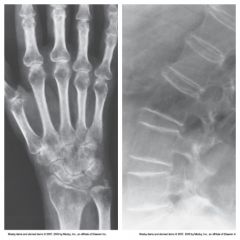
Caused by accelerated resorption of bone (bone destruction) - also caused by hormonal changes
Deficiency of Calcium in Bone - makes them more frail and easy to fx
Most common in postmenopausal females
Visualized with cortical thinning - after 50% loss
Use low kVp
Prevent with weight bearing exercise, hormonal replacement, and supplements |
|
|
Thoracic Vertebroplasty |
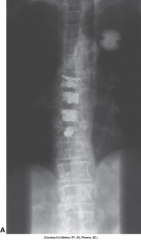
Done on 81 year old osteoportic woman to prevent vertebral collaspe |
|
|
Osteomalacia |
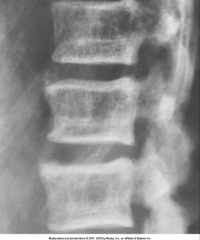
Insufficient mineralization of the adult skeleton (low calcium, phosphorus, vit. d)
Most commonly caused by poor diet or chronic renal failure
Bones become soft and easily fracture or bow
Cortical bone may appear to be indistinct, bones may bend under weight bearing, acetabulum may bend into pelvic brim
Treatment: Vit D supplements with calcium |
|
|
Rickets |
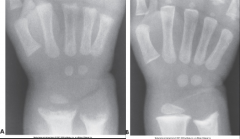
Systemic disease of infancy/children
Equivalent to Osteomalacia
Deficiency of Vit D causes defect in calcification - causes "cupping" on ligaments attached to bones
Treatment: Vit D & Calcium |
|
|
Gout |
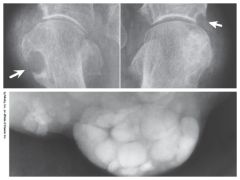
Disorder in the metabolism of purine where high levels of uric acid in blood leads to deposition of uric acid crystals in joints, cartilage, & kidneys
Pt suffers joint pain, swelling, & decreased function of joint
Can lead to arthritis & bone destruction
Treatment: Antihyperuricemic drugs - if not treated renal failure occurs |
|
|
Paget's Disease A.K.A. Osteitis Deformans |
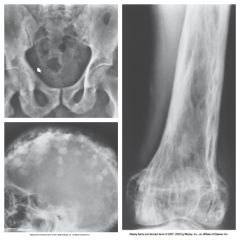
Destruction of bone, followed by reparative process, results in weakened, deformed, & thickened bony structures that fx easily. Occurs in pelvis, femur, tibia, skull, vertebrae, clavicle, & ribs
Most common in middle aged men
Mottled appearance, with irregular islands of sclerosis & thickening
Treatment: None Calcitonin reduces resorption rate - inhibits osteoclasts
|
|
|
Fibrous Dysplasia |
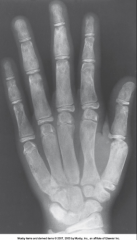
Disorder that begins during childhood - characterized by proliferation of fibrous tissue within the medullary cavity - proliferation causes loss of trabecular marks and widening of bones
Occurs primarily in long bones and fractures easily
Locally expanded and well defined medullary cavity appearance
Treatment: Curettage and Fx repair
|
|
|
Ischemic Necrosis |
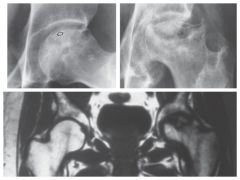
Caused by ischemia (loss of blood supply)
Most commonly appears in femoral head
Treatment: Antibiotics, Immobilization, and analgesics |
|
|
Osteochondroma |
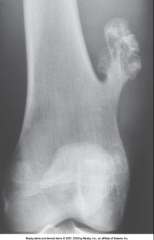
*Benign*
Exostosis occurs in the epiphyseal plate and grows laterally in long bones
Arises in childhood or in teen years - most commonly on knee, also points away from nearest joint
Treatment: Surgery, in certain circumstances |
|
|
Enchondroma |
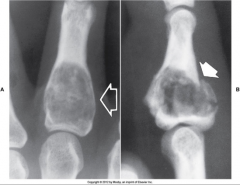
*Benign*
Very slow growing tumor that arises in the medullary canal of hands & feet
Treatment: Curettage of lesion |
|
|
Giant Cell Osteoclastoma |
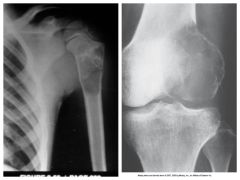
*Benign*
Metaphysis extends into subarticular cortex - does not involve joint
Treatment: Curettage & local resection |
|
|
Osteoma |
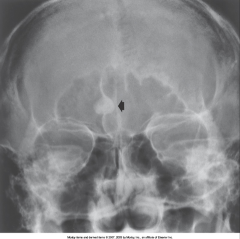
*Benign*
Most commonly occur in outer table of skull or sinuses
Very Dense - Very Lucient
Treatment: none required |
|
|
Osteoid Osteoma |
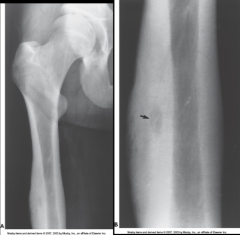
*Benign*
Usually develop in teens or young adults
Lucent - surrounded by dense cortical thickening
Most commonly found in femur, tibia, and osteoblastic cells
Treatment: Surgery |
|
|
Bone Cyst |
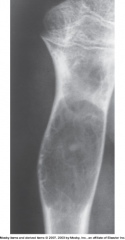
*Benign*
Fluid filled cyst that is common in femur & humerus
resembles neoplasm b/c or irregular edges - also has expanded lucent areas with sharp edges and sclerotic rim
Treatment: Surgical curettage & implant bone chips |
|
|
Bone Islands |
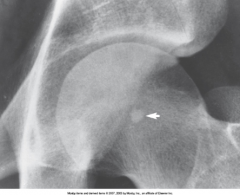
*Benign*
Solitary, sharply demarcated areas if dense compact bone that occur most commonly in pelvis and upper femur
Treatment: None required |
|
|
Osteogenic Sarcoma A.K.A. Osteosarcoma |
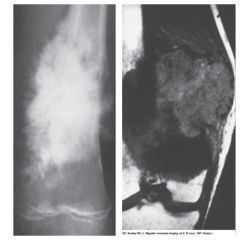
*Malignant*
Generally occurs in the end of long bone in the metaphysis
Pts 10-25 years old
2nd most common primary bone malignancy - highly malignant w/ early lung mets
"Sunburst Pattern"
Treatment: Surgery, Chemo/Rad Therapy - 30% cure rate |
|
|
Chondrosarcoma |
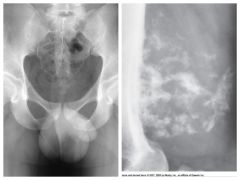
*Malignant*
Tumor of Cartilage that contains calcifications
Pts 35-60 years old
Pt may have swelling & pain
Slow growing - slow to mets
Treatment: Surgery - 50% cure rate
|
|
|
Ewing's Sarcoma |
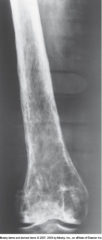
*Malignant*
Arises from bone marrow
Pts 10-20 years old
Pt has swelling, fever, and malaise
Rare
Treatment: Rad Therapy/Chemo - 30% cure rate |
|
|
Multiple Myeloma |
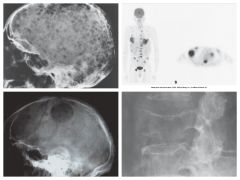
*Malignant*
Most common bone malignancy - occurs from plasma cells of bone marrow
Pts 40-70 years old
"Punched out" appearance - destructive with little rebuilding
Treatment: Rad Therapy/Chemo |
|
|
Malignant Bone Tumors |
Soft tissue swelling
Cortical bone erosion
Poorly defined margins
Nuc Med & PET for early detection
CT & MRI for precise localization |
|
|
Bone Metastasis |
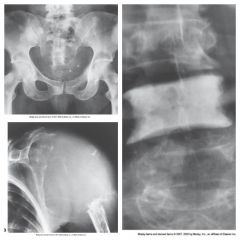
*Malignant*
Most common malignant bone tumor
Spreads
Occurs throughout entire body |
|
|
Spondylolysis |
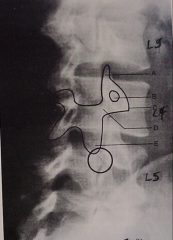
Cleft in pars articularis of vertebrae (scotty dog neck) |
|
|
Spondylolisthesis |
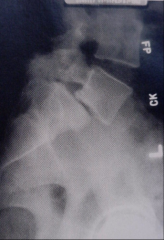
Displacement of pars articularis
Usually involves L5
Common in 5% of population |
|
|
Malunion |
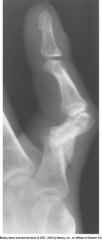
Healing of fx fragments in faulty position
Leads to impairment of normal function or a cosmetic appearance that may require surgical correction |
|
|
Nonunion |
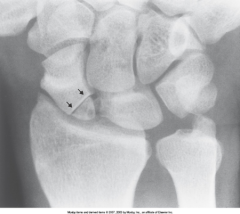
Condition in which fx healing process has completely stopped and the fragments remain ununited even with prolonged immobilization |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Produce new bone around the outer circumference from the periostenum
"New bone around" |
|
|
Osteoclast |
Enlarge the diameter of the medullary cavity by removing bone from the diaphysis wall
"Remove old bone from cavity" |
|
|
Ossification |
Bone formation |
|
|
Resorption |
Bone destruction |
|
|
Intramembranous Ossification |
Bone formation from connective tissue |
|
|
5 Basic Functions of Bone |
1) Frameword of body 2) Protect vital organs 3) Levers for joint movement 4) Red bone marrow is major site for blood cell production 5) Storage for calcium salts |

