![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Gradient wind balance forces
|
Hurricanes- pgf =coriolis + centrifugal
|
|
|
|
Cyclostrophic balance forces
|
Tornadoes- pgf = centrifugal geo
|
|
|
|
Geostrophic wind balance forces
|
Pgf = coriolis
|
|
|
|
Surface wind balance forces
|
Pgf = coriolis + friction
|
|
|
|
500 mb map
|

|
|
|
|
Surface pressure map
|

|
|
|
|
Thunderstorm scale
|
Small
|
|
|
|
Tornado scale
|
Small
|
|
|
|
Tropical cyclone scale
|
Large scale
|
|
|
|
Extratropical cyclone
|
Large scale
|
|
|
|
How are thunderstorms formed?
|
•cool dry air with an environmental lapse rate similar to dry adiabatic above low level moisture air
• forced lifting |
|
|
|
What time of year do thunderstorms form?
|
Spring most common but all year round in tropics ITCZ and central US
|
|
|
|
Thunderstorm disasters
|
•Heavy rain
•hail •lightning •form tornadoes |
|
|
|
How does a thunderstorm gain energy
|
Condensation of water vapor during up drafts (cloud formation)
|
|
|
|
How are tornadoes formed
|
•horizontal vorticity bent into the vertical by updrafts
•column of spinning air is stretched (conservation of angular momentum) and wind speed increases |
|
|
|
How are tornadoes formed
|
•horizontal vorticity bent into the vertical by updrafts
•column of spinning air is stretched (conservation of angular momentum) and wind speed increases |
|
|
|
What time of year do tornadoes form
|
Spring in late afternoon
|
|
|
|
How are tornadoes formed
|
•horizontal vorticity bent into the vertical by updrafts
•column of spinning air is stretched (conservation of angular momentum) and wind speed increases |
|
|
|
What time of year do tornadoes form
|
Spring in late afternoon
|
|
|
|
Tornado disasters
|
Strong winds
|
|
|
|
How are tornadoes formed
|
•horizontal vorticity bent into the vertical by updrafts
•column of spinning air is stretched (conservation of angular momentum) and wind speed increases |
|
|
|
What time of year do tornadoes form
|
Spring in late afternoon
|
|
|
|
Tornado disasters
|
Strong winds
|
|
|
|
Swirl ratio
|
V/w = tangential wind/vertical velocity
|
|
|
|
Formation of tropical cyclone
|
•Initial conditions: Strong low-level vorticity, weak vertical wind shear, high relative humidity, warm SST, deep layer of warm water
• tropical disturbance forms over warm water (storm is powered by latent heat from condensation) Strong winds |
|
|
|
What time of year do tropical cyclones occur
|
Warm seasons when SST highest J-A-S
|
|
|
|
Disasters of tropical cyclones
|
Heavy rain, flooding, strong winds
|
|
|
|
Properties of tropical cyclones
|
No fronts, warm eye, forms over tropics, strongest winds near surface, 200-500 mi, lives about a week, weak shear environment, small horizontal T gradient, Gradient wind balance
|
|
|
|
Properties of tropical cyclones
|
No fronts, warm eye, forms over tropics, strongest winds near surface, 200-500 mi, lives about a week, weak shear environment, small horizontal T gradient, Gradient wind balance
|
|
|
|
Extratropical cyclone formation
|
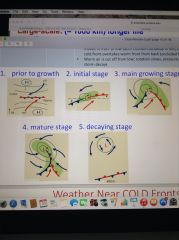
|

|
|
|
Extratropical most common location
|
Along fronts with significant vertical shear (land or ocean) outside of tropics
|
|
|
|
Extratropical disasters
|
Heavy rains, flooding cold temp, severe ones cause blizzards
|
|
|
|
Extratropical properties
|
Strong fronts, cold in eye, strongest winds above, forms outside tropics, 500-1000 mi
|
|
|
|
Extratropical properties
|
Strong fronts, cold in eye, strongest winds above, forms outside tropics, 500-1000 mi
|
|
|
|
Energy source of extratropical
|
Horizontal temp contrast
|
|
|
|
Tropical energy source
|
Energy fluxes from warm water
|
|
|
|
3 stages of thunderstorm
|
Early growth (Cumulus stage)
Mature stage Dissipating stage |

|
|
|
Storm splitting
|
Supercell formation- updrafts bend the horizontal overturning resulting from the vertical wind shear
(Cyclonic circulation survives) |
|
|
|
Separating charge in cloud
|
Hail and ice pellets collide with lighter ice crystals and because of the different surface charge characteristics, electrons prefer hail/ice pallets (-) and net positive charges are left on small ice crystals lofted up to cloud top
|
|
|
|
Blizzards need
|
An intense frontal cyclone
High surface winds Big t contrast between warm and cold air masses Copious snow on only n and NW sides of storm |
|
|
|
Tropical cyclone stages
|

|
|

