![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
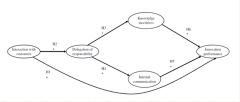
Illustrating structural equation modeling |
|
|
|
Why do we need experimental research? |
–Descriptive studies describe how people think, feel, behave –Correlational studies allow to see wether certain variables are related to another –Neither of these approaches allows to know about the causes of behavior –An experiment must be conducted to see wether or not one variable may cause another variable |
|
|
What is experimental research? |
–Experiments are research designs in which the researcher manipulates one or more variables and measures any change in other variables while controlling for the influence of extraneous variables |
|
|
Basic ingredients of designing experiments |
–Independent variables •Researcher manipulates one or more independent variables •Must have two or more levels (values) –Dependent variables •response being measured in a study, typically a measure of participants’ thoughts, feeling, behavior –Different conditions •Experimental group: people who receive a nonzero level of the independent value •Control group: people who receive a zero level of the independent level |
|
|
Five essential properties of an experiment |
–Besides the three basic ingredients, there are five essential properties: 1.Control 2.Randomization 3.Systematic manipulation 4.Descriptiveness 5.Reproducibility |
|
|
Essential properties: (1) Control |
–Researcher needs to control for influence of extraneous variables –Confounding variable = extraneous variable affects the variables that are being studied –How to eliminate? (Randomization, statistical control, holding other variables constant) |
|
|
Essential properties: (2) Randomization |
–Random assignment: everyone can be in every test condition |
|
|
Essential properties: (3) Systematic manipulation |
The researcher needs to purposely manipulate (vary) the independent variable in a systematic manner |
|
|
Essential properties: (4) Descriptiveness |
The researcher needs to be able to thoroughly describe what exactly was done in the experiment |
|
|
Essential properties: (5) Reproducibility |
–Other researchers need to be able to repeat (= replicate) the experiment based on the descriptions of the researcher who originally conducted it –When repeated, the experiment should reveal the same result |
|
|
Treats to internal validity |
–Failed random assignment –Different drop-out rates –Extraneous events (noise) –Experimenter expectancy –double-blind procedures: neither researcher nor participant knows which condition the participant is in |
|
|
The trade-off between internal and external validity |
–The more tightly controlled an experiment, the stronger its internal validity –a high degree of experimental control makes the experiment more unique and less like other settings, thereby lowering external validity |

