![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name all requirements for sensor networks.
|
• Energy efficiency
• Memory capacity • Computing performance • Bandwidth • Quality of Service • Fault tolerant • Life-time • Scalability • Sensor density • Programmability • Maintainability |
|
|
What classes of sensor networks are available?
|
• Wired/hybrid type: fieldbus systems
• Wireless sensor networks – WSN |
|
|
What is DCS? / What is CCS?
|
• Distributed Control System
• Centralized Control System |
|
|
Draw picture of CCS/DCS.
|

|
|
|
Define sensor network.
|
A sensor network consists of numerous intelligent devices (sensor nodes) that are distributed building a network.
|
|
|
What topologies are possible in Fieldbus?
|
• Bus
• Ring • Tree |
|
|
What kind of types are available in WSN?
|
• Source
• Sink • Actuator |
|
|
What interaction patterns are possible in WSN?
|
• Event detection
• Periodic measurement • Function approximation: • Edge detection • Tracking |
|
|
How can be sensor nodes deployed in the environment?
|
• Random deployment
• Regular deployment • Mobile |
|
|
What are the differences of MANET compared to WSN?
|
• Self-organization, energy efficiency, (often) wireless multi-hop
• Applications, equipment: MANETs more powerful (read: expensive) equipment assumed, often “human in the loop”-type applications, higher data rates, more resources • Application-specific: WSNs depend much stronger on application specifics; MANETs comparably uniform • Environment interaction: core of WSN, absent in MANET • Scale: WSN might be much larger (although contestable) • Energy: WSN tighter requirements, maintenance issues • Dependability/QoS: in WSN, individual node may be dispensable (network matters), QoS different because of different applications • Data centric vs. id-centric networking • Mobility: different mobility patterns (sinks or nodes might be mobile) |
|
|
Name all components of a sensor node.
|
• Controller
• Communication unit Sensors/Actuators • Memory • Energy supply |
|
|
What transceiver states exist?
|
• Transmit
• Receive • Idle • Sleep |
|
|
What is energy scavenging? Give two examples.
|
• Obtaining energy from the environment
• Batteries • Vibration • Solar |
|
|
What is the best to do in order to save energy?
|
• Do not run sensor node at full operation all the time
• Power Save mode |
|
|
What is the problem in switching between modes?
|
Time and power consumption required reaching higher modes not negligible
ESaved < EOverhead |
|
|
What is Dynamic Voltage Scaling?
|
Time and power consumption required reaching higher modes not negligible
ESaved < EOverhead |
|
|
What is Dynamic Voltage Scaling?
|
Low supply voltage & clock
|
|
|
Which operation in memory usage is more expensive in terms of energy consumption?
|
Writing / erasing is expensive
|
|
|
Transmitter Power:(eqn)
|
Etx = Tstart Pstart + [n / (R x Rcode)] (PtxElec+ αamp + βamp Ptx)
|
|
|
Receiver Power:
|
Erx = Tstart Pstart + [n / (R x Rcode)] PrxElec + EdecBits (R)
|
|
|
What is multi-hop communication?
|
• Send packets to an intermediate node
• Intermediate node forwards packet to its destination • Store-and-forward multi-hop network |
|
|
How much energy consumes a single-hop?
|
c*d^α
|
|
|
How much energy consumes multi-hop?
|
N*c*(d/N)^ α
|
|
|
What sources of mobility do exist?
|
• Node mobility
• Sink mobility • Event mobility |
|
|
Which Quality of Service goals are defined in WSN?
|
• Throughput/delay/jitter
• Event detection/reporting probability • Event classification error, detection delay • Probability of missing a periodic report • Approximation accuracy • Tracking accuracy |
|
|
Name all optimization goals in WSN.
|
Quality of Service
Energy efficiency Scalability |
|
|
What is temporal correlation?
|
Same values don’t change very often send every minute or more
|
|
|
What is spatial correlation?
|
In an area neighbors of a node might have same values ask only once
|
|
|
Give an example for adaptive fidelity
|
Adapt the effort with which data is exchanged to the currently required accuracy/fidelity
If no important event low messages unless event happens Ex. When temperature is in acceptable range, only send temperature values at low resolution |
|
|
What means data-centric networking?
|
Focus networking transactions on the data directly instead of their senders and transmitters, ID is not important who sent it
|
|
|
What implementation options exist for data-centric networking?
|
• Overlay networks & distributed hash tables
• Publish/subscribe • Databases |
|
|
Why are ISM bands preferred for WSN?
|
Industrial, scientific, medicine– license-free operation
|
|
|
What is the formula for a radio wave? Name the parameters.
|
s(t) = A(t) * sin( 2πf(t) * t ∅(t) )
A(t) : Amplitude f (t): Frequency ∅(t) : Phase |
|
|
Which options for modulation (keying) do exist?
|
• Amplitude Shift Keying
• Frequency Shift Keying • Phase Shift Keying |
|
|
Name all ranges for signal propagation.
|
• Transmission range
• Detection range • Interference range |
|
|
What sources of distortion do exist in wireless transmissions?
|
• Attenuation – energy is distributed to larger areas with increasing distance
• Reflection/refraction – bounce of a surface; enter material • Diffraction – start “new wave” from a sharp edge • Scattering – multiple reflections at rough surfaces • Doppler fading – shift in frequencies (loss of center) |
|
|
What does Friis free-space equation describe?
|
Describes signal strength over a distance d relative to distance do
|
|
|
What is noise and interference?
|
• Noise: due to effects in receiver electronics, depends on temperature
• Interference: caused by third party parallel senders ➢ Co-channel interference: another sender uses the same spectrum ➢ Adjacent-channel interference: another sender uses some other part of the radio spectrum, but receiver filters are not good enough to fully suppress it |
|
|
What are the requirements for medium access in wireless networks?
|
• high throughput
• low overhead • low error rates • energy-efficient • handle switched off devices |
|
|
What are the main options for wireless medium access?
|

|
|
|
What causes energy problems in MAC protocols?
|
• Collisions – wasted effort when two packets collide
• Overhearing – waste effort in receiving a packet destined for another node • Idle listening – sitting idly and trying to receive when nobody is sending • Protocol overhead |
|
|
What is the difference between schedule based and contention based MAC protocols?
|

|
|
|
Give two examples for contention based MAC protocols.
|
Sender B asks receiver C whether C is able to receive a transmission:
Request to Send (RTS). Receiver C agrees sends out a: Clear to Send (CTS). Potential interferers hear either RTS or CTS and know about impending transmission and for how long it will last. This information is stored in a Network Allocation Vector.
|
|
|
What are synchronized islands in S-MAC?
|
• Nodes try to pick up schedule synchronization from neighboring nodes
• If no neighbor found, nodes pick some schedule to start with • If additional nodes join, some node might learn about two different schedules from different nodes. Having to bridge and apply 2 schedules |
|
|
Give two examples for schedule based MAC protocols.
|
• LEACH
• SMACS • TRAMA |
|
|
Explain main idea of LEACH. What do clusterheads organize?
|
Low-Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy: Group nodes into “clusters”, controlled by clusterhead using hierarchal networks.
Clusterhead organizes CDMA & TDMA |
|
|
What is the goal in SMACS?
|
Set up directional links between neighboring nodes
|
|
|
Explain idea in TRAMA.
|
• Nodes are synchronized
• Time divided into cycles, divided into Random & Schedules access periods • Nodes exchange neighborhood information • Nodes exchange schedules |
|
|
What approaches are given for error control?
|
• Backward error control – ARQ
• Forward error control – FEC |
|
|
What are standard ARQ protocols?
|
• Alternating bit
• Go-back N • Selective Repeat |
|
|
How does piggybacking with alternating-bit work?
|
Data is sent in the following sequence (Data, Sequence-No, ACK) and each packet includes the previous packets sequence no in the ACK field if it has arrived or lost.
|
|
|
How does Go-back-N work?
|
Send packets P1, P2, P3 one by one in a group and the receiver will acknowledge packet by packet but if a packet is lost it will keep on resending the last correctly received packet in the beginning of the sequence. Sender will have to resend the entire group after the correctly received packet. When timer goes off, retransmit all unacknowledged packets
|
|
|
How does selective repeat work?
|
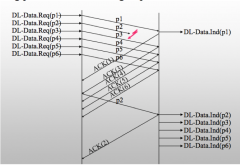
Just resend the missing packet not the entire group
|
|
|
When is the best moment to retransmit a packet?
|
• In a BSC channel, any time is as good as any
• In fading channels, try to avoid bad channel states – postpone transmissions • Instead (e.g.): send a packet to another node if in queue (exploit multi-user diversity) |
|
|
What is the main idea in FEC?
|
• Endow symbols in a packet with additional redundancy to withstand a limited amount of random permutations
|
|
|
Compare FEC vs. ARQ.
|

|
|
|
FEC Code Rate: (Eqn)
|

|
|
|
Which roles can a device take in ZigBee?
|
• End Device
• Router • Coordinator |
|
|
How many maximum nodes can operate in ZigBee?
|
2^16
|
|
|
What topologies are possible in IEEE 802.15.4?
|
• Star
• Peer-to-peer • Cluster Tree |
|
|
How are devices discovered?
|
• Active scanning
• Passive scanning |
|
|
What means GTS and how it is used?
|
• Guaranteed Time Slot: Nodes can choose contention-free communication
• node has to send a request to PAN coordinator • PAN coordinator accepts request, if enough free time slots are available • Max. seven GTS possible |
|
|
Explain time sensitive vs. scalability problem.
|
• GTS in IEEE 802.15.4 offers real time guarantee
• GTS is only used for direct communication between node and PAN coordinator • Only star topology possible -> Not Scalable |
|
|
Explain functionality of Network Layer in ZigBee
|
• Packet routing
• Route management • Topologies: Mesh, P2P, Cluster-Tree • Security management: Key distribution |
|
|
Explain functionality of Application Layer in ZigBee.
|
• Endpoint Multiplexing
• Fragmentation of data packets • Implementation of profiles • Application objects |
|
|
What are the main reasons for cross layer design?
|
• Limitations: energy, memory, and performance
• High overhead in layer model inefficient • Features of low-power transceivers and radio channel states should be considered in protocol design |
|
|
What can you suggest for interaction of transport layer and physical layer (PHY)?
|
Transmission capacity and sending rate should be controlled conjointly
|
|
|
What can you suggest for interaction of routing and physical layer (PHY)?
|
Divide throughput optimization problem into two areas
• Multi-hop routing optimization in network layer • Power optimization in PHY-layer |
|
|
Explain the disadvantage of cross layer design.
|
Loss of exchangeability and conformity of different approaches. Restricts propagation and usage
|
|
|
What is middleware? Explain
|
Middleware constitutes a layer in a complex software system, which offers services to other decoupled software components in order to ensure a communication between them.
• Middleware may realize different layers of communication • Middleware offers interfaces to the outside |
|
|
Which classifications of middleware systems exist? Name all.
|
• Classic
• Data-Centric • Virtual Machines • Adaptive |
|
|
What is the difference between physical and logical location?
|
Physical Location: with respect to coordinate system ex. 48° 44‘ 42.85‘‘ N
Logical Location: your own interpretation of the place ex. Room 230 |
|
|
What main approaches for location estimation exist? Name and explain.
|
• Proximity: Exploit finite range of wireless communication
• (Tri-/Multi-) lateration and & angulation: Use distance or angle estimates, simple geometry to compute position estimates • Scene analysis: Radio environment has characteristic “signatures”. Can be measured beforehand, stored, compared with current situation. |
|
|
What is ToA? Explain functionality.
|
Time of arrival: Use time of transmission, propagation speed, time of arrival to compute distance
|
|
|
What is TDoA? Explain functionality.
|
Time Difference of Arrival: Use two different signals with different propagation speeds. Compute difference between arrival times to compute distance
|
|
|
What is overlapping connectivity?
|
Position is estimated in the center of area where circles from which signal is heard/not heard overlap
|
|
|
How does approximate point in triangle work?
|
• Determine triangles of anchor
nodes where node is inside,
overlap them
• Check whether inside a given triangle – move node or simulate movement by asking neighbors |
|
|
What are the options for topology control?
|

|
|
|
What is Relative Neighborhood Graph (RNG) and how does it work?
|

Edge between nodes u and v if and only if there is no other node w that is closer to either u or v
|
|
|
What is Gabriel graph and how does it work?
|
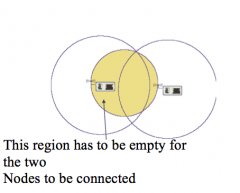
Smallest circle with nodes u and v on its circumference must only contain node u and v for u and v to be connected
|
|
|
How does centralized power control algorithm work?
|
• Use a centralized, greedy algorithm
• Initially, all nodes have transmission power 0 Connect those two components with the shortest distance between them (raise transmission power accordingly) • Second phase: Remove links (= reduce transmission power) not needed for connectivity |
|
|
What are the key concepts of security?
|
• Loss of Confidentiality
• Loss of Integrity • Loss of Availability |
|
|
What happens if you lose confidentiality? /integrity? /availability?
|
• Loss of Confidentiality: Unauthorized disclosure of information
• Loss of Integrity: Unauthorized modification or destruction of information • Loss of Availability: Disruption of access to use of information or an information system |
|
|
What types of attacks are possible?
|
• Passive attacks: gaining information
• Active attacks: modify/fake data |
|
|
Explain Eavesdropping. What kind of attack is it?
|
When someone listens to an ongoing conversation between two parties without modifying the data being transferred. It is a passive attack.
|
|
|
What happens in masquerading attacks? / replay attacks? / denial of service attacks?
|
• Masquerading attack: Attacker pretends to be a legitimate user and steals the identity
• Replay attack: Attacker records a message from an ongoing conversation between two parties and then replays this message. • Denial of service attack: Attacker stops Alice from reaching Bob and pretends to be Alice. |
|
|
What defensive measures are available in WSN?
|
• Key establishment & management
• Secure routing • Verification of sensor data |
|
|
Explain functionality of symmetric encryption
|
A mechanism to provide confidentiality using symmetric keys. That is same key has to be shared between sender and receiver and it is used to decrypt/ encrypt messages.
|
|
|
Explain functionality of asymmetric encryption
|
A mechanism to provide confidentiality using asymmetric keys (public / private keys). The sender uses the public key of the person it wants to send to which is found publicly to everyone and uses it to encrypt the message, then the receiver uses his private key which is only available to him to decrypt the message.
|
|
|
How does message authentication code (MAC) work?
|
Sender and receiver share symmetric keys.
Sender produces a hash of the message to be sent using the key and sends it along with the message. Message is sent in plain text. Receiver receives message and the hash. He then computes the hash of the message and compares it to hash received to check integrity. |

