![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the 4 muscles of rotator cuff? |
1. supraspinatus (abduction, internal rotation, flexion) 2. infraspinatus (external rotation) 3. teres minor (external rotation) 4. subscapularis (internal rotation) |
|
|
What are the 3 x-ray views to order for the shoulder? |
1. AP view 2. Lateral view (Y view) 3. Axillary view |
|
|
What holds the humerus in place? |
1. mainly rotator cuff muscles 2. glenohumeral ligaments 3. deepening of the glenohumeral socket by glenoid labrum |
|
|
What are the areas that might be damaged in shoulder dislocations? |
Anterior: subscapularis, axillary vessels, brachial vessels Posterior : infraspinatus, teres minor Superior: supraspinatus, subacromial bursa, coracoacromial ligament, deltoid Inferior: axillary nerve, posterior circumflex humeral vessels, long head of triceps |
|
|
What is the mechanism of injury for anterior shoulder dislocation? What are the clinical features? What are the complications? |
MOI: fall back on backward stretching arm, arm forced into abduction, external rotation and extension clinical features: - prominent acromion - small bulge seen below clavicle - squaring of shoulder complications: - rotator cuff tear - axillary nerve injury --> regimental patch sign - axillary artery injury - fracture dislocation - subsequent adhesive capsulitis in subsequent stages - anterior shoulder instability |
|
|
What are the physical examinations to do for a patient with recurrent shoulder dislocation? |
1. Anterior apprehension sign 2. Beighton score to determine ligamentous laxity 3. O brien's tear for SLAP tear 4. Sulcus sign for inferior instability 5. Posterior drawer test for posterior instability |
|
|
What is the management of anterior dislocation? |
manipulation and reduction, with sedation 1. Stimson's technique 2. Hippocratic method 3. Spaso's method 4. Kocher's method - X-ray done pre and post reduction - sling for 2 weeks - avoid abduction and lateral rotation for 3 weeks) |
|
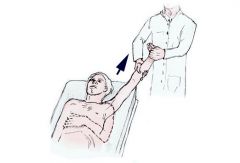
what is this method? |
Spaso's method: - traction of arm in vertical and external rotation - assistant help to push humerus into joint |
|
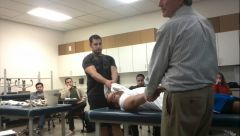
what is this method? |
Hippocrates method: - counter-traction applied to stabilize patient - slightly abduct shoulder, and pull the shoulder |
|
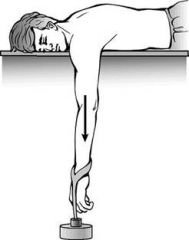
what is this method? |
Stimson's technique: - lie patient prone - let the affected shoulder hang over the side of the bed for 15-20 mins |
|
|
What are the classifications for recurrent shoulder instability? |
TUBS: traumatic, unilateral, bankart lesion AMBRII: atraumatic, multidirectional, bilateral; rehabilitation, inferior capsular shift, interval closure |
|
|
What are the clinical features of anterior shoulder instability? |
- recurrent dislocations with trivial actions
- recurrent subluxation (when throwing a ball, there is catching sensation, followed by numbness or weakness - dead arm syndrome) - sulcus sign - anterior apprehension sign - examine for ligamentous laxity (worse prognosis) |
|
|
What are the X-ray features of anterior dislocation? What are the MR arthrogram features? |
1. Hill-sachs lesion (depression in postero-supero-lateral part of the humeral head) ** best seen in AP 2. Subluxation of the humeral head towards anterior lip of glenoid MRI: Bankart lesion |
|
|
What are the treatment options for anterior instability? |
Conservative:
- Avoid deep sea diving and climbing Surgical(if frequent, painful, and affect daily life) - Bankart surgery (repair/re-attach glenoid labrum) - Putti-platt (shorten and tighten anterior capsule and muscles) - Bristow (reinforce capsule using adjacent muscles) |

