![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The hair cells have thick projections called _______, which stick out at the top of the cells? |
Stereocilia |
|
|
In the posterior chamber, contains a clear jelly like fluid called the ... |
Vitreous humour mechano |
|
|
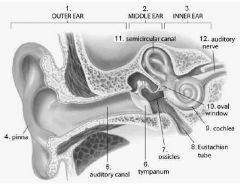
Mechanoreceptors that detect head and body rotation (rotational equilibrium) are found in what structure? |
Semicircular canal |
|
|
In order, what are the three ossicles called? |
Malleus Incus Stapes |
|
|
Because the inner ear is fluid filled, vibrations in the oval window must be converted to ... |
Pressure waves |
|
|
The cochlea is used for .... |
Hearing |
|
|
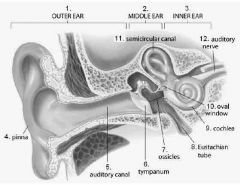
The middle ear is connected to the throat by the thin ... |
Eustachian tube |
|
|
_______ is a round, elastic structure that vibrates in response to sound waves. Also known as the eardrum |
Tympanum |
|
|
Three tiny interconnected bones in the middle ear |
Ossicles |
|
|
The _______ is a tube that leads to the eardrum in the middle of the ear |
Auditory canal |
|
|
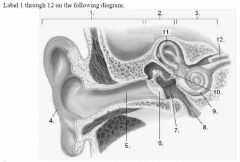
________ is the outside flap is the ear, made of skin and cartilage |
Pinna |
|
|
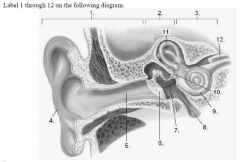
The middle ear consists of what structures.... |
Tympanum Ossicle Oval window Eustachian tube |
|
|
The outer ear consists of what structures..... |
Pinna Auditory canal |
|
|
What are the three main divisions of the ear? |
Inner ear Middle ear Outer ear |
|
|
Mechanoreceptors in the inner ear convert the energy of ________ into electrochemical energy the brain perceives as sound. |
Sound waves |
|
|
The specialized sensory receptor cells for both hearing and balance are ..... |
Mechanoreceptors |
|
|
The ability of the lens to change shape in order to focus images clearly on the retina is a reflex called .... |
Accommodation |
|
|
Humans have forward facing eyes, known as .... |
Binocular vision |
|
|
Before the brain can integrate visual information, the retina must send information to the _________, from there the info travels to the _________, then to the ________, of the cerebral cortex. |
Optic never Thalamus Occipital lobe |
|
|
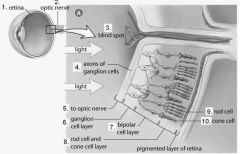
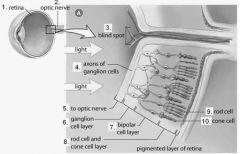
The blind spot does not contain what? |
Photoreceptors |
|
|
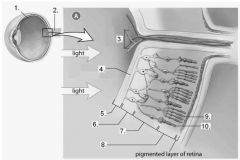
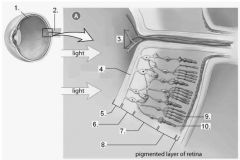
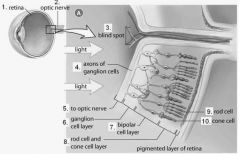
The _______ is located where the two ganglion cells merge to form the optic nerve. |
Blind spot |
|
|
The axons of the ganglion cells form the .... |
Optic nerve |
|
|
What are the three main layers of neurons in the retina? |
Bipolar layer Rods and cones layer Ganglion layer |
|
|
The rods contain a light absorbing pigment called ..... |
Rhodopsin |
|
|
The perception of odour occurs in the ________ lobe |
Frontal lobe |
|
|
Chemoreceptors called _________, line the upper nasal cavity. |
Olfactory cells |
|
|
The tongue contains ________ that allow us to taste substances entering the mouth. |
Chemoreceptors |
|
|
_________ are another type of mechanoreceptor involved in coordination. |
Proprioceptors |
|
|
Gravitation equilibrium depends on the _______ and ________ which together make up the fluid filled _______ of the inner ear. |
Utricle Saccule Make up the vestibule |
|
|
What three major structures in the inner ear help us stand upright? |
Semicircular canal Utricle Saccule |
|
|
________ is due to uneven curvature of part of the cornea. Because the cornea is asymmetrical it cannot bend light rays to that they meet at the correct focal point. |
Astigmatism |
|
|
The far ends of the stereocilia are embedded within the ..... |
Tectorial membrane |
|
|
_________ transmits sensory information to the brain |
Optic nerve |
|
|
Along the base of the organ of corti is the ________ to which sensory mechanoreceptors known as _________ are attached. |
Basilar membrane Hair cells are attached |
|
|
Aqueous humour is produced everyday and drained by small ducts if these ducts become plugged, pressure can build up in the eye, causing blood vessels to rupture. The cells of the eye then deteriorate due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. This results in what? |
Glaucoma |
|
|
On the cross section of a cochlea - the middle chamber contains the ______ which is the organ of hearing |
Organ of corti |
|
|
It is within the structures of the _________ that the mechanical energy of sound is converted into electrochemical impulses that are transmitted to the brain. |
Cochlea |
|
|
What structure of the ear contains sensors for balance? |
Semicircular canal and vestibule |
|
|
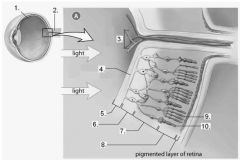
The rods are sensitive to ... |
Dim light / light intensity |
|
|
Cones are sensitive to ... |
Different colour |
|
|
Membrane covered opening in the wall of the inner ear, called the ..... |
Oval window |
|
|
The inner ear consists of what structures ? |
Semicircular canal The vestibule The cochlea |
|
|
Color blindness is caused by a lack of .... |
Particular cones (usually red and green) |
|
|
Human senses include... |
Hearing Taste Touch Smell Internal sense such as balance |
|
|
Cones are packed most densely at the ... |
Fovea centralis |
|
|
Where are photoreceptors found? What is an example of the receptors? What stimulates them? |
Found in the eye Rods and cones Stimulated by visible light |
|
|
_______ are colour detecting sensors of the eye |
Cones |
|
|
Cones contain a pigment called ...... |
Photopsin |
|
|
People who have no problem seeing distant objects are far sighted. They cannot focus on near objects because the eyeball is to short. This is called ________. Where does the focussed light fall? |
Hyperopia - the light rays do not meet before they reach the retina , the image is focussed behind the retina |
|
|
As the lens ages, it's protein structure can start to degenerate making it opaque and preventing light from passing through it. This condition can cause white spots called ........ |
Cataracts |
|
|
What is sensory adaptation?, Give an example |
When the brain filters out insignificant or repetitive information Example, you no longer notice the ticking of a clock of the feel of clothes on your skin |
|
|
_________ supports the eyeball with the pressure of the fluid they contain |
Humours |
|
|
The lens focussed light rays on the ... |
Fovea centralis |
|
|
Rods are spread through the ... |
Retina |
|
|
To see near objects you can wear ______ lenses |
Convex |
|
|
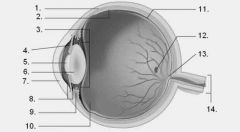
The internal layer of the eye consists of what three structures? |
Rods Cones Fovea centralis |
|
|
The intermediate layer of the eye consists of what four structures ? |
Choroid Iris Pupil Ciliary muscle |
|
|
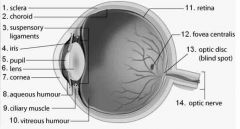
What is the function of the choroid ? |
Absorbs scattered light and contains blood vessels |
|
|
What is the function of the iris? |
Regulates the amount of light that enters the eye |
|
|
What is the function of the pupil? |
Is the opening for light to enter the inner eye |
|
|
What is the function of the ciliary muscles ? |
Changes the shape of the lens in order to focus |
|
|
The external layer of the eye consists of .... |
Sclera Cornea |
|
|
What is the function of the sclera ? |
Protects and supports the eyeball |
|
|
What is the function of the cornea? |
Bends light rays into the eye |
|
|
What is the retina ? |
The internal layer of the eye. A thin layer of tissue that contains the photoreceptors |
|
|
behind the iris the choroid thickens and forms the .... |
Ciliary muscles |
|
|
The ______ allows light to enter the inner eye through the pupil. |
Iris |
|
|
The intermediate layer of the eye that absorbs light rays that are not detected by photoreceptors. Contains blood vessels that nourish the eye? |
Choroid |
|
|
Light enters the eye through here, the transparent part of the sclera at the front of the eye ? |
Cornea |
|
|
The eye has three layer, what are they? |
Sclera Cornea Choroid |
|
|
What are the four types of mechanoreceptors? |
Touch/pressure or pain Hearing Balance Body position |
|
|
What are three types of chemoreceptors? |
Taste Smell Internal senses |
|
|
What are three types of chemoreceptors? |
Taste Smell Internal senses |
|
|
Human sensory receptors can be classified into four categories ... |
Photoreceptors Chemoreceptors Mehanoreceptors Thermoreceptor |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
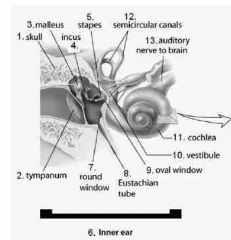
Back (Definition) |

