![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The three stages of cell signaling |
reception transduction response |
|
|
Reception |
target cell's detection of a signaling molecule, from outside the cell, binding to an extracellular or intracellular receptor protein |
|
|
General term for molecule that binds the receptor |
ligand |
|
|
transduction |
step(s) that convert signal to form that can bring about cellular response |
|
|
response |
cellular activity triggered by transduction of a signal |
|
|
signal transduction pathway |
sequence of changes in a series of different molecules that transmits the signal from the receptor protein to a point or event that triggers the cellular response |
|
|
Most signal receptor proteins are found in the |
plasma membrane |
|
|
Characteristics of ligands that bind cell-surface receptor proteins |
water-soluble, hydrophilic, too large to pass through plasma membrane |
|
|
True or False: all ligands must enter the target cell to trigger a response |
False: most ligands bind to cell-surface receptors and do not enter the cell themselves. Only hydrophobic ligands can enter the cell. |
|
|
True or False: steroid hormones bind to an intracellular receptor protein |
True: steroid molecules are hydrophobic lipids that pass through the cell membrane and bind to their receptor protein in the cytoplasm, or in some cases, in the nucleus |
|
|
Transmembrane protein |
protein molecule with multiple domains that pass through the cell membrane, with extracellular and intracellular domains as well. A G protein coupled receptor would be an example. |
|
|
Three types of cell-surface receptors |
i. G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) ii. Receptor-tyrosine kinase iii. Ligand-gated ion channel |
|
|
Phosphorylation cascade |
transduction mechanism that involves series of protein kinases, each of which adds a phosphate group (phosphorylates) to the next kinase in the series, activating it |
|
|
kinase |
enzyme that phosphorylates its substrate |
|
|
phosphatase |
enzyme that removes a phosphate from its substrate |
|
|
phosphorylation |
addition of a phosphate to a substrate by a kinase enzyme |
|
|
dephosphorylation |
removal of a phosphate from a substrate by a phosphatase enzyme |
|
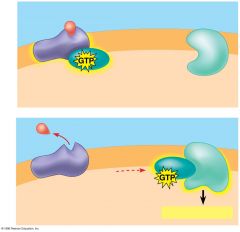
What type of receptor activity is shown? |
G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) |
|
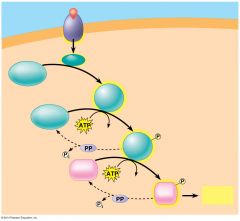
The image shows a ____________________ cascade |
phosphorylation |
|
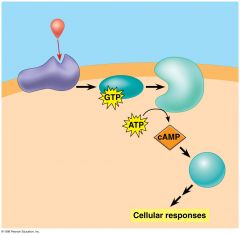
in the image shown, cAMP acts as a _____________________ _____________________ |
second messenger |
|
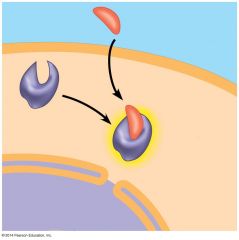
The hormone shown in the figure must be a _________________ hormone |
steroid |
|
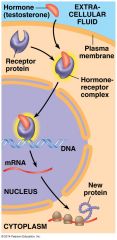
In the picture shown, the hormone/receptor complex exerts its effect by acting as a __________________ ___________________ to activate gene expression |
transcription factor |
|
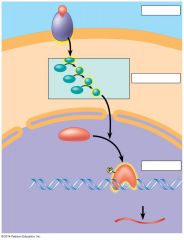
In the picture shown, the target of the phosphorylation cascade is a protein that enters the nucleus and acts as a _________________ _________________ |
transcription factor |
|
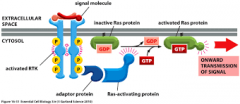
The picture shows that Ras functions as a "____" protein in signal transduction |
"G" protein |
|
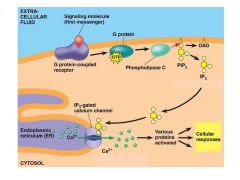
In the picture shown, IP3 and Ca2+ act as __________________ ___________________ in the signal transduction pathway |
second messengers |
|
|
Many G protein-coupled receptors are referred to as "Beta receptors" and have roles in human diseases like hypertension and cardiovascular disease. If a patient was prescribed a "Beta blocker" medication that binds to a specific G protein coupled "Beta" receptor, what would be the effect on the specific signaling pathway? |
the Beta blocker would reduce or eliminate signaling for the particular G protein-coupled receptor pathway |

