![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dew Point |
the temperature to which a sample of air must be cooled for the air to be saturated
|
|
|
Humidity |
measure of how much water is in a sample of air |
|
|
Relative Humidity |
how much humidity is in the air compared to how much can be
|
|
|
Copper Cable Types |
|
|
|
CAT5 Copper Cable |
|
|
|
CAT5e |
CAT5 enchanced
|
|
|
CAT6 |
|
|
|
UTP vs STP |
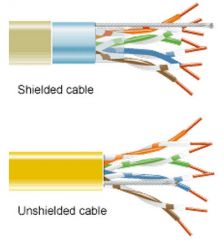
|
|
|
Fiber Cable Components |
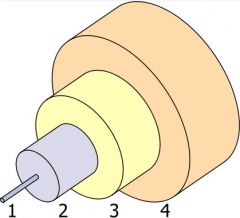
|
|
|
How fiber optic cable works |
|
|
|
Advantages to Fiber Cabling |
|
|
|
Fiber Cable Naming Convention |
ex: 62.5/125 m and 50/125 m (multi-mode) ex: 8.3/150 m (single mode)
#'s are in millionth of a meter |
|
|
Types of Fiber Cables |
|
|
|
Single Mode Fiber |
|
|
|
Multi Mode Fiber |
|
|
|
Storage Area Network (SAN) |
|
|
|
Types of Building to Building Network Connectivity |
- expensive, re-occuring costs
- one time fee, time consuming
- cover long distances
- uses lasers, highly secure, long distance |
|
|
Network Installation Best Practices |
|
|
|
Test and Verify Structured Cabling |
|
|
|
Test and Verify Fiber |
return loss / insertion loss |
|
|
Fire Sources in a DC |
- most fires originate from electrical sources
|
|
|
Fire Suppression Requirements |
|
|
|
Fire Suppression Standards |
|
|
|
Fire Suppression Standards state "" |
|
|
|
Cardio-toxicity and Allowable Exposure levels |
|
|
|
Fire Detection Systems |
|
|
|
Types of Smoke Detectors for Fire Panels |
Ionization detectors - uses radiation to analyze air sample for smoke - more sensitive than photoelectric
Photoelectric detector - uses light - deflection of light sets alarm |
|
|
Fire Suppression Systems |
|
|
|
Halon 1301 |
- fire suppression method - gas form - decommissioned method - harmful to environment |
|
|
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) |
- fire suppression method - gas - cheap - harmful to humans, not environment |
|
|
FM200 |
- fire suppression method - low pressure gas - needs to be close to room (20-40m) - harmful to environment, not humans |
|
|
Inergen |
- fire suppression method - high pressure, requires pressure values - large storage tanks - can be stored far away - not harmful to humans or environment |
|
|
Argonite |
- fire suppression method - gas system - not harmful to humans or environment |
|
|
Novec |
- fire suppression method - gas - environmentally friendly |
|
|
FE13 |
- fire suppression method - gas - can be used in rooms with higher ceilings |
|
|
Best Practices for Fire Suppression |
|
|
|
Types of Fire Extinguishers |
|
|
|
Class A Fire Extinguisher |
- involving wood, cloth, paper, plastic - uses pressurized water or water based agent |
|
|
Class B Fire Extinguisher |
- involving combustible/flamible liquids - uses CO2 or dry chemical agent |
|
|
Class C Fire Extinguisher |
- main data center concern - involving electrical equipment - uses CO2, Halon, dry chemical agent |
|
|
Class D Fire Extinguisher |
- involves combustable metals - uses dry power agent |
|
|
Class K Fire Extinguisher |
- involves cooking fats, oils - uses liquid chemical |
|
|
Safety Regulation Requirements |
|
|
|
EMS |
environmental monitoring system - only monitoring functions - low level monitoring - in-expensive solution |
|
|
BMS |
building management system - monitoring and controlling functions - high level monitoring - expensive solution |
|
|
Types of Water Detection |
pads - cheap - only cover a small area
cable - placed under raised floor - covers large loop |
|
|
Current |
flow of electric charge |
|
|
Voltage |
force of electrical charge flow |
|
|
Water Hose Electricity Analogy |
water flowing through hose = electrons in a wire
amount of water going through hose = current
pressure used to push the water = voltage |
|
|
Types of Electricity |
alternating current (AC)
direct current (DC) |
|
|
Alternating Current (AC) |
- completes a cycle 60x second - 1 cycle = 1 hertz - hertz = Hz |
|
|
Static Transfer Switch vs Automatic Transfer Switch |
* both utilize "break before make" principle STS - semiconductor technology - faster switching (4 milliseconds) - complex, small MTBF - large switching capacity
ATS - electromechanical technology - slow switching (8-16 milliseconds) - simple design, large MTBF - small switching capacity
|
|
|
Power Cables vs Busbar |
Cabling - less flexible - fixed power rating - inexpensive
Busbar - flexible in phase or power rating - expensive |
|
|
Types of Cable Distribution |
Trunking - PDU to racks Trays - used in switch rooms Ladders - run cables between floors Baskets - used for networking |
|
|
Grounding |
*ground resistance should be less than 1 ohm not to exceed 5 ohm |
|
|
Isolation Transformers |
- a way to rebond a device closer to the power load - based o a Delta-Wye configuration - Delta is primary, Wye is secondary - Delta and Wye separated by a magnet - output can only travel max 75ft |

