![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a hypothesis? |
a prediction made with the information available as a starting point for an investigation |
|
|
What is an independent variable? |
the variable changed in an experiment to see the change on the dependent variable |
|
|
What is a dependent variable? |
the variable that changes as a result of the change to the independent variable |
|
|
What is a constant variable? |
a variable kept the same throughout all the tests in the experiment |
|
|
What is the result of an experiment? |
a summary of the changes to the dependent variable that were observed by the researcher |
|
|
What is a statement of trend? |
an explanation of a trend, or pattern in data |
|
|
What is a discussion? |
an evaluation of the results of the experiment and an attempt to explain what caused them |
|
|
What is an error? |
a part of the investigation that is incorrect can be related to the fact that information was recorded incorrectly; or that a variable was not kept constant |
|
|
What is an improvement? |
a measure that could be taken if the experiment is reproduced that would improve the accuracy of the data |
|
|
What is a conclusion? |
a summary of the results, errors, improvements and discussion, concluding with the researcher's feelings on the topic |
|
|
What is the correct order of: cells, organisms, organs, tissues and organ systems? |
Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms |
|
|
Define cell |
the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism |
|
|
Define tissue |
a group of similar cells of the same origin that together carry out a specific function |
|
|
Define organ |
a group of tissues in a living organism that have been adapted to perform a specific function |
|
|
Define organ system |
a group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions |
|
|
Define organism |
any contiguous living system, such as an animal, plant, fungus, archaeon, or bacterium |
|
|
What are the organs of the excretory system? |
kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra |
|
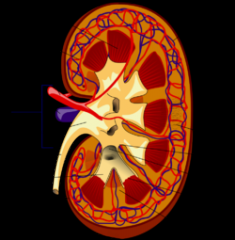
Name the key organs of a kidney on the diagram |
renal pelvis, renal artery, renal vein, major calyx, minor calyx, renal medulla, renal pyramid, renal cortex, renal capsule, ureter |
|
|
Where is the kidney located? |
below the ribs. left kidney is slightly higher than the right kidney next to the spine |
|
|
What is the function of the nephron? |
filters blood through a microscopic filter called the glomerulus allows fluids and waste products through it, but not large molecules and blood cells fluid passes through the tubule, where nutrients are absorbed and sent to the bloodstream waste products after this filtration become urine |
|
|
What are the organs of the digestive system? |
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus |
|
|
Define chemical digestion
|
breaking food down into simpler nutrients that can be used by cells begins in the mouth when food mixes with saliva, and amylase in saliva begins to digest starches |
|
|
Define mechanical digestion |
physically breaking food into smaller pieces begins in the mouth as the food is chewed and broken into smaller pieces |
|
|
What are the organs of the respiratory system? |
nose and nasal cavity, mouth, pharynx, larynx, bronchi and bronchioles, lungs, alveoli and muscles of respiration (diaphragm and intercostal muscles) |
|
|
How does the structure of the alveoli suit their function? |
walls of the alveoli are extremely thin have a large surface area in relation to volume, are fluid lined enabling gases to dissolve. As well as this, they are surrounded by numerous capillaries, which makes it easier for the gas to enter the bloodstream. |
|
|
How does gas exchange occur? |
blood in capillaries surrounding alveoli reaches equilibrium with air in lungs oxygen from air breathed in moves through capillary and alveolus's shared membrane into bloodstream, as carbon dioxide moves other way: from bloodstream to lungs to be breathed out |
|
|
Name the parts of the heart |
Vena cava and inferior vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary arteries; Pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta and descending aorta; septum; myocardium, endocardium |
|
|
What is the function of the heart? |
The heart's role is to: a) pump blood around the body, supplying oxygen to the body b) pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs so that it can become re-oxygenated through gas exchange. |
|
|
What is the function of the heart valves? |
to prevent blood from flowing backwards |
|
|
How is the structure of an artery suited to its function? |
carry blood away from heart at high pressure, and so have thick, elastic, muscular walls to withstand pressure |
|
|
How is the structure of a capillary suited to its function? |
allow the exchange of materials between blood and tissues have adapted to have thin permeable walls so this is easier |
|
|
How is the structure of a vein suited to its function? |
return low pressure blood to heart have a large diameter to offer the least flow resistance valves to prevent back-flow. |
|
|
What are the key components of blood? |
red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets |
|
|
What are platelets? |
produced in the bone marrow make up 20% of the blood are fragments of bone marrow cells contain proteins on surface that allow them to stick to breaks in the blood vessel wall and to each other so they form a clot and stop bleeding. |
|
|
What are red blood cells? |
most common cells in the bloodstream contains haemoglobin release the enzyme carbonic anhydrase which allows water in the blood to carry carbon dioxide to the lungs where it is breathed out control pH of the blood by acting as acid-base buffer |
|
|
What are white blood cells? |
protect body against both infectious diseases and foreign invaders produced from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. found throughout body, including in blood and lymphatic system |
|
|
State the unit energy is measured in |
joules |
|
|
Name the different types of energy |
Kinetic energy, Thermal energy, Chemical energy, Electrical energy, Electrochemical energy, Electromagnetic energy, Acoustic energy, Nuclear energy, Elastic potential energy, Gravitational potential energy |
|
|
State the difference between energy transfer and energy transformation |
when energy is transferred from one object to another without changing its form in energy transformation, the energy changes forms |
|
|
State the difference between useful and wasted energy |
energy transferred efficiently into desired outcome, whereas wasted energy is energy transferred into energy forms such as heat and randomly dispersed throughout space in a way that means that they are effectively useless |
|
|
How can a household become more energy efficient? |
replace all incandescent lightbulbs with LEDs, as LEDs produce less heat (wasted energy) buy appliances with a higher energy rating, which means that they do not waste as much energy as an appliance with a low energy rating |
|
|
What does the energy rating on electrical appliances mean? |
shows the energy performance of appliances and equipment allows consumers to understand how much a model will cost to run how energy efficient it is in comparison to similar models |
|
|
Identify the relative age of rocks in a diagram of rock layers |
lower rocks are older than the rocks above them principle of cross-cutting relationships: fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks it cuts through |
|
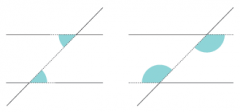
What are these angles? |
alternate are equal |
|
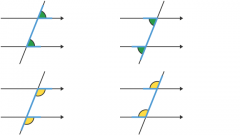
What are these angles? |
corresponding are equal |
|
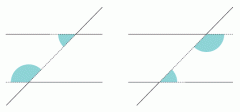
What are these angles? |
co-interior supplementary (add to 180 degrees) |
|
|
What is the formula for the angle sum of a polygon if n = number of angles? |
angle sum = 180(n – 2) |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a sedimentary rock? |
generally layered may contain fossils almost always contain either quartz or calcite |
|
|
What are the characteristics of an igneous rock? |
formed as a result of molten rock cooling on the surface or in the core of the Earth. hard in nature consist of crystals non porous do not contain fossils. |
|
|
What is the formula for the area of a circle? |
πr squared |
|
|
What is the formula for the circumference of perimeter of a circle? |
2πr |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a metamorphic rock? |
formed through changes to preexisting rocks in response to changing environmental conditions rarely contain fossils often have alternate bands of light and dark minerals may have layers of visible crystals are rarely porous |

