![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
152 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hepatitis =
|
'inflammation of the liver'
|
|
|
List non-infectious causes of hepatitis
|
Immunologic Damage, Toxic Damage (such as alcohol, drugs, poisons)
|
|
|
HAV was isolated in what year?
|
1973
|
|
|
HBV was isolated in what year?
|
1960s
|
|
|
5 Hep Viruses
|
Picornaviridae,
Hepadnaviridae, Flaviviridae, Deltavirus (viroid-like), Hepeviridae |
|
|
How are HAV and HEV transmitted?
|
Fecal-orally
|
|
|
How are H(B/C/D)V transmitted?
|
Parenteral, perinatal, sexually
|
|
|
Define Acute
|
Short term and/or severe.
|
|
|
Define Chronic
|
Lingering or lasting - may or may not be severe.
|
|
|
Define Fuliment
|
Developing quickly and lasting a short time, high
mortality rate. |
|
|
Define Cirrhosis
|
Hardening: may be the result of infection or toxins (e.g.
alcohol) |
|
|
Define Jaundice
|
Yellowing of the skin, eyes, etc due to raised levels of
bilirubin in the blood due to liver damage. |
|
|
nonAnonB hep = hep __
|
C
|
|
|
Hep __ has a more crystalline structure
|
A
|
|
|
Hep ___ has a more rod like structure
|
B
|
|
|
Hep ___ has enveloped particles
|
C
|
|
|
Hep ___ & ___ are considered heterogenous
|
D and E
|
|
|
True or False
Acute hep infections can develop into fuliment |
True
|
|
|
Draw the Types of Hep virus infections
|
Hint- 5 categories are
1. Acute hep 2. chronic carrier (risk) 3. chronic hep (risk) 4. cirrhosis 5. Hepatocellular carcinoma (15541) See Slide 8 if you need help |
|
|
___ is the largest cause of chronic liver disease
|
HCV
|
|
|
Characteristics of liver damage caused by hepatitis
|
councilman-like bodies, bridging necrosis, cirrhosis, ground glass bodies
|
|
|
For which types of Hep are there vaccinations for?
|
Hep A and Hep B
|
|
|
What hep vaccine is currently in developement?
|
HEV
|
|
|
What are some challenges to hep vaccines?
|
_large amount of genetic variability
_in general, HCV elicits a weak immune response _characteristics of protective immunity are difficult to determine |
|
|
____ and ____ analyses can determine the type and severity of Hepatitis virus infections
|
Antibody and antigen
|
|
|
Basic characteristics of Hep A virus
|
Family: Picornaviridae
Genus Hepatavirus Non-enveloped, small icosahedral virus. Acute, self-limiting liver infection. ≤ Enterically transmitted |
|
|
Draw the genome of HAV
|
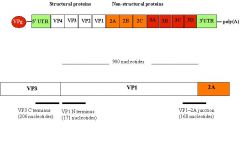
(+) ssRNA genome 7.5 KB
5’ terminal VPg, polyprotein - functions as a primer for RdRp to use in replication |
|
|
HAV genome uses a polyprotein strategy- draw it out
|

Here it is.
|
|
|
True or False
HAV replication is poorly understood |
True
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms of Hep A
|
jaundice, nausea, fatigue, abdominal pain, diarrhea, loss of appetite
|
|
|
True or False
You can have recurrent bouts of hepA |
False - it is an accute infection, you can get it only once
|
|
|
Why do kids have a tendency to get hep A?
|
Cause they poop and they dont wash their hands. Then they eat oreos.
|
|
|
True or False
Hep A is sometimes asymptomatic in kids |
True- this is why its spread among kids faster as well- THEY DONT KNOW they have it
|
|
|
Hep ____ always needs a helper virus
|
D
|
|
|
Besides food and water- what else is a high risk factor for hep A?
|
International travel
|
|
|
What does ALT indicate?
|
it is an indication of liver damage
|
|
|
When does viremia and fecal shedding generally occur in HepA?
|
3-7 DAYS
|
|
|
Draw the HAV events during the infection cycle
|
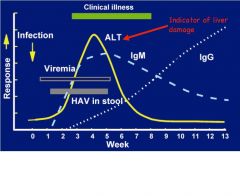
*note IGM antibodes eventually are replaced by IgG antibodies
|
|
|
What bodies fluids can you find HAV in?
|
Feces, serum, and saliva (highest to lowest)
|
|
|
Approximately what percent of people have been infected with HAV?
|
33%
|
|
|
How can you prevent HAV?
|
Hygiene
Sanitation Vaccination Immune globin |
|
|
True or False
In countries where children are the main reason high endemics of Hep A, vaccination is a MUST |
False - it's not recommended because kids can pass through the disease asymptomatically and not suffer like adults
|
|
|
Quick details on HBV
|
Family: Hepadnaviridae
Circular dsDNA with RT 42 nm enveloped icosahedral capsid. ≤ Four serotypes: o S Polymorphism o No pathological differences |
|
|
What are the two hepanavirus generas?
|
orthohepadnavirus and avihepadnavirus
|
|
|
•Orthohepadnavirus
|
Hepatitis B virus,
Ground Squirrel Hepatitis B Woodchuck Hepatitis B |
|
|
Avihepadnavirus
|
•Duck Hepatitis B
•Heron Hepatitis B Viruses. |
|
|
Characteristics of viruses found in blood of hepB infected individuals?
|
Blood from infected hosts contains large amounts
of small spherical and long filamentous particles with surface antigens. |
|
|
Besides liver cells, what other cells do hep B viruses attack?
|
Blood, spleen, pancreas
|
|
|
HBV causes:
|
chronic liver damage, hepatic carcinoma, and hepatitis
|
|
|
Whats a Dane particle?
|
The complete hepatitis B virion is called the Dane particle. It is a DNA virus of the Hepadna family and consists of an outer envelope and core.
|
|
|
The envelopes of hepB have what surface antigen?
|
HbsAG
|
|
|
Core particles in hep B viruses are covered in what?
|

HbcAG and viral DNA
|
|
|
In Hep B which are more infectious - dane particles, or coreless particles.
|
Dane- the empty spherical
envelopes & long filamentous envelopes consisting of cellular lipids and HBsAg are non infectious |
|
|
HAV is inactivated by what?
|
Formulin treatment
|
|
|
How many doses total do you need for HAV immunity?
|
3
|
|
|
How many inactivated hepA vaccinations are there?
|
About 4
|
|
|
Whats the point of Hep B's empty shell?
|
It can still attach and neutralize the host cell because the surface proteins can still be infectious
|
|
|
Review Dane particle assembly
|
See slide 34 and 35
|
|
|
Give the characteristics of Hep B Genome
|
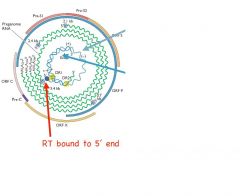
ss and dsDNA genome
≤ Long Strand (-) DNA -5’ covalently linked RT with 3’ & 5’ ends overlapping. ≤ Short Strand (+) DNA Variable length - 5’ end covalently attached to capped RNA oligomer ≤ Overlapping genes! |
|
|
Where does hep B transcription occur?
|
In nucleus!
|
|
|
True or False
Hep B uses its own RNA polymerase |
False - it uses host polymerase
|
|
|
List the products of hep B transcription
|
5 different promoters
5 transcripts (mRNAs) all capped and polyadenylated all share the same 3’ end 2 enhancer elements- EN1 and EN2 |
|
|
List the proteins of Hep B and their functions
|
E protein: made early, may suppress host immune system
C protein: major component of nucleocapsid P protein - reverse transcriptase LS, MS, SS - surface proteins have common C-termini involved in envelope formation X protein - ? implicated in development of hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
HBV Entry into Hepatacytes
|
Little is known!
≤ PreS1 proteins bind cellular receptors ≤ Entry is pH independent plasma membrane fusion (probably!). ≤ Viral cores transported to nucleus where DNA is released. |
|
|
True or False
Almost all HBV DNA is produced by RT |
True
|
|
|
Review Slide 40 & 41
|
Use other book if you dont get it still
|
|
|
True or False
Symptoms of HBV resemble those of HAV |
True
|
|
|
Symptoms of HBV include
|
Jaundice, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of apetite, nausea, vomitting, joint pain
|
|
|
Chronic infection in HBV occurs in...
|
90% of children infected at birth, 30% of children infected at age 1-5, 6% infected after age 5,
and! death occurs in 15-25% of chronically infected persons |
|
|
HBV prevention?
|
Get vaccinated!
Preggos with Hep B should get HBIG (hep b immune globin) to protect their babies |
|
|
Acute infection Hep B characteristics?
|
-Asymptomatic incubation period 1-6 months with hi viremia, infection (though not necessarily to toxic effect) of hepatocytes, clearance from serum (HBsAG neg), clearance from liver
|
|
|
Chronic infection of Hep B characteristics?
|
High expression of viral X genes and tumor supressor gene mutation (p53)
|
|
|
Draw Acute HBV infection with
recovery. |
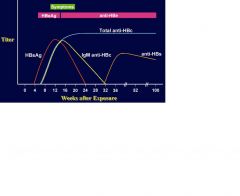
NOTICE HBsAG eventually goes to zero!
|
|
|
Draw Progression to chronic
HBV infection. |
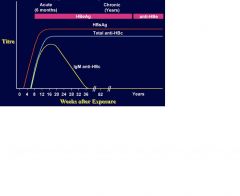
NOTICE- HBsAg NEVER goes to zero!
|
|
|
Describe the Mechanism of HBV Liver Injury
|
CTL affects against HBcAg + or HBeAg+
-Direct cytotoxic effects of HBcAg -High levels of large HBsAg - ineffecient secretion (ground glass) |
|
|
90% of chronic Hep B carriers are ______
|
infants
|
|
|
Demographic of chronic hep B infections?
|
More than 8% of
population in all of sub-Saharan Africa, South East Asia, China, India, Indonesia, North Korea, the Phillipines, Haiti and others. China: 500,000 - 1 million new cases of hepatocellular carcinoma per year. Taiwan: Relative risk of getting HCC is 217 x risk of non-carriers. Hainan Island: Has highest levels of HBV in China and the highest levels of liver cancer. |
|
|
People with chronic
hepatitis are more than ____ times more likely to develop liver cancer than the general population. |
100
|
|
|
When and who should you give passive immunisation with HB immuneglobin?
|
Within 12 hours after birth (infants)
48 hours after Body splash/NSI |
|
|
Recombinant HBsAG vaccine works against _____ and should be given at ___ intervals
|
surface proteins
0,1,6 month (dose time intervals) |
|
|
What reverse transcriptase inhibitors are used in antiviral drugs for HBV
whats the problem, yo? |
Lamivudine, Famciclovir, Adefovir,
They all have to be given for a long time, and some HBV have developed drug resistant mutants |
|
|
What cytokines are used in antiviral drugs for HBV?
|
Interferon, liver transplant
Note- interferone blocks cirrhosis and cancer - but has to be given for 6 months up to a year! |
|
|
What is the plasma derived vaccine for Hep B and its characteristics?
|
Heptavax-B
1,1,6 intramuscular injections with 96% of young adults seroconverting Both vaccines protect against active Hepatitis B, asymptomatic HBV, the Carrier State, & HDV. |
|
|
What is the recombinant DNA vaccine for Hep B and its characteristics?
|
Recombivax engerix-B
Uses recombinant DNA in yeast with a 99% seroconversion rate in ages 20-29 Both vaccines protect against active Hepatitis B, asymptomatic HBV, the Carrier State, & HDV. |
|
|
How long you should you wait after you get hep B vaccine to see if it is effective?
|
6 months
|
|
|
What should you treat chronic hep B with?
|
Interferon alfa-2b, pegylated interferon alfa-2a, adefovir, lamivudine, entecavir, telebivudine
(there are 6) |
|
|
What is GAVI?
|
Global alliance for vaccine for vaccines and immunization distributes funds for 3 year supply of autosyringes
|
|
|
Pregnant women who have hep B are ____ positibe
|
HBeAg
|
|
|
___ % of chronic hep B infections are aquirred perinatally.
|
30
|
|
|
Hep B vaccination in SEAR (what does SEAR stand for?)
|
Southeast asia region
|
|
|
GAVI provides for ____ newborns in china to get hep B vaccine.
|
50 -But chinese govt kicks in the other 50 so ALL newborns get vaccinated
|
|
|
India: ___ hepatitis B vaccine and safe injection projects.
|
45
|
|
|
Single use disposable syringe used in indonesia (provided by GAVI - who provides other treatments?)
|
Uniject
Indonesia provides doses 2 & 3 |
|
|
Quick details on HDV
|
Viroid (ribozyme) & mRNA
(protein coding) ≤ Relies on HBV for packaging. |
|
|
Outer proteins on HDV envelope are what?
|
HBV, L, M, and S
|
|
|
Inner nucleocapsid of HDV consists of what?
|
HDV genomic RNA with HDAg-D, and HDAg-S
|
|
|
define satellite virus and give an example.
|
term used in plant virology for a virus associated functionally, at least for the purpose of its own replication, with another virus.
dependoviruses are DNA satellites of Adenoviruses. |
|
|
True or False
Satellite Viruses are often parasitic on the helper virus by reducing symptoms and interfering with the replication of the helper virus. |
True
|
|
|
The smallest pathogens are ____.
|
viroids
|
|
|
True or False
Viroids do not have enough DNA to self replicate |
False- they do self replicate
|
|
|
VIroids are known to induce disease in ____.
|
plants
|
|
|
Whats weird about viroids?
|
They don't have any mRNA or encoded proteins!
They replicate using a rolling circle mechanism! |
|
|
Draw a viroid and list its characteristics
|
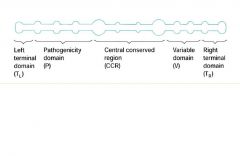
Very small, covalently closed, circular RNA molecules capable of
autonomous replication and induction of disease. • Sizes range from 246-401 nucleotides. • Ten Times smaller than the smallest RNA viruses. • No coding capacity - do not encode their own polymerase. • Use host-encoded polymerases for replication. • “Classical” viroids have been found only in plants. |
|
|
True or False
Viroids can induce severe symptoms |
TRUE
|
|
|
HDV needs ___.
|
HBV
|
|
|
Viroids replicate using _____ enzymes
|
host
|
|
|
Whats beneficial about satellites
|
They can encode a protein not found in a virus
|
|
|
In HDV the genomic RNA is the ____ strand
|
+
|
|
|
Draw the rolling circle mechanism
|
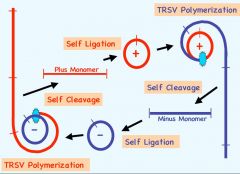
Explain
|
|
|
Define ribozymes
|
RNA molecules with enzymatic activity. They
are able to cut themselves and other RNAs into smaller pieces. |
|
|
Which hep virus utilizes ribozyme activities?
|
HDV- in both positive and negative rolling strands
|
|
|
______ and ______ ribozymes are used in processing of
viroids and some satellite RNAs. |
hammerhead and hairpin
|
|
|
Hepatitis Delta is a chimeric molecule- what does that mean?
|
half viroid/half satellite RNA
|
|
|
What are the viroid like properties of the HDV virus?
|
Rod-like circular RNA.
- Central conserved region similar to plant viroids. - Rolling circle replication - Ribozyme Self-cleaving activty. |
|
|
What are the satellite like properties of HDV?
|
encodes a protein
|
|
|
Why does HDV need HBV?
|
For surface membrane proteins used in encapsidation- can replicate okay by itself however
|
|
|
HDV is ___ sense ____
|
- sense
SSRNA |
|
|
Nuclear RNA synthesis of HDV
via ____ |
DdRp !!!
|
|
|
How does HDV switch to strand replication from
mRNA transcription? |
Switch to full length (+)
via suppression of poly (A) tail. |
|
|
What is the most highly active ribozyme known?
|
HDV
|
|
|
simultaneous HBV & HDV infections = ___
|
coninfection
(high initial IgM (anti HDV) |
|
|
infection by HBV followed by infection with HDV =
|
superinfection
|
|
|
Coninfection
|
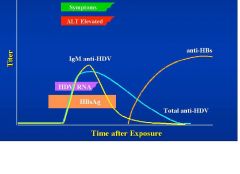
Coinfection or superinfection of HDV?
|
|
|
Superinfection
|
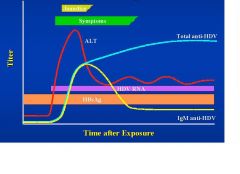
Coinfection or Superinfection of HDV
|
|
|
Envelop glycoproteins of hep C?
|
E1 and E2
|
|
|
Basics of Hep C
|
Enveloped capsid with
icosahedral symmetry. Family: Flaviviridae +SS RNA |
|
|
Flaviviridae causes what diseases?
|
Yellow fever virus, dengue, west nile
|
|
|
Three Flaviviridae Genera?
|
Flavivirus
Pestavirus Hepacivirus |
|
|
Flavivirus genera causes -
(flaviviridae) |
Central European encephalitis (TBE-W), Japanese encephalitis (JE), St. Louis
encephalitis (SLE), West Nile virus (WN), Dengue (DEN), Yellow fever (YF) |
|
|
Pestivirus Genus causes
(Flaviviridae) |
Bovine viral diarrhea (BVDV), hog cholera or classical swine fever (CSFV)
Very important Animal Diseases |
|
|
Genus Hepacivirus causes
(flaviviridae) |
Hep C
|
|
|
HCV genome describe it
|

5’ non-translated region (IRES)
≤ Single ORF of ~9,000 nts. o Translated into polyprotein and processed by viral & cell proteases ≤ Short 3’ non-translated region |
|
|
Symptoms of Hep C
|
jaundice, nausea, vomitting, abdominal pain, dark urine, fatigue, loss of appetite
|
|
|
Chronic infection of hep c occurs in ___% of individuals and of these chronic liver disease occurs in ___% of the individuals
|
55-85%
70% |
|
|
Ways to get hep C
|
Yo Mama and sharing drug needles
|
|
|
Incubation period for hep C?
|
6-8 weeks
|
|
|
Damage from hep c due to?
|
damage due to cell mediated immune response
|
|
|
Extrahepatic manifestatiosn of HCV?
|
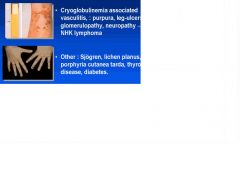
EW
|
|
|
Highest cause of hep C (in order?
|
Drug use - 60%
Sexual - 18% Unknown - 9% Perinatal (occupational) - 5% |
|
|
True or False
Blood transfusions are a high source of hep C |
False - diagnostic tests have virtually eliminated this pathway
|
|
|
Why isn't there a hep c vaccine yet?
|
Vaccines have not been developed because:
-virus is poorly immunogenic -immune responses are thought to cause more serious disease. -variation in DNA protein sequences between isolates |
|
|
True or False
Several HCV Subtypes Exist |
True
|
|
|
Two drugs for chronic hep C?
|
Interferon and ribavirin
|
|
|
Read the medical treatment part for Hep C
|

This is weird because I thought there wasnt any cure for hep C!
|
|
|
True or False
Over the next decade liver cancer deaths caused by HCV may exceed Those caused by HIV/AIDS. |
True
|
|
|
Course of disease in Hep C please
|
Accute hep C --> chronic infectioin --> chronic liver disease -->cirrhosis --> HCC and decomposition
|
|
|
Hepatitis E virus (HEV)QUICKIE
|
Hepeviridae
≤ Wide genetic variation. ≤ Icosahedral nonenveloped capsid. ≤ Difficult to isolate authentic viral particles. |
|
|
HEP E is usually caused by
|
drinking poopy water in weird foreign countries
|
|
|
Clinical features of Hep E?
|

Fatality rate is higher than HIV!
|
|
|
How do avoid hep E
|
Dont drink funny water with funny ice
Dont eat funny shellfish dont eat uncooked fruits or veggies unless you peeled or made it yourself |
|
|
True or False
IG from western donors was helpful in the production of a vaccine |
FALSE
|
|
|
Is there a hep E vaccine?
|
Sort of- only a 6 month trial so far, glaxosmithkline makes it.
|

