![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two principles the scientific method is based on? |
The events in the natural world have natural causes and uniformity (nature acts the same ways in different places and times). |
|
|
What are the main steps in the scientific method (in order)? |
Scientific Method Steps 1. Make an Observation 2. Form a hypothesis (If..Then...) 3. Make a prediction 4. Do an experiment 5. Draw conclusions (analyze data) 6. Communicate the results |
|
|
When there is an experimental group and a control group, which only has a single variable, what does this make? |
A Controlled Experiment |
|
|
What is the difference between an independent and a dependent variable? |
Independent variable: is manipulated Dependent variable: is observed and affected by the independent variable |
|
|
What is a "blind" control experiment? And why is it done? |
"Blind" Control Experiment: the scientist can get results without being aware of whether or not the subject is part of the control or experimental group Why it is Done: to eliminate bias |
|
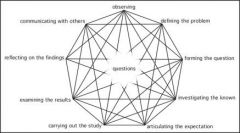
Why is this model a more accurate representation versus the one we learned in junior high? |
Science is NOT linear |
|
|
Where do facts in science come from? |
Observation and data from experiments as well as research |
|
|
What is the central theme of all scientific inquiries? |
Questions |
|
|
What help refine your question for an experiment? |
Observations |
|
|
What are the 2 types of observations? And what is their contrast? |
Qualitative: describes characteristics of an object Quantitative: invovle measurement and numbers |
|
|
What is an independent and a dependent variable? |
Independent Variable: is what you change in the experiment Dependent Variable: is what you're looking for a change in |
|
|
The experimental group is given the treatment, situation or other factor being studied and the control group is kept under exactly the same conditions except for the factor being studied. The control group is used as a standard for comparison. What are the things that you keep the same so they don't effect the outcome? |
Constants |
|
|
The more ______ you gather, the more reliable the results. Ideally the measurements should be repeated at least __ times then average the results. |
The more data you gather, the more reliable the results. Ideally the measurements should be repeated at least 10 times then average the results. |
|
|
What is precision and what is accuracy? |
Precision (aka reproducibility or repeatability): is how well repeated measurements agree with one another Accuracy: is the agreement between the measure quantity and the actual value a measure of correctness |
|
|
What is the SI Base Unit for Length? How should small lengths, such as cells, be measured? How should long distances, such as the distance between cities, be measured?
|
Meter (m) micrometers (µm) kilometers (km) |
|
|
What is area? What is volume? |
Area: Length x Width Volume: is how much space an object occupies or Length x Width x Height |
|
|
Why did the scientific community adopt the SI system of measurements? |
To be able to communicate easier with other scientists. |
|
|
What is the purpose for scientists to use data tables? |
...for the purpose of communicating and interpreting information. |
|
|
When parts of the data is in relation to all the data (parts of a whole), what type of data table is more appropriate to use than a bar graph? |
Circle Graph |
|
|
When the data is not continuous, what kind of data table is more appropriate to use than a line graph? |
Bar Graph |
|
|
When are lines graphs best used? |
...when the data is continuous and can be predicted. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of life? |
-Organization and Cells -Response to Stimuli -Homeostasis -Metabolism -Growth and Development -Reproduction -Change Through Time (Evolution) Optional: Based on Genetic Code |
|
|
What is the organization of life? (smallest to biggest) |
Organization of Life 1. Atom 2. Molecules 3. Cells 4. Tissues 5. Organs 6. Organ Systems 7. Organisms |
|
|
What is an atom? (4 examples) What are molecules? (4 examples) What are cells? What are tissues? What are organs? What is a system? What is an organism? |
Atom: the smallest unit of an element Molecules: two or more atoms bonded together Cells: basic units of life (smallest living thing) Tissue: groups of cells that carry out a specific function Organs: groups of tissues that interact to perform a specific function System: a group of organs that work together to perform a set of related tasks Organism: anything that possesses all characteristics of life |
|
|
What is differentiation? |
Differentiation: when cells in a multi cellular organism become specialized or different |
|
|
As cells differentiate, they produce proteins that are characteristic of the cell's shape and specific function. Why do cells become different? |
Cells become different because many segments of DNA are activated or inactivated during the development of the embryo. |
|
|
What is homeostasis? |
Homeostasis: the process of maintaining stability or balance within living things or the maintenence of a stable level of internal conditions |
|
|
_______ in multicellular organsims means that different types of cells carry on different functions. |
Specialization |
|
|
What limits a cell's size and why? What are 2 strategies to overlook this issue? |
A cell's size is limited by the relationship of its surface area-to-volume ratio because volume increases faster than surface area. Folding and cells remaining small. |
|
|
Why do cells come in many shapes? |
Its shape reflects on its function. |
|
|
What do cells have that functions to control what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis? This also provides protection and support to the cell. |
Cell Membrane |
|
|
Why do cells regulate water? And how? |
Cells regulate water be filling the vacuole with water and contracting and they do this to make sure the cells won't rupture or shrivel. |
|
|
What would happen without the homeostasis mechanisms? |
Without these homeostasis mechanisms, organisms can die if things aren't kept at consistent and normal levels. |
|
|
Plant cells do not burst like blood cells in a hypotonic solution because they have ____ _____ that can withstand the pressure. |
Plant cells do not burst like blood cells in a hypotonic solution because they have cell walls that can withstand the pressure. |
|
|
What is the structure of the cell membrane called? |
Lipid Bilayer (2 layers of phospholipids) |
|
|
Membranes have _____ and _____. Cell membranes also have _____ (holes) in them making them selectively permeable which means that they allow _____ molecules in and keep other molecules out. |
Membranes have proteins and carbohydrate. Cell membranes also have pores (holes) in them making them selectively permeable which means that they allow some molecules in and keep other molecules out. |
|
|
What are the two types of cellular transports and what is the difference? |
Passive Transport: cells don't use energy Active Transport: cells do use energy |
|
|
What are the three types of passive transport? (High to Low) |
Diffusion: random movement of particles from an area of high concentration to a lower one (continues until equilibrium) Facilitated Diffusion: movement of specific particles through a transport protein (channels) which is used for larger molecules like glucose Osmosis: diffusion of water through a membrane from high to low concentrations (the concentration of water depends on the amount of dissolved solute) |
|
|
What are the three types of active transport? (Low to High) |
Protein Pumps: transport proteins (the protein pumps to move molecules like sodium) Endocytosis: taking bulky materials into the sell by folding the membrane around material (white blood cells eats bacteria) Exocytosis: forces materials out of the cell in bulk (hormones and wastes released from cells) |
|
|
Why can't the cell stop the movement of water through the membrane? |
...because water molecules are too small and there is too much of it. |
|
|
Describe a hypotonic solution, hypertonic solution and an isotonic solution. |
Hypotonic Solution: has a lower solute concentration and higher water than inside the cell (water moves in cell swells and bursts) Hypertonic Solution: has a higher solute concentration and lower water that inside the cell (water leaves the cell and shrivels/shrinks) Isotonic Solution: the concentration of solutes is equal to the solutes in the cell (water moves equally in both directions and the cell remains the same or equilibrium) |
|
|
What are the organ systems in the body? |
-nervous -respiratory -skeletal -cardiovascular -muscular -excretory -integumentary -endocrine -digestive -immune/lymphatic** |
|
|
What controls hormone secretion and is one in which the last the last step in a series of events that controls the first (negative or positive)? |
Feedback Mechanisms |
|
|
What is negative feedback? |
Negative feedback: is a mechanism of homeostasis whereby a step in a series of events inhibits the initial signal in the series |
|
|
How is positive feedback different from negative feedback? |
Positive feedback: the response to the stimulus tends to increase the stimulus Negative feedback: the response to the stimulus tends to decrease or eliminate the stimulus |
|
|
What are antagonistic hormones? |
Antagonistic hormones: hormones that work together in pairs to regulate the levels of critical substances |
|
|
Glucagon and Insulin are both examples of what? |
Antagonistic hormones |
|
|
What is feedback? |
Feedback: the process in which information about the past or present influences the same phenomenon in the present or future (chain of cause and effect) |
|
|
What is an internal system in the body allowing mechanisms to turn "on" then feedback is given to turn "off" the response? |
A feedback loop |
|
|
How is homeostasis maintained? |
Through feedback loops |
|
|
What are two other names for Feedback Loops and what shape is it? |
Two Names: Negative feedback and Feedback inhibition Shape: circle |
|
|
What are the 5 steps of negative feedback? |
Step 1: Stress or stimulus Step 2: Receptor Step 3: Interpretor/Control Center Step 4: Effector Step 5: Response |
|
|
What takes up space and has mass? |
Matter |
|
|
_________ _________ in matter are essential to all life processes. |
Chemical changes in matter are essential to all life processes. |
|
|
Why are the following for element significant: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen? |
They make up 90% of the mass of living things. |
|
|
Atoms combine to make what? |
Compounds |
|
|
_________ _______ are attractive forces that hold atoms together. __________ is the simplest part of a substance that retains all of the properties of that substance. |
Chemical bonds are attractive forces that hold atoms together. Molecule is the simplest part of a substance that retains all of the properties of that substance. |
|
|
Living organisms are made up mostly of molecules based on what element? Organic compounds are also primarily made of this. |
Carbon |
|
|
Define energy. |
Energy: the ability to work (occurs in a variety of forms and can be converted) |
|
|
What are the 5 forms of energy? |
Forms of Energy -chemical -thermal -electrical -mechanical -radiant |
|
|
What are the classes of organic compounds? |
Carbohydrates, proteins (amino acids), lipids, and nucleic acids. |
|
|
What kind of energy is in food and what happens to it? |
Chemical; the chemical energy from food gets converted into thermal and mechanical energy. |
|
|
When is energy absorbed or released? |
...when chemical bonds are broken and new ones are formed. |
|
|
Your body gets energy from ___, ___, and ___ in food, undergoes a series of ___ ___ to break them down into ___ ___ and ___. |
Your body gets energy from sugars, proteins and fats in food, undergoes a series of chemical reactions to break them down into carbon dioxide and water. |
|
|
Why is ATP an example of the unity and diversity of life? |
ATP is an example of the unity and diversity of life because all cells in every organism use the same energy carrier for almost all of their energy-driven actions. |
|
|
What are some examples ATP is used for? |
-the contraction of muscles -pumping substances -supplying chemical potential energy |
|
|
What are some reasons why ATP is the universal currency rather then other energy storing molecules? |
-the ability to couple to so many different endergonic reactions -the availability of the other molecules aren't reliable or predictable -is in a variety of food molecules -provides a manageable amount of energy |
|
|
ATP is a molecule in the cell that allows for quick and easy access to energy. It is a type of chemical energy that is realeased when ___________________. |
ATP is a molecule in the cell that allows for quick and easy access to energy. It is a type of chemical energy that is realeased when chemical bonds are broken. |
|
|
How is ATP recharged like a battery? |
ATP is recharged by using the mitochondria adding another phosphate. |
|
|
Energy for living things comes from food, but originally comes from where? |
the sun |
|
|
What are autotrophs? What are heterotrophs? |
Autotrophs: Organisms that use light energy from the sun to produce food Heterotrophs: Organisms that CANNOT use the sun’s energy to make food |
|
|
What is photosynthesis? |
Photosynthesis: is the process by which the energy of sunlight is converted into the energy of glucose |
|
|
What is the formula for photosynthesis? |
carbon dioxide + water + light → glucose + oxygen or 6CO2 + 6H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
|
|
|
What is a light dependent reactant? |
Light Dependent Reactant: H2O is broken down and light energy is stored temporarily in inorganic energy carriers, ATP and NADPH |
|
|
What is the Calvin Cycle? |
Calvin Cycle: energy is tranferred from carriers to glucose |
|
|
What is the process of cellular respiration? |
Cellular respiration is the process by which the energy of glucose is released in the cell for use. |
|
|
Where and when can respiration take place? |
Respiration takes place in all cells and can take place with or without oxygen present. |
|
|
Describe aerobic respiration. |
Aerobic Respiration: requires oxygen •Occurs in the mitochondria of the cell •Total of 36 ATP molecules produced •General formula for aerobic respiration:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP
|
|
|
What are the 3 steps for aerobic respiration? |
Steps: 1. Glycolysis in the cytoplasm makes 2 ATP. 2. Krebs Cycle in the mitchondria makes 2 ATP. 3. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) in the mitochondria makes 32 ATP. |
|
|
When does anaerobic respiration occur? What is is also called? |
Anaerobic respiration occurs when there is no oxygen available and is also known as fermentation. |
|
|
Define interdependence. |
Interdependence: the dependence of every organisms' interactions/connections with living/nonliving components of its environment. |
|
|
What are ecological models? |
Ecologicial Models: a model that represents/describes the relationships between the components of an ecological system |
|
|
What are the 5 levels of organization on an ecological level? (biggest to smallest) |
Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Organism |
|
|
What is habitat? |
The place where an organism lives. |
|
|
Contrast abiotic and biotic factors. |
Abiotic: the physical and chemical characteristics of an environment Biotic: the living components of an environment |
|
|
What are the 5 different types of consumers? How are they different? |
Producers Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Decomposers They are different because of the type of food they eat... (make their own, plants, meat, both, the dead organisms). |
|
|
Why are decomposers so important to the environment? |
Decomposers are important to the environment because the remaining carbon in the dead organisms would not be able to enter the atmosphere again, and if the carbon in the atmosphere is low, then the producers won't be able to do photosynthesis. Without producers, the consumers would die from starvation. Decomposers break down dead organisms that release the carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. |
|
|
Define population. |
Population: a group of organisms that belong to the same species that live in a particular place at the same time |
|
|
What are the three patterns of population dispersal? |
Random Distribution Uniform Distribution Clumped Distribution |
|
|
What are the 4 processes that determine population growth? |
Birth, death, emigration, and immigration. |
|
|
What are limiting factors? |
Limiting Factors: things that limit/control the population size for example, food, space, and predators |
|
|
What is carrying capacity? |
Carryinf Capacity: the number of individuals the environment can support over a lone period of time or the largest number of individuals the environment can support |
|
|
Define density dependent and density independent. |
Density Dependent: relies on numbers of a dense population and reduces it Density Independent: resource limitations that are powered by an increasing population density |
|
|
Why are small populations more vulnerable to extinction? |
They are more vulnerable to extinction because predators or environmental disturbances can kill off the whole population or leave too few to maintain; inbreeding will also decrease the genetic variability, thus slowly becoming extinct. |
|
|
What is distribution? What is density? What is growth rate? |
-where organisms live -number of individuals in an area -how fast or slow it grows |
|
|
What is mortality rate? What is birthrate? |
Mortality rate: how many individuals die over a certain period of time (decrease) Birthrate: the number of individuals born over a period of time (increase) |
|
|
Define immigration and emigration. |
Immigration: individuals entering the population Emigration: individuals leaving the population |
|
|
What determines the growth of a population? |
The environment |
|
|
Define exponential and logistic growth. |
Exponential growth: no limits; ideal conditions unlimited resources Logistic growth: limited as resources become less available growth stops |
|
|
What is symbiosis? |
Symbiosis: a close long-tern relationship between organisms |
|
|
What is mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism? |
Mutualism: both benefits Commensalism: one benefits, other is unharmed (protection) Parasitism: one benefits, the other is harmed |
|
|
What is resilience? |
Resilience: the ability to stablize and recover |
|
|
Stable ecosystems have what? |
High Biodiversity |
|
|
What is an ecological pyramid? |
Ecological Pyramid: a diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web |
|
|
List 4 ways that energy is used up and not passed on the the next trophic level. |
-respiration -movement -reproduction -heat energy (released into the environment) |
|
|
How much energy is transferred to organisms at the next level? |
Only about 10% of the energy available within one trophic level. |
|
|
What is biomass? |
Biomass: is the total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level |
|
|
Where do humans fit on the ecological pyramids? And what is the impact of energy pyramids on our species? |
Humans fit at the top of the ecological pyramids. The impact of energy pyramids on our species in the amount of energy we absorb from the plant foods versus animal foods we eat. |
|
|
How is a pyramid of numbers different from energy and biomass pyramids? |
Energy and biomass pyramids are different from the pyramids of numbers because the pyramids of numbers doesn't resemble a typical pyramid at all. |
|
|
Why is it good to be an Alien? |
It is good to be an Alien because their are no competitors or predators. |

