![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Set |
A clearly defined collection of elements |
|
|
Element |
A member of the set |
|
|
Sets are denoted using |
Capital letters |
|
|
Elements are denoted using |
Lowercase letters |
|
|
Prime number |
Any number greater than one whose only factors are one and itself
Examples: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29 |
|
|
Integer |
Any number without a fractional part or numbers after the decimal point |
|
|
Cardinality |
The number of elements in a set |
|
|
Subset |
A set whose elements are present in a set that has additional elements or a set with the same elements |
|
|
Proper subset |

A set whose elements are present in a larger set |
|
|
Every set is a |
subset of itself |
|
|
Universal set |
A set that contains all the possible elements under consideration |
|
|
Unit set |
A set that consists of only one element |
|
|
Null set |
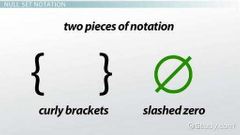
A set that contains no elements |
|
|
Complement of a set |
The elements not in that set (region when it comes to the Venn diagram) |
|
|
Disjoint Sets |
Sets that do not share any elements |
|
|
Power set |
The set of all the subsets of a particular set |
|
|
An empty set is a |
subset of every set |
|
|
Equation for the subsets of a set |
2 to the power of n
(n being the cardinality of the set) |
|
|
B' can be thought of as |
Omission/Exclusion |
|
|
(A u B)' can be thought of as |
Inversion (inverting) |
|
|
P' n Q' = |
(P u Q)' |
|
|
A u B |
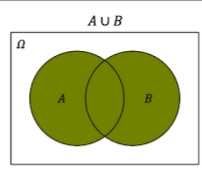
|
|
|
A n B |
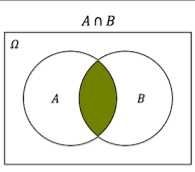
|
|
|
A' |
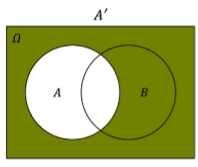
|
|
|
A n B' |
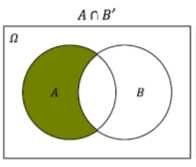
|
|
|
A' n B |
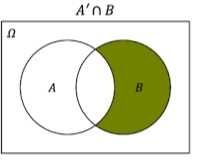
|
|
|
A u B' |
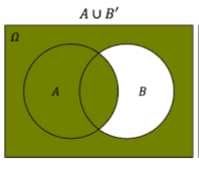
|
|
|
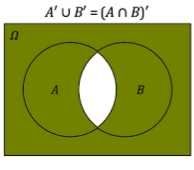
(A n B)' |
|
|
|
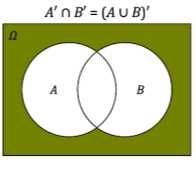
(A u B)' |
|
|
|
' is read as |
Not |
|
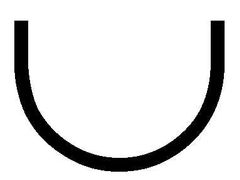
The union symbol is read as |
Or |
|
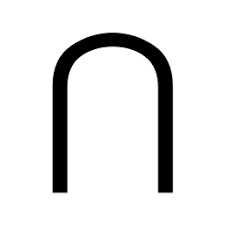
The intersection symbol is read as |
While also/and |

